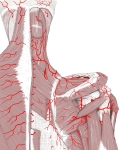
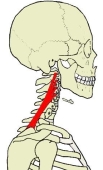
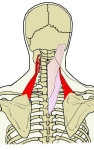
肩甲挙筋 ( けんこうきょきん、 英 : levator scapulae muscle )
・ 概 要 |
・ 作 用 |
・ イラスト掲載サイト |
|
・ イラスト |
・ 神経 / 脈管 |
||
・ 起始 / 停止 |
・ Wikipedia |
![]()


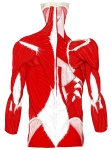
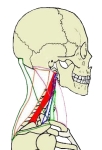
・ 名称通り肩甲骨を上げる筋肉となり、この筋肉が収縮することにより肩こりの原因となる。
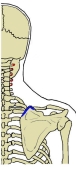
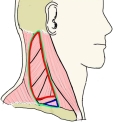
・ 外側頚三角部 に確認できる筋の1つになるので、その一部は皮下に確認が可能である。⇒ イラスト
![]()
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |

|
![]()
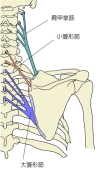
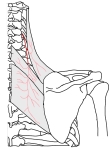
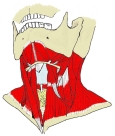
【 起 始 】 : 第1~第4(又は5)頸椎の横突起の後結節
【 停 止 】 : 肩甲骨の内側縁上部1/3 ( 主に上角 )
![]()
![]()
・ 神 経 : 肩甲背神経 ( C5 )
The levator scapulae is a skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.
【 Structure 】
The levator scapulae originates from the posterior tubercle of the transverse process of cervical vertebrae one to four. The muscle is inserted into medial border of the scapula extending from superior angle to junction of spine and medial border of scapula.[1]
The levator scapulae may lie deep to the Sternocleidomastoid at its origin, deep or adjacent to the splenius capitis at its origin and mid-portion, and deep to the trapezius in its lower portion.
【 Relations 】
One of the muscles within the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck, the superior part of levator scapulae is covered by sternocleidomastoid and its inferior part by the trapezius.[2] It is bounded in front by the scalenus medius and behind by splenius cervicis. The spinal accessory nerve crosses laterally in the middle part of the muscle and the dorsal scapular nerve may lie deep to or pass through it.[3]
【 Variation 】
The number of attachments varies; a slip may extend to the occipital or mastoid, to the trapezius, scalene or serratus anterior, or to the first or second rib. The muscle may be subdivided into several distinct parts from origin to insertion. Levator claviculæ from the transverse processes of one or two upper cervical vertebræ to the outer end of the clavicle corresponds to a muscle of lower animals. More or less union with the serratus anterior muscle.[4]
【 語 句 】
・ posterior tubercle : 後結節 ・ transverse process : 横突起 ・ cervical vertebrae : 頚椎 ・ Sternocleidomastoid : 胸鎖乳突筋 ・ splenius capitis : 頭板状筋 ・ adjacent : 隣接した ・ trapezius : 僧帽筋 ・ posterior triangle of the neck : 後頚三角 ・ scalenus medius : 中斜角筋 ・ splenius cervicis : 頚板状筋 ・ spinal accessory nerve : 副神経 ・ dorsal scapular nerve : 肩甲背神経 ・ occipital : 後頭骨 ・ mastoid : 乳様突起 ・ distinct : 明瞭な
【 Nerve supply 】
The levator scapulae is supplied by two or three branches of the third and fourth cervical nerves,[1] and frequently by a branch from the dorsal scapular nerve.[4]
【 Blood supply 】
The levator scapulae is supplied by the dorsal scapular artery. Normally, this artery has a small branch which passes laterally to the supraspinatus fossa of the scapula, and in a third of cases, this branch supplies the muscle. If the dorsal scapular artery comes off the transverse cervical artery, the parent transverse cervical artery splits, the dorsal scapular artery passes medially, while the transverse cervical artery passes laterally.[3]
【 Function 】
When the spine is fixed, levator scapulae elevates the scapula and rotates its inferior angle medially.[1] It often works in combination with other muscles like the rhomboids and pectoralis minor to produce downward rotation of the scapula.
Elevating or rotating one shoulder at a time would require muscles to stabilize the cervical spine and keep it immobile so it does not flex or rotate. Elevating both at once with equal amounts of pull on both side of cervical spinal origins would counteract these forces. Downward rotation would be prevented by co-contraction of other muscles that elevate the spine, the upper fibers of the trapezius, which is an upward rotator.
When the shoulder is fixed, levator scapulae rotates to the same side and flexes the cervical spine laterally. When both shoulders are fixed, a simultaneous co-contraction of both levator scapulae muscles in equal amounts would not produce lateral flexion or rotation, and may produce straight flexion or extension of the cervical spine.
【 語 句 】
・ cervical nerves : 頚神経 ・ supraspinatus fossa : 棘上窩 ・ transverse cervical artery : 頚横動脈 ・ rhomboids : 菱形筋 ・ pectoralis minor : 小胸筋 ・ immobile : 不動の、固定した ・ counteract : 邪魔する ・ simultaneous : 同時に起こる
![]()