坐骨神経とは



「 プロメテウス解剖学アトラス 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 坐骨神経は、腓骨部より数本の筋枝を大腿二頭筋短頭へ与えた後、大腿下1/3付近で脛骨神経と総腓骨神経に分かれる。」
「 坐骨神経脛骨部は、大腿部を走行中に半腱様筋、半膜様筋、大腿二頭筋(長頭)と大内転筋(内側部)へ数本の枝を送る。」

「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」には 以下のような解説文が見られる。 」には 以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 分岐は、これよりもさらに上方で起こり、往々にして小骨盤腔を出る前にすでに起こることがある。このような場合を 高位分岐 といい、約10% の頻度で見られる。」
仙骨神経叢 |
臀部の神経 |
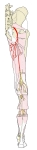
右下肢(後面)
|
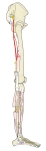
右下肢(側面)
|
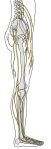
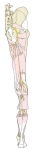
腰/仙骨神経叢
からの主な神経 |
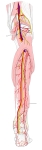
右下腿(後面) |
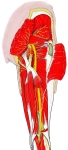
右大腿(後面) |
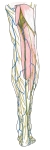
右足下腿の神経 |
|
|
以下が坐骨神経が分岐するまでの主な走行となる。
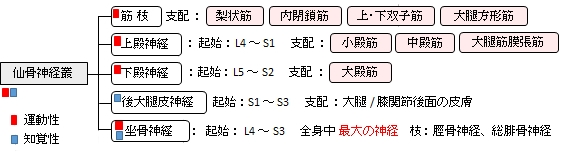
1. 第4腰神経 ~ 第3仙骨神経 を起始とする。
2. 梨状筋 の前面で1本の神経幹となる。
3. 梨状筋下孔 を通過して 小骨盤 を出る。
4. 大転子 と 坐骨結節 のほぼ中間を 大殿筋 と 大腿方形筋 に挟まれて通過する。
5. 大腿二頭筋 の長頭の前を交差するように通過する。
6. 大腿の屈筋群に筋枝を出しながらほぼ垂直に下行する。
7. 膝窩 の上方(だいたい大腿の下方の1/3の高さ)で 脛骨神経 と 総腓骨神経 に分岐する。

また、非常に稀(約0.5%)ではあるが 坐骨神経の一部( 総腓骨神経となる神経線維 )が梨状筋上孔を通過することもある。
⇒ イラスト解説
ここでは起始部から膝窩の上方において2つに分岐するまでの神経幹が分布する領域を示すが、「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」を参考にしても今一つ明瞭になっていないように思われる。 」を参考にしても今一つ明瞭になっていないように思われる。
■ 知覚性 ■
脛骨神経と総腓骨神経の2つに分岐するまでに知覚性の神経線維は分岐していないと思われる。
■ 運動性 ( 筋 枝 )■
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」の「坐骨神経」の解説では以下のような解説文が見られる。 」の「坐骨神経」の解説では以下のような解説文が見られる。
「(坐骨神経は)大腿二頭筋長頭の前をこれと交叉しつつ垂直に下り、大腿屈筋群に枝を与えたのち… 」
また、坐骨神経の筋枝として以下のように解説している。
「 大腿方形筋 に至る 」
つまり、坐骨神経の神経幹が支配する筋肉として「大腿方形筋と大腿の屈筋群」ということになる。そして、その大腿の屈筋群だが、同書の「下肢の筋」の分類の図では以下の3つの筋を挙げている。
・ 大腿二頭筋 ・ 半腱様筋 ・ 半膜様筋
ただ、同書のそれぞれの筋の解説をみると「神経支配」は以下のようになっていて、坐骨神経の名称は見られない。
・ 大腿二頭筋 : 長頭 ) 脛骨神経( L5 ~ S 2)、 短頭 ) 総腓骨神経 ( L4 ~ S1 )
・ 半腱様筋 : 脛骨神経( L4 ~ S2 )
・ 半膜様筋 : 脛骨神経( L4 ~ S2 )
一応、ここでは坐骨神経の神経幹が支配する筋として以下の4つを挙げておきたいと思う。

「 プロメテウス解剖学アトラス 」では(このページの上部参照のこと)、 筋枝が支配する筋として以下の4つの筋を挙げている。
・ 大腿二頭筋 ( 両頭 ) ・ 半腱様筋 ・ 半膜様筋 ・ 大内転筋 ( 内側部 )
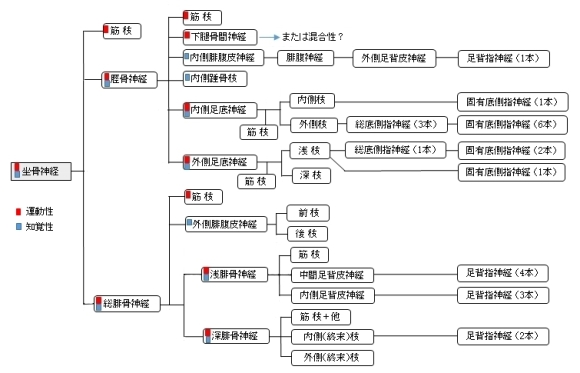
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では、坐骨神経の枝として、筋枝、総腓骨神経、浅腓骨筋、深腓骨神経、および脛骨神経の5つを挙げている。しかしここでは、浅腓骨筋と深腓骨神経に関しては総腓骨神経の枝とすることにする。 」では、坐骨神経の枝として、筋枝、総腓骨神経、浅腓骨筋、深腓骨神経、および脛骨神経の5つを挙げている。しかしここでは、浅腓骨筋と深腓骨神経に関しては総腓骨神経の枝とすることにする。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The sciatic nerve (/sa??æt?k/; also called ischiadic nerve, ischiatic nerve) is a large nerve in humans and animals. It begins in the lower back and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect.[1] The sciatic nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for nearly the whole of the skin of the leg, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.
【 structure 】
The sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of the spinal cord. The fibres unite to form a single nerve in front of the piriformis muscle. The nerve passes beneath piriformis and through the greater sciatic foramen, exiting the pelvis.[2]:422–4 From here, it travels down the posterior thigh to the popliteal fossa. The nerve travels in the posterior compartment of the thigh behind (superficial to) the adductor magnus muscle, and is itself in front of (deep to) one head of the biceps femoris muscle. At the popliteal fossa, the nerve divides into its two branches.
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body.[2]:422–4
【 function 】
The sciatic nerve supplies sensation to the skin of the foot, as well as the entire lower leg (except for its inner side). Sensation to skin to the sole of the foot is provided by the tibial nerve, and the lower leg and upper surface of the foot via the common fibular nerve
The sciatic nerve also innervates muscles. In particular:[2]:422–4
【 語 句 】
・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・:
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ(起始部)
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|