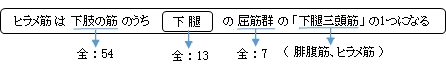
ヒラメ筋 ( ひらめきん、英:soleus muscle )
・ 概 要 |
・ 作 用 |
・ イラスト掲載サイ |
|
・ イラスト |
・ 神経 / 脈管 |
||
・ 起始 / 停止 |
・ Wikipedia |



腓腹筋とヒラメ筋の違い |
|||
腓腹筋 |
ヒラメ筋 |
||
1 |
筋の構成 |
速筋 が多い |
遅筋 が多い |
2 |
関節筋 |
単関節筋(足関節) |
|
・アキレス腱から伸びた膜様の停止腱がヒラメ筋のかなりの部分を覆う。また、裏面の中央部にはアキレス腱から分岐した腱が存在し、左右には起始腱がかなり下部まで延びている。 ⇒ イラスト解説
・「ヒラメ筋が完全に欠如、また重複することがある。ヒラメ筋腱弓の下を膝下動・静脈および脛骨神経が通る。」(日本人体解剖学)
⇒ イラスト解説
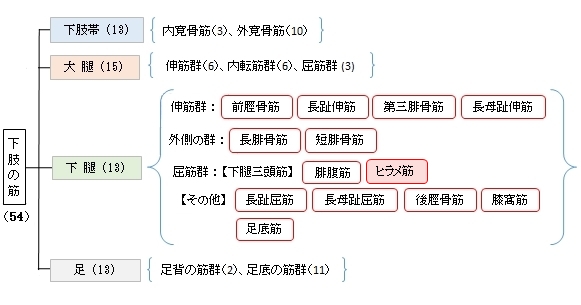
筋連結 : 膝窩筋、腓腹筋、長腓骨筋、長趾屈筋、後脛骨筋、足底筋
以下は「船戸和也のHP」の解説文となる。
「ヒラメ筋の下腿後区浅層の筋の1つ。大半は腓腹筋におおわれ、腓骨頭から腓骨後面、腱性弓(ヒラメ筋腱弓)および脛骨(ヒラメ筋線と内側縁)に起始する。ヒラメ筋腱弓は腓骨から脛骨へ至り、神経血管索をまたぐ。ヒラメ筋はアキレス腱を介して踵骨隆起に停止する。ヒラメ筋の筋腹は腓腹筋の筋腹よりも遠位に伸び、微細な腱様層によっておおわれている。その上を腓腹筋が滑走する。ヒラメ筋は複合羽状筋で、前頭平面に位置する腱様膜によって浅層の筋層に分けることができる。脛骨神経の支配を受ける。この筋は腓腹筋、足底筋とともに距腿関節における足の底屈を生じさせる。すなわち、これらの3筋は歩行、歩行時に、地面を後方に蹴るための力を出すのである。」
【 停 止 】: 踵骨の踵骨隆起 ※腓腹筋の停止腱とともにアキレス腱 《踵骨腱》となる。
「足を足底側に屈曲しかかとを上げ、足を固定するときは下腿を後方に引く。」 ( 日本人体解剖学 )
・膝関節が曲がっている状態での、足関節の底屈(かかとを上げる)はほとんどがヒラメ筋による作用となる。
・ 神 経 : 脛骨神経(L5,S1,S2,S3) ※場合によってはL4を含む。
In humans and some other mammals, the soleus is a powerful muscle in the back part of the lower leg (the calf). It runs from just below the knee to the heel, and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the gastrocnemius muscle and some anatomists consider them to be a single muscle, the triceps surae. Its name is derived from the Latin word "solea", meaning "sandal".
【Structure】
The soleus is located in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg.
The soleus exhibits significant morphological differences across species. It is unipennate in many species. In some animals, such as the rabbit, it is fused for much of its length with the gastrocnemius muscle.
In humans, the soleus is a complex, multi-pennate muscle, usually having a separate (posterior) aponeurosis from the gastrocnemius muscle. A majority of soleus muscle fibers originate from each side of the anterior aponeurosis, attached to the tibia and fibula. Other fibers originate from the posterior (back) surfaces of the head of the fibula and its upper quarter, as well as the middle third of the medial border of the tibia.
The fibers originating from the anterior surface of the anterior aponeurosis insert onto the median septum and the fibers originating from the posterior surface of the anterior aponeurosis insert onto the posterior aponeurosis. The posterior aponeurosis and median septum join in the lower quarter of the muscle and then join with the anterior aponeuroses of the gastrocnemius muscles to form the calcaneal tendon or Achilles tendon and inserts onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus, or heel bone.
In contrast to some animals, the human soleus and gastrocnemius muscles are relatively separate, such that shear can be detected between the soleus and gastrocnemius aponeuroses.
The Soleus is vestigial in the horse.
【 語 句 】
・gastrocnemius muscle: ・triceps surae: ・morphological :形態学的な ・unipennate:単翼状 ・aponeurosis: ・tibia: ・fibula: ・calcaneal tendon: ・Achilles tendon: ・calcaneus: ・In contrast to~:~とは対照的に ・・such that~:~であるように ・shear:?(Weblioでは「大ばさみ、植木ばさみ」となっているが…) ・detect:見つける ・vestigial:退化した
【Relations】
The gastrocnemius muscle is superficial to (closer to the skin than) the soleus, which lies below the gastrocnemius.
The plantaris muscle and a portion of its tendon run between the two muscles. Deep to it (farther from the skin) is the transverse intermuscular septum, which separates the superficial posterior compartment of the leg from the deep posterior compartment.
On the other side of the fascia are the tibialis posterior muscle, the flexor digitorum longus muscle, and the flexor hallucis longus muscle, along with the posterior tibial artery and posterior tibial vein and the tibial nerve.
Since the anterior compartment of the leg is lateral to the tibia, the bulge of muscle medial to the tibia on the anterior side is actually the posterior compartment. The soleus is superficial middle of the tibia.
【Function】
The action of the calf muscles, including the soleus, is plantarflexion of the foot (that is, they increase the angle between the foot and the leg). They are powerful muscles and are vital in walking, running, and keeping balance. The soleus specifically plays an important role in maintaining standing posture; if not for its constant pull, the body would fall forward.
Also, in upright posture, the soleus is responsible for pumping venous blood back into the heart from the periphery, and is often called the skeletal-muscle pump, peripheral heart or the sural (tricipital) pump.
Soleus muscles have a higher proportion of slow muscle fibers than many other muscles. In some animals, such as the guinea pig and cat, soleus consists of 100% slow muscle fibers. Human soleus fiber composition is quite variable, containing between 60 and 100% slow fibers.
The soleus is the most effective muscle for plantarflexion in a bent knee position (Hence called the first gear muscle). This is because the gastrocnemius originates on the femur, so bending the leg limits its effective tension. During regular movement (i.e., walking) the soleus is the primary muscle utilized for plantarflexion due to the slowtwitch fibers resisting fatigue.
【 語 句 】
・plantaris muscle:足底筋 ・transverse intermuscular septum:横(下腿)筋間中隔? ・fascia:筋膜 ・tibialis posterior muscle:後脛骨筋 ・flexor digitorum longus muscle:長趾屈筋 ・flexor hallucis longus muscle:長母屈筋 ・posterior tibial artery:後脛骨動脈 ・tibial nerve:脛骨神経 ・bulge:ふくらみ ・upright posture:直立姿勢 ・venous blood:静脈血 ・peripheral:周辺の、末梢の ・sural:腓腹の ・tricipital:三頭筋の ・proportion:割合 ・femur: ・utilized:利用する、役立たせる
・イラストを掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ


