【概 要】

・神経節の膨大は細胞体が密集していることによる。また、シナプス結合がある場合はそれも一因とはなる。

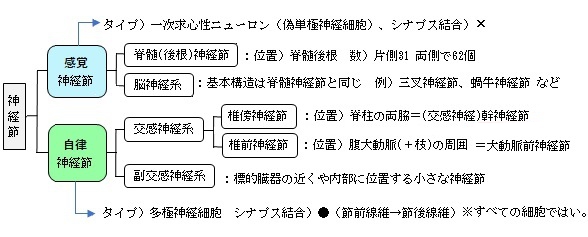
【感覚神経節】

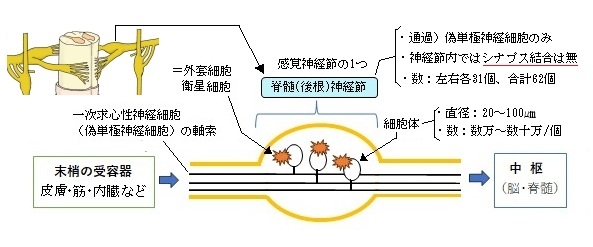
■ 脊髄(後根)神経節 dorsal root ganglion ■
脊髄の後根に位置する神経節、脊髄の前根、後根合わせて神経節は1つしかないので脊髄神経節と同義となる。
数は脊髄神経の数と同じで、左右各31個、合計で62個ある。
「ChatGPT」によると
・神経節の直径は数㎜程度
・感覚ニューロン(偽単極神経細胞)の細胞体の直径は20~100㎛程度
・1つの神経節の中には数万~数十万の細胞体が存在
※数に関しては資料によってかなり数字が異なる。
以下に成人の脊髄後根神経節の部位による大きさの違いを簡単に記す。
|
部 位 |
DRG直径(概算) |
備 考 |
1 |
頸椎(C5–C8) |
約5–7 mm |
上肢の感覚情報を多く集める |
2 |
胸椎(T1–T12) |
約3–5 mm |
胸部皮膚の感覚中心 |
3 |
腰椎(L1–L5) |
約6–8 mm |
下肢の感覚情報を多く集める |
4 |
仙椎(S1–S5) |
約4–6 mm |
骨盤・下肢末端の感覚 |
※DRG=dorsal root ganglion
| |
名 称 |
備 考 |
1 |
三叉神経節 |
神経: 三叉神経(CN V)
感覚: 顔面の触覚・痛覚・温度覚
特徴: 偽単極神経細胞が主体 |
2 |
上頸神経節 |
少数文献で触れる場合あり
厳密には脳神経節ではなく頸神経に属する感覚節だが、頭部感覚と関連 |
3 |
前庭神経節 |
神経: 前庭神経(CN VIII)感覚: 平衡覚 |
4 |
蝸牛神経節 |
神経: 蝸牛神経(CN VIII
感覚: 聴覚 |
5 |
舌咽神経節 |
上神経節/下神経節
感覚: 舌後1/3の味覚・咽頭の感覚 |
6 |
迷走神経節 |
上神経節/下神経節
感覚: 咽頭・喉頭・内臓の感覚 |
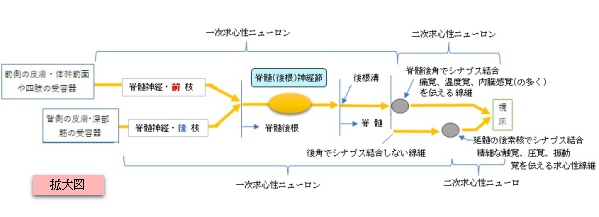
・感覚神経節には、末梢で感覚刺激を受容した場合に、その情報を中枢に伝達する感覚ニューロンの細胞体が集合している。
・感覚ニューロンは、形態学的には双極性ニューロンあるいは偽単極性ニューロンである。
■脳神経に属する感覚神経節の主なもの■
以下、脳神経に属する感覚神経節をできるだけ多く一覧にしてみたが、そのすべてが挙げられているかどうかは定かではない。
| |
名 称 |
別 名 |
求心性神経 |
位 置 |
1 |
|
半月神経節 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
スカルパ神経節 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
上舌咽神経節 |
|
|
6 |
|
下舌咽神経節 |
|
|
7 |
|
頚静脈神経節 |
|
|
8 |
|
節状神経節 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
三叉神経節/膝神経節 |
|
舌咽神経 |
脊髄後根神経節 |
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia which contain the cell bodies of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons respectively.
A pseudoganglion looks like a ganglion, but only has nerve fibers and has no nerve cell bodies.
【 語 句 】
・peripheral nervous system:末梢神経系 ・somatic nervous system:体性神経系 ・dorsal root ganglia:(脊髄)後根神経節 ・trigeminal ganglia:三叉神経節 ・autonomiic nervous system:自律神経系 ・sympathetic:交感神経の ・parasympathetic:副交感神経の ・respectively:それぞれ ・pseudoganglion:偽性神経節
【Structure】
Ganglia are primarily made up of somata and dendritic structures which are bundled or connected. Ganglia often interconnect with other ganglia to form a complex system of ganglia known as a plexus. Ganglia provide relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body, such as the peripheral and central nervous systems.
Among vertebrates there are three major groups of ganglia:
In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the central nervous system to the ganglia are known as preganglionic fibers, while those from the ganglia to the effector organ are called postganglionic fibers.
【 語 句 】
・ganglia:ganglionの複数形 ・somata:細胞体 ・dendritic:樹状突起の ・plexus:叢 ・relay points:中継点 ・intermediary:中間の、中継の ・vertebrate:脊椎動物 ・cranial nerve:脳神経 ・preganglionc fiber:節前繊維 ・effector organ:効果器 ・postganglionc fiber:節後繊維
【Basal ganglia】
The term "ganglion" refers to the peripheral nervous system.
However, in the brain (part of the central nervous system), the "basal ganglia" is a group of nuclei interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, associated with a variety of functions: motor control, cognition, emotions, and learning.
Partly due to this ambiguity, the Terminologia Anatomica recommends using the term basal nuclei instead of basal ganglia; however, this usage has not been generally adopted.
【Pseudoganglion】
A pseudoganglion is a localized thickening of the main part or trunk of a nerve that has the appearance of a ganglion but has only nerve fibers and no nerve cell bodies.
Pseudoganglia are found in the teres minor muscle and radial nerve.
【 語 句 】
・basal gaglia:脳幹神経節 ・cerebral cortex:大脳皮質 ・thalamus:視床 ・brainstem:脳幹 ・motor control:運動制御 ・cognition:認知 ・ambiguity:両義性、あいまいさ ・pseudoganglion:偽性神経節 ・teres minor muscle:小円筋 ・radial nerve:橈骨神経
