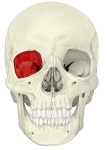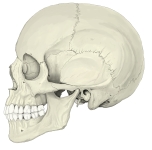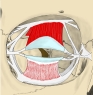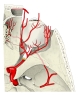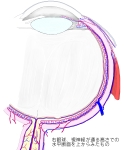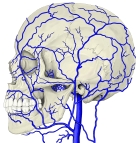

・「成人で眼窩の大きさは約30mlで、そのうち眼球が約6.5mlとなる」(Wikipedia)
「日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」には以下のような解説が見られる。 」には以下のような解説が見られる。
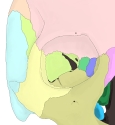
「 眼窩は、四面錐体形を呈し、錐体の基底は前外側方に向かい眼窩口に一致し、尖端は後内側方に向かい視神経管に一致する。したがって、左右の眼窩の長軸を延長すると、内後頭隆起の部で会合する。」
以下に眼窩内に見られる主なものを一覧にしてみた。

【4つの壁】
眼窩は、上・下・内・外の4つの壁に分けることができる。

1 |
眼窩上縁 |
supraorbital border |
2 |
眼窩下縁 |
infraorbital border |

眼窩は以下の孔や裂孔から頭蓋の他の場所に連絡をし、神経や血管を通している。

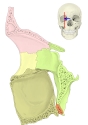
ここでは眼窩内にある筋肉を、大きく以下のように3つに分けている。
※ここでは眼輪筋よりも内側にある筋を「眼窩内の筋」として扱っている。なるべくすべての筋を列挙したつもりだが、取りこぼしの可能性もありうる。
1 |
内眼筋 |
1 |
毛様体筋 |
3 |
瞳孔散大筋(虹彩筋) |
2 |
瞳孔括約筋(虹彩筋) |
|
|
2 |
外眼筋 |
1 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
6 |
|
3 |
その他 |
1 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
5 |
滑車張筋 |
3 |
|
6 |
睫毛筋(ショウモウキン) |
おそらく靭帯は、眼瞼の周囲のみで、眼窩の奥には存在していないと思われる。

以下の眼窩内の神経の一覧は取りこぼしがある可能性がある。

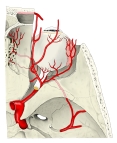
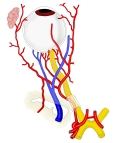
眼窩内に見られる脈管には以下のようなものがある。
※なるべく多くを挙げてみたが取りこぼしの可能性はありえる。
【 動 脈 】
動脈のほとんどが眼動脈から分岐したものとなる。
| |
名 称 |
備 考 |
1 |
|
内頚動脈の枝の1つで、眼窩に見られる動脈お大元となる。 |
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
6 |
|
眼球に進入して強膜を貫き脈絡膜に分布する。 |
7 |
|
内側・外側があり虹彩に達するため虹彩動脈とも呼ばれる。 |
8 |
|
上下の2枝があり、 外側眼瞼動脈と吻合して上・下眼瞼動脈弓を形成 |
9 |
|
視神経内に進入して網膜に至る。 |
10 |
|
|
【 静 脈 】
※なるべく多くを挙げてみたが取りこぼしの可能性は十分にある。
| |
名 称 |
備 考 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
上眼静脈に注ぐ静脈の1つで、涙腺からの血液を集めている。 |
5 |
|
上眼静脈に注ぐ静脈の1つで、毛様体血管系の静脈により構成される。 |
6 |
|
上眼静脈に注ぐ静脈の1つで、毛様体からの血液を集めている。 |
7 |
|
上眼静脈に注ぐ静脈の1つで、強膜上に見られる細い静脈 |
8 |
|
上眼静脈に注ぐ静脈の1つで、網膜に分布する静脈が集まって形成される。 |
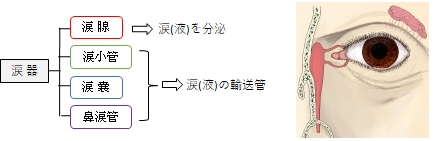
【 涙 器 】
眼窩には涙(液)を作る器官とそれを輸送する器官が見られる。
【 脂 肪 】
眼窩に存在する眼球、筋肉、脈管、そして神経の間は脂肪で満たされていて、それぞれの位置の安定を図っている。
This article is about the anatomical space that contains the eye. For other uses, see Orbit (disambiguation) and Orbita (disambiguation).
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres (1.06 imp fl oz; 1.01 US fl oz), of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml (0.23 imp fl oz; 0.22 US fl oz).[3] The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, check ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
【 語 句 】
・cavity: ・appendage:付属物 ・imply:含む ・retrobulbar:眼球後の ・fascia:筋膜 ・exraocular muscles:外眼筋 ・cranial nerves:脳神経 ・lacrimal gland:涙腺 ・sac:嚢 ・duct:輸送管 ・lateral palpebral ligaments:外側眼瞼靭帯 ・suspensory ligament:提靱帯 ・septum:隔膜 ・ciliary ganglion:毛様体神経節 ・short ciliary nerves:短毛様体神経
【Structure】
The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls.
【Openings】
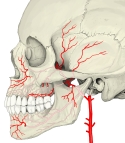
There are two important foramina, or windows, two important fissures, or grooves, and one canal surrounding the globe in the orbit. There is a supraorbital foramen, an infraorbital foramen, a superior orbital fissure, an inferior orbital fissure and the optic canal, each of which contains structures that are crucial to normal eye functioning. The supraorbital foramen contains the supraorbital nerve, the first division of the trigeminal nerve or V1 and lies just lateral to the frontal sinus. The infraorbital foramen contains the second division of the trigeminal nerve, the infraorbital nerve or V2, and sits on the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus. Both foramina are crucial as potential pathways for cancer and infections of the orbit to spread into the brain or other deep facial structures.
The optic canal contains the (cranial nerve II) and the ophthalmic artery, and sits at the junction of the sphenoid sinus with the ethmoid air cells, superomedial and posterior to structures at the orbital apex. It provides a pathway between the orbital contents and the middle cranial fossa. The superior orbital fissure lies just lateral and inferior to the optic canal, and is formed at the junction of the lesser and greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It is a major pathway for intracranial communication, containing cranial nerves III, IV, VI which control eye movement via the extraocular muscles, and the ophthalmic branches of cranial nerve V, or V1. The second division of the trigeminal nerve enters the skull base at the foramen rotundum, or V2. The inferior orbital fissure lies inferior and lateral to the ocular globe at the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus. It is not as important in function, though it does contain a few branches of the maxillary nerve and the infraorbital artery and vein.Other minor structures in the orbit include the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramen and zygomatic orbital foramen.
【 語 句 】
・conical:円錐の ・pyramidal:ピラミッド形の ・foramina:孔 ・fissure:裂け目 ・groove:溝 ・canal:管 ・supraorbital foramen:眼窩上孔 ・superior orbital fissure:上眼窩裂 ・optic canal:視神経管 ・supraorbital nerve:眼窩上神経 ・trigeminal nerve:三叉神経 ・frontal sinus:前頭洞 ・maxillary sinus:上顎洞 ・ophthalmic artery: ・ethmoid air cells:篩骨蜂巣 ・middle cranial fossa:中頭蓋窩 ・greater wing:大翼 ・sphenoid bone:蝶形骨 ・foramen rotundum:正円孔 ・ocular globe:眼球? ・ posterior ethmoidal foramen:後篩骨孔 ・zygomatic orbital foramen:頬骨眼窩孔
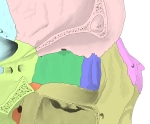
【Bony walls】
The bony walls of the orbital canal in humans do not derive from a single bone, but a mosaic of seven embryologically distinct structures: the zygomatic bone laterally, the sphenoid bone, with its lesser wing forming the optic canal and its greater wing forming the lateral posterior portion of the bony orbital process, the maxillary bone inferiorly and medially which, along with the lacrimal and ethmoid bones, forms the medial wall of the orbital canal. The ethmoid air cells are extremely thin, and form a structure known as the lamina papyracea, the most delicate bony structure in the skull, and one of the most commonly fractured bones in orbital trauma. The lacrimal bone also contains the nasolacrimal duct. The superior bony margin of the orbital rim, otherwise known as the orbital process, is formed by the frontal bone.
The roof (superior wall) is formed primarily by the orbital plate of frontal bone, and also the lesser wing of sphenoid near the apex of the orbit. The orbital surface presents medially by trochlear fovea and laterally by lacrimal fossa.
The floor (inferior wall) is formed by the orbital surface of maxilla, the orbital surface of zygomatic bone and the minute orbital process of palatine bone. Medially, near the orbital margin, is located the groove for nasolacrimal duct. Near the middle of the floor, located infraorbital groove, which leads to the infraorbital foramen. The floor is separated from the lateral wall by inferior orbital fissure, which connects the orbit to pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossa.
The medial wall is formed primarily by the orbital plate of ethmoid, as well as contributions from the frontal process of maxilla, the lacrimal bone, and a small part of the body of the sphenoid. It is the thinnest wall of the orbit, evidenced by pneumatized ethmoidal cells.
The lateral wall is formed by the frontal process of zygomatic and more posteriorly by the orbital plate of the greater wing of sphenoid. The bones meet at the zygomaticosphenoid suture. The lateral wall is the thickest wall of the orbit, important because it is the most exposed surface, highly vulnerable to blunt force trauma.
【 語 句 】
・mosaic:寄せ集めの ・embryologically:発生学的に ・distinct:性質が異なる、明瞭な ・lacrimal bone:涙骨 ・ethmoid bone:篩骨 ・lamina papyracea:眼窩板 ・trauma:外傷 ・nasolacrimal duct:鼻涙管 ・orbital process:眼窩突起 ・orbital surface:眼窩面 ・trochlear fovea:滑車窩 ・lacrimal fossa:涙腺窩 ・palatine bone:口蓋骨 ・infraorbital groove:眼窩下溝 ・infraorbital foramen:眼窩下孔 ・pterygopalatine fossa:翼口蓋窩 ・infratemporal fossa:側頭下窩 ・ethmoid:篩骨 ・pneumatized:含気の ・zygomaticosphenoid suture:蝶頬骨縫合? ・vulnerable:傷つきやすい ・blunt force:鈍力
【Borders】
The base, orbital margin, which opens in the face, has four borders. The following bones take part in their formation:
- Superior margin: frontal bone
- Inferior margin: maxilla and zygomatic bone
- Medial margin: frontal bone and maxilla
- Lateral margin: zygomatic bone and frontal bone
The orbit holds and protects the eye.
【Eye movement】
Main article: Eye movement
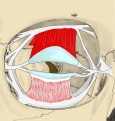
The movement of the eye is controlled by six distinct extraocular muscles, a superior, an inferior, a medial and a lateral rectus, as well as a superior and an inferior oblique. The superior ophthalmic vein is a sigmoidal vessel along the superior margin of the orbital canal that drains deoxygenated blood from surrounding musculature. The ophthalmic artery is a crucial structure in the orbit, as it is often the only source of collateral blood to the brain in cases of large internal carotid infarcts, as it is a collateral pathway to the circle of Willis. In addition, there is the optic canal, which contains the optic nerve, or cranial nerve II, and is formed entirely by the lesser wing of the sphenoid, separated from the supraorbital fissure by the optic strut. Injury to any one of these structures by infection, trauma or neoplasm can cause temporary or permanent visual dysfunction, and even blindness if not promptly corrected. The orbits also protect the eye from mechanical injury.
【 語 句 】
・lateral rectus:外側直筋 ・inferior oblique:下斜筋 ・superior ophthalmic vein:上眼静脈 ・deoxygenated blood:脱酸素化した血液=静脈血 ・crucial:重要な ・infarct:梗塞 ・circle of Willis:ウィリス動脈輪 ・optic strut:? ・neoplasm:腫瘍 ・dysfunction:機能障害 ・promptly:敏速に ・mechanical injury:機械的損傷
|