脛骨神経とは



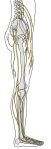
腰神経叢・仙骨神経叢(外側面) |
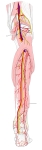
右下腿・後面
|
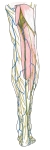
右下腿・後面
|
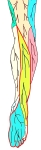
右下腿/足・後面
|
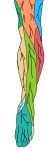
右下腿/足・後面
|
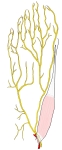
右足・底面 |
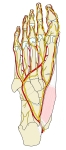
右足・底面
|

右足・底面
|

右足・底面
|
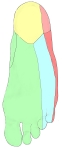
右足(底部)
|
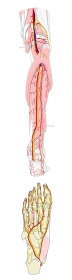
以下が脛骨神経が坐骨神経から分岐してからの主な走行となる。
1. 膝窩の上方(およそ大腿の下方1/3の高さ)で坐骨神経より分岐する。
2. 膝窩動・静脈とともに、腓腹筋の両頭の間を膝窩に向かう。
3. ヒラメ筋腱弓を通過する。
4. 長指屈筋と後脛骨筋の間を後脛骨動・静脈とともに下行する。
5. 内果の後方に向かう。
6. 後脛骨筋の停止腱と併走するように足底に回る。
7. 足底で2終枝である内側足底神経と外側足底神経に分岐する。
※ 資料によっては「屈筋支帯の下部(足底に至る前)で分岐する」と解説しているものもある。
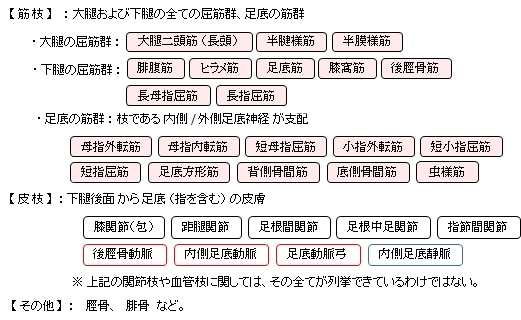
以下は、脛骨神経がその枝も含めて分布する主な筋肉や皮膚となる。
 以下は「 Wikipedia 」の膝窩からの関節枝 (articular branches) の解説文となる。膝関節にいく枝として以下の3つの神経を挙げている。 以下は「 Wikipedia 」の膝窩からの関節枝 (articular branches) の解説文となる。膝関節にいく枝として以下の3つの神経を挙げている。
・superior medial genicular nerve
・middle genicular nerve
・inferior genicular nerve
日本語訳としては、それぞれ上内側膝神経、中膝神経、下膝神経となると思われるが、「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」や「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では一切それらの名称の神経は見当たらない。 」や「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では一切それらの名称の神経は見当たらない。
「Articular branches - There are three articular branches arises from the upper part of the fossa: superior medial genicular nerve (located on the surface of medial condyle of femur, middle genicular nerve (pierces the posterior capsule of the knee joint to supply the structures located in the intercondylar notch of the femur, and inferior genicular nerve (runs along the upper border of the popliteus to reach the medial condyle of tibia).」
|
|
|
|
|
|

右足(底部)
|
|
|
|
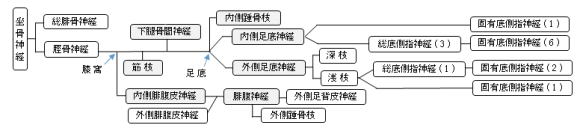
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では、脛骨神経の枝として以下を挙げている。 」では、脛骨神経の枝として以下を挙げている。

以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
【 structure 】
■ Popliteal fossa ■
Tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root values of L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3. It lies superficial (or posterior) to the popliteal vessels, extending from the superior angle to the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, crossing the popliteal vessels from lateral to medial side. It gives off branches as shown below:[1]
- ・Muscular branches - Muscular branches arises from the distal part of the popliteal fossa. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and popliteusmuscles. Nerve to popliteus crosses the popliteus muscle, runs downwards and laterally, winds around the lower border of the popliteus to supply the deep (or anterior) surface of the popliteus.
This nerve also supplies the tibialis posterior muscle, superior tibiofibular joint, tibia bone, interosseous membrane of leg, and the inferior tibiofibular joint.[1]
- ・Cuteneous branches - Tibial nerve also gives off a cutaneous nerve called the sural nerve from the middle of the popliteal fossa and exits at the inferior angle. It supplies the skin of the lower half of the back of the leg and lateral border of the foot until the tip of the little toe.[1]
- ・Articular branches - There are three articular branches arises from the upper part of the fossa: superior medial genicular nerve (located on the surface of medial condyle of femur, middle genicular nerve (pierces the posterior capsule of the knee joint to supply the structures located in the intercondylar notch of the femur, and inferior genicular nerve (runs along the upper border of the popliteus to reach the medial condyle of tibia).[1]
■ back of the leg ■
At the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, tibial nerve passes deep to the tendinous arch of soleus to enter the back of the leg. In the leg, it runs downwards and medially to reach the posteromedial side of the ankle, midway between the medial malleolus and medial tubercle of the calcaneum. It terminates deep to the flexor retinaculum at the origin of the abductor hallucis by dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves to supply the foot. The tibial nerve gives off several branches to supply the back of the leg:[1]
- ・Muscular branches - Supplies tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and deep part of soleus.[1]
- ・Cutaneus branches - The medial calcaneal nerve pierces the flexor retinaculum to supply the skin of the back and lower surface of the heel.[1]
- ・Articular branches - Supplies the ankle joint[1]
■ foot ■
In the foot, the nerve terminates by dividing into medial and lateral plantar branches.
- ・Medial plantar nerve - It is the larger terminal branch of the tibial nerve. It passes between the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis to divides further into branches. Its distribution resembles to that of the distribution of median nerve in the hand. Its muscular branches supplies the abductor hallucis, the flexor digitorum brevis, the flexor hallucis brevis and the first lumbrical. Cutaneous distribution of the medial plantar nerve supplies the medial sole and medial three and one half toes through four digital branches. Each digital branch give off a dorsal branch to supply the nail beds on the dorsum. This nerve also gives off articular branches to supply the tarsus and metatasus bones. [1]
- ・Lateral plantar nerve - It is the smaller terminal branch of the tibial nerve. It courses laterally and forward until the base of fifth metatarsal bone, where it divideds into superficial and deep branches. Its distribution resembles to the distribution of ulnar nerve in the hand. The main trunk of the nerve supplies two muscles: flexor digitorum accessorius and abductor digiti minimi. This nerve also supplies the skin of the sole.[1] The superficial branch is divided into medial and lateral branches. The lateral branch supplies three muscles: flexor digiti minimi, 3rd and 4th interossei, and the skin over the lateral side of the toe. The medial branch communicates with the medial plantar nerve and supplies the skin over the fourth interdigital cleft.[1] The deep branch supplies the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th lumbricals, first and second plantar interossei and adductor hallucis.[1]」
【 語 句 】
・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・:
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|