【 構 成 】

【構 造】
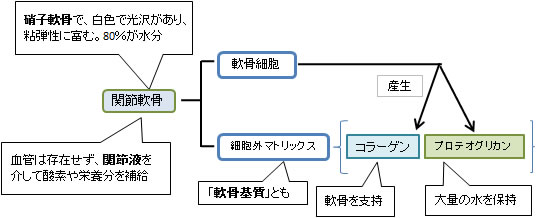
関節軟骨は以下のような4層の構造をなしている。
1 |
表 層 |
superficial tangential zone 10%~20% |
2 |
中間層 |
middle zone 40~60% |
3 |
深 層 (or 放射層) |
zeep (or radial) zone 30% |
4 |
石灰下層 |
calcified zone
下部の骨成分と強固に連結
|
⇒ 構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイトⅠ
⇒ 構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイトⅡ
⇒ 構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイトⅢ
⇒ 構造が分かる細胞組織学的写真を掲載しているサイト
The articular cartilage function is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM consists mainly of proteoglycan and collagens. The main proteoglycan in cartilage is aggrecan, which, as its name suggests, forms large aggregates with hyaluronan. These aggregates are negatively charged and hold water in the tissue. The collagen, mostly collagen type II, constrains the proteoglycans. The ECM responds to tensile and compressive forces that are experienced by the cartilage. Cartilage growth thus refers to the matrix deposition, but can also refer to both the growth and remodeling of the extracellular matrix. Due to the great stress on the patellofemoral joint during resisted knee extension, the articular cartilage of the patella is among the thickest in the human body.
【 語 句 】
・molecular composition:分子組成 ・extracellular matrix:細胞外マトリックス ・proteoglycan:プロテオグリカン ・collagen:コラーゲン ・aggrecan:アグリカン ・aggregate:集合体 ・hyaluronan:ヒアルロン酸 ・tissue:組織 ・tensile:引き延ばすことができる ・cartilage:軟骨 ・deposition:? ・patellofemoral joint:膝蓋大腿関節