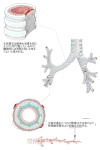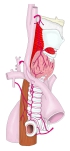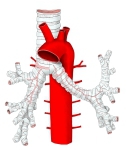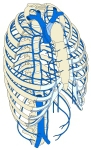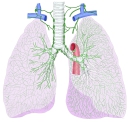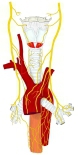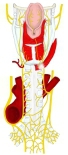
・概 要 (左・右主気管支)
・構 造 (粘 膜)
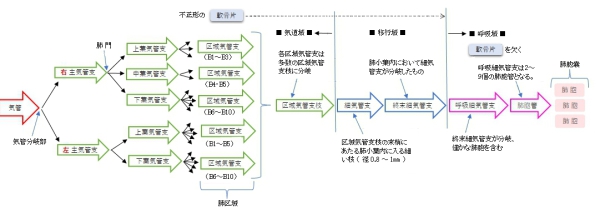
・区 分
・周辺の臓器との位置関係
・脈管/神経
・Wikipedia
・イラスト掲載サイト
![]()


![]()
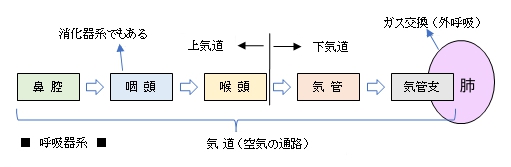
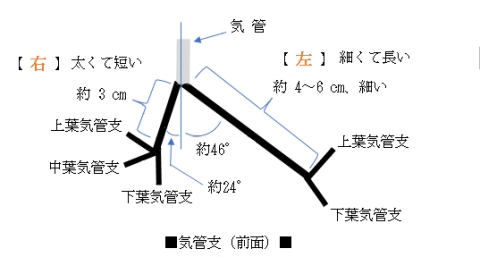
以下に「日本人体解剖学」を参考にして左右の主気管支の特徴を簡単に記してみた。
左(主)気管支 |
|
右(主)気管支 |
「日本人体解剖学」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
気管分岐部から、左・右気管支への走行の違いにより、異物の混入はしばしば右気管支に起こる。
なお、小児の気管分岐角は約110°で、左右の気管支の分岐角の差はない。
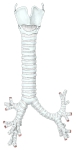
甲状軟骨~気管支(前面) |
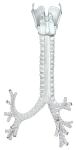
甲状軟骨~ 気管支(後面) |
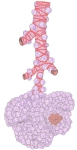
区域気管支~肺胞嚢 |
気管支末端 |
![]()


・「The bronchial wall normally has a thickness of 10% to 20% of the total bronchial diameter.」(Wikipedia)
構造解説 |
以下は「日本人体解剖学」を参考にしたものとなる。
1 |
lober bronchus |
肺門において(主)気管支から分岐する(左2本、右3本)。肺実質内に入り、構造的には気管支をほぼ同一となるが、異なる点もいくつか見られる。 特徴) ・膜性壁を欠く。 ・C字形の軟骨片は次第に退縮 ⇒ 不正形の軟骨片(径1㎜大の枝にまで見られる) ・多列線毛円柱上皮は次第に上皮細胞の丈が低くなる。 |
2 |
segmental bronchus |
|
3 |
bronchiole |
|
4 |
terminal bronchiole |
|
5 |
respiratory bronchiole |
区域気管支~肺胞嚢 |
か行 |
は行 |
||
| さ行 | |||
ま行 |
|||
や行 |
気管に分布する脈管・神経として以下のものが挙げられる。
動脈 |
・下甲状腺動脈からの気管枝 ・気管支動脈(胸大動脈の臓側枝の一つ) ・内胸動脈の気管支枝 |
静脈 |
|
リンパ管 |
気管前リンパ節、気管傍リンパ節、上・下気管気管支リンパ節にそそぐ。 |
神経 |
動脈-1 |
動脈-2 |
静脈 |
||
リンパ節・リンパ本幹 |
神経-1 |
神経-2 |
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory system that conducts air into the lungs. The first bronchi to branch from the trachea are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest and enter the lungs at each hilum, where they branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi when too narrow to be supported by cartilage are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.
【語句】
・respiratory system:呼吸器系 ・trachea:気管 ・hilum:へそ ・lobar bronchi:葉気管支 ・tertiary:第3の ・segmental bronchi:区気管支 ・bronchiole:気管支梢、 細気管支
Structure
The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic vertebra (at rest).
The right main bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left main bronchus. It enters the right lung at approximately the fifth thoracic vertebra. The right main bronchus subdivides into three secondary bronchi (also known as lobar bronchi), which deliver oxygen to the three lobes of the right lung—the superior, middle and inferior lobe. The azygos vein arches over it from behind; and the right pulmonary artery lies at first below and then in front of it. About 2 cm from its commencement it gives off a branch to the superior lobe of the right lung, which is also called the eparterial bronchus. Eparterialrefers to its position above the right pulmonary artery. The right bronchus now passes below the artery, and is known as the hyparterial branch which divides into the two lobar bronchi to the middle and lower lobes.
【語句】
・carina:気管竜骨 ・primary bronchi:主気管支 ・sternal angle:胸骨角 ・thoracic vertebra:胸椎 ・at rest:安静時? ・lobe:葉 ・azygos vein:奇静脈 ・pulmonary artery:肺動脈 ・commencement:開始 ・eparterial bronchus:右肺動脈の上を通る気管支 ・hyparterial:動脈下の
The left main bronchus is smaller in caliber but longer than the right, being 5 cm long. It enters the root of the left lung opposite the sixth thoracic vertebra. It passes beneath the aortic arch, crosses in front of the esophagus, the thoracic duct, and the descending aorta, and has the left pulmonary artery lying at first above, and then in front of it. The left bronchus has no eparterial branch, and therefore it has been supposed by some that there is no upper lobe to the left lung, but that the so-called upper lobe corresponds to the middle lobe of the right lung. The left main bronchus divides into two secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, to deliver air to the two lobes of the left lung—the superior and the inferior lobe.
【語句】
・caliber:口径 ・esophagus:食道 ・thoracic duct:胸管 ・descending aorta:下行大動脈
The secondary bronchi divide further into tertiary bronchi, (also known as segmental bronchi), each of which supplies a bronchopulmonary segment. A bronchopulmonary segment is a division of a lung separated from the rest of the lung by a septum of connective tissue. This property allows a bronchopulmonary segment to be surgically removed without affecting other segments. Initially, there are ten segments in each lung, but during development with the left lung having just two lobes, two pairs of segments fuse to give eight, four for each lobe. The tertiary bronchi divide further in another three branchings known as 4th order, 5th order and 6th order segmental bronchi which are also referred to as subsegmental bronchi. These branch into many smaller bronchioles which divide into terminal bronchioles, each of which then gives rise to several respiratory bronchioles, which go on to divide into two to eleven alveolar ducts. There are five or six alveolar sacs associated with each alveolar duct. The alveolus is the basic anatomical unit of gas exchange in the lung.
【語句】
・segmental bronchi:区(域)気管支 ・bronchopulmonary segment:気管支肺区域 ・connective tissue:結合組織 ・tertiary:第3の ・terminal bronchiole:終末細気管支 ・respiratory bronchiole:呼吸細気管支 ・alveolar duct:肺胞管 ・alveolar sacs:肺胞嚢 ・alveolus:肺胞
The main bronchi have relatively large lumens that are lined by respiratory epithelium. This cellular lining has cilia departing towards the mouth which removes dust and other small particles. There is a smooth muscle layer below the epithelium arranged as two ribbons of muscle that spiral in opposite directions. This smooth muscle layer contains seromucous glands, which secrete mucus, in its wall. Hyaline cartilage is present in the bronchi, surrounding the smooth muscle layer. In the main bronchi, hyaline cartilage forms an incomplete ring, giving a "D"-shaped appearance, while in the smaller bronchi, hyaline cartilage is present in irregularly arranged plates and islands. These plates give structural support to the bronchi and keep the airway open.
The bronchial wall normally has a thickness of 10% to 20% of the total bronchial diameter.
【語句】
・lumen:内腔 ・respiratory epithelium:呼吸上皮 ・cilia:線毛 ・smooth muscle:平滑筋 ・seromucous gland:混合腺 ・secrete:分泌する ・mucus:粘液 ・hyaline cartilage:硝子軟骨
【Histology】
The cartilage and mucous membrane of the primary bronchi are similar to those in the trachea. They are lined with respiratory epithelium, which is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. The epithelium in the main bronchi contains goblet cells, which are glandular, modified simple columnar epithelial cells that produce mucins, the main component of mucus. Mucus plays an important role in keeping the airways clear in the mucociliary clearance process. As branching continues through the bronchial tree, the amount of hyaline cartilage in the walls decreases until it is absent in the bronchioles. As the cartilage decreases, the amount of smooth muscle increases. The mucous membrane also undergoes a transition from ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium to simple cuboidal epithelium to simple squamous epithelium.
【語句】
・ciliated:線毛性の ・pseudostratified columnar epithelium:偽重層上皮 ・goblet cell:杯細胞 ・glandular:腺の ・modified:変形した? ・simple columnar epithelial cell:単層円柱上皮細胞 ・mucins:ムチン ・mucociliary clearance:粘液線毛クリアランス ・cuboidal:立方状の ・squamous:扁平上皮の
【Variation】
In 0.1 to 5% of people there is a right superior lobe bronchus arising from the main stem bronchus prior to the carina. This is known as a tracheal bronchus, and seen as an anatomical variation. It can have multiple variations and, although usually asymptomatic, it can be the root cause of pulmonary disease such as a recurrent infection. In such cases resection is often curative
The cardiac bronchus has a prevalence of ≈0.3% and presents as an accessory bronchus arising from the bronchus intermedius between the upper lobar bronchus and the origin of the middle and lower lobar bronchi of the right main bronchus. Accessory cardiac bronchus is usually an asymptomatic condition but may be associated with persistent infection or hemoptysis. In about half of observed cases the cardiac bronchus presents as a short dead ending bronchial stump, in the remainder the bronchus may exhibit branching and associated aerated lung parenchyma.
【語句】
・prior to ~:~より先に ・asymptomatic:無症状の ・recurrent infection:反復感染 ・resection:切除、摘出 ・curative:病気に効く ・cardiac bronchus:(気管支中間部の内側から起こる異常な気管支)・prevalence:いきわたっている ・persistent:しつこい ・hemoptysis:喀血 ・remainder:残り ・exhibit:表す ・aerate:酸素を供給する ・associate:関連付ける ・lung parenchyma:肺実質
【Function】
See also: Respiratory tree
The alveolar ducts and alveoli consist primarily of simple squamous epithelium, which permits rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Exchange of gases between the air in the lungs and the blood in the capillaries occurs across the walls of the alveolar ducts and alveoli.
【語句】
・alveolar ducts:肺胞管 ・alveoli:肺胞 ・simple squamous epithelium:単層扁平上皮 ・diffusion:拡散 ・carbon dioxide:二酸化炭素 ・capillary:毛細血管