【概要】

|
|
|
|
|
右鼓膜(外側面) |
右鼓室・前面 |
右鼓室・前面(模型図) |
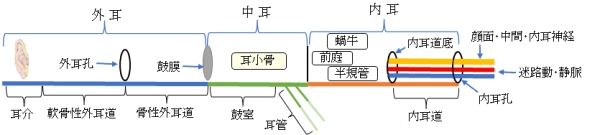
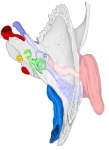
右外耳~中耳 |
右側頭骨(上面)
|
【区分】

鼓膜の区分 |
弛緩部 |
flaccid portion(Shrapnell 膜)
・鼓膜の上部に位置する部分で、ツチ骨隆起、前・後鼓膜ヒダよりも上方の部分のこと。
・側頭骨の鼓膜切痕の嵌入している。
|
緊張部 |
tense portion
・鼓膜の大部分を締める部分で、ツチ骨柄の付着によって鼓室に向かって漏斗状に牽引されている。
・側頭骨の鼓室部の鼓膜溝に嵌入し、線維軟骨輪によって固定される。
・中央よりもやや下方はツチ骨柄の先端の付着によって陥凹が見られる。これを鼓膜臍という。
|

以下は「日本人体解剖学」の解説文となる。
「ツチ骨条を下方に延長した線と鼓膜臍を通る仮の横線とをひくことによってできる4つの部分(4象限)をそれぞれ前上1/4,後上1/4、前下1/4および後下1/4と呼び、これらの4つの部分のほかに、さらに第5の部分として弛緩部を加える。鼓膜の切開は前下1/4から後下1/4部(前下象限から後下象限)にかけて行われる。」
【外耳道との関係】
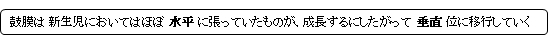
以下は「日本人体解剖学」の解説文となる。
「鼓膜は新生児ではほとんど水平に張っているが、成人になるにしたがって垂直位に近づく(成人では40~45°)。しかし、上壁とは明らかな角度をつくらずに移行する。すなわち140°の角度である。前壁とは約27°の角度をなす。」
【層構造】

鼓膜は外方から内方に向かって以下の層が区別される。 ※参考:「日本人体解剖学」
1 |
皮膚層 : 外耳道の皮膚の続きとなる。 |
a |
表皮 |
重層扁平上皮ででき、角化層の細胞は一般の皮膚とはことなり、その場で脱落せずに鼓膜周辺に移動する。 |
b |
真皮 |
結合組織からでき、表皮との間には乳頭を示さない。汗腺、皮脂腺、毛も見られない。 |
2 |
固有層 : 強靭な線維性結合組織からでき、鼓膜の中層を形成する。 |
a |
外側放線状線維層 |
|
b |
内側輪状線維層 |
鼓膜臍を同心円状に取り巻く線維束よりなり、辺縁部が厚い。
「緊張部と異なり弛緩部の線維は走行が不規則で、鼓室の圧の変化に対して鋭敏な部分である。」(日本人体解剖学) |
3 |
粘膜層 : 鼓室粘膜の続きとなる。 |
a |
粘膜固有層 |
リンパ様組織からでき、外方に存在する。 |
b |
単相扁平(/立方)上皮 |
内方にあって、鼓膜粘膜に移行する部位を除き線毛はみられない。 |
【関連語句】
【脈管/神経】
1 |
動 脈 |
|
静 脈 |
|
2 |
リンパ管 |
皮下リンパ管網→耳介後リンパ節、粘膜リンパ管網→鼓室のものと合流 |
3 |
神 経 |
|
【Wikipedia】
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles.
Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss. Collapse or retraction of the eardrum can cause conductive hearing loss or cholesteatoma.
【 語 句 】
・tetrapods: ・membrane:膜 ・external ear:外耳 ・middle ear:中耳 ・ossicles:小骨 ・oval window:卵円窓 ・cochlea:蝸牛 ・ultimately:最後に、結局 ・convert:変換する ・amplify:増幅する ・malleus:ツチ骨 ・rupture:破裂 ・conductive hearing loss:伝導性難聴 ・retraction:引っ込めること ・cholesteatoma:真珠腫
Orientation and relations
The tympanic membrane is oriented obliquely in the anteroposterior, mediolateral, and superoinferior planes. Consequently, its superoposterior end lies lateral to its anteroinferior end.
Anatomically, it relates superiorly to the middle cranial fossa, posteriorly to the ossicles and facial nerve, inferiorly to the parotid gland, and anteriorly to the temporomandibular joint
【Regions】
The eardrum is divided into two general regions: the pars flaccida and the pars tensa. The relatively fragile pars flaccida lies above the lateral process of the malleus between the notch of Rivinus and the anterior and posterior malleal folds. Consisting of two layers and appearing slightly pinkish in hue, it is associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction and cholesteatomas.
The larger pars tensa consists of three layers: skin, fibrous tissue, and mucosa. Its thick periphery forms a fibrocartilaginous ring called the annulus tympanicus or Gerlach's ligament. while the central umbo tents inward at the level of the tip of malleus. The middle fibrous layer, containing radial, circular, and parabolic fibers, encloses the handle of malleus. Though comparatively robust, the pars tensa is the region more commonly associated with perforations.
【 語 句 】
・consequently:従って ・middle cranial fossa:中頭蓋窩 ・parotid gland:耳下腺 ・temporomandibular joint:顎関節 ・pars flaccida:弛緩部 ・pars tensa:緊張部 ・fragile:もろい ・lateal process of the malleus:ツチ骨の外側突起 ・notch of Rivinus:リビウス切痕 ・anterior and posterior malleal folds:前・後ツチ骨ヒダ ・pinkish:ピンクがかった ・hue:色合い ・Eustachian tube dysfunction:耳管機能障害 ・cholesteatomas:真珠腫中耳炎 ・mucosa:粘膜 ・periphery:周囲、表面 ・annulus tympanicus:鼓膜輪 ・umbo:鼓膜臍 ・parabolic:放物線状の ・handle of malleus:ツチ骨柄 ・robust:強固な
【Umbo】
The manubrium (Latin: handle) of the malleus is firmly attached to the medial surface of the membrane as far as its center, drawing it toward the tympanic cavity. The lateral surface of the membrane is thus concave. The most depressed aspect of this concavity is termed the umbo.
【Nerve supply】
Sensation of the outer surface of the tympanic membrane is supplied mainly by the auriculotemporal nerve, a branch of the mandibular nerve (cranial nerve V3), with contributions from the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X), the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), and possibly the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX). The inner surface of the tympanic membrane is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
【 語 句 】
・tympanic cavity:鼓室 ・concave:凹状の ・concavity:陥没部 ・sensation:知覚 ・auriculotemporal nerve:耳介側頭神経 ・mandibular nerve:下顎神経 ・vagus nerve:迷走神経 ・glossopharygeal nerve:舌咽神経
【イラストを掲載しているサイト】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
