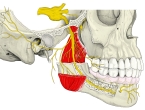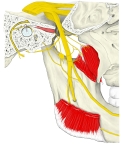


■中硬膜動脈との関係■

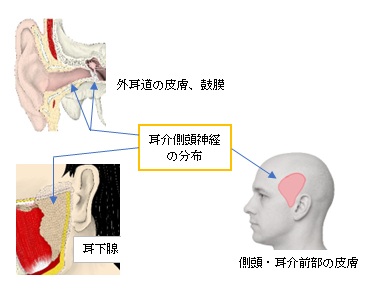
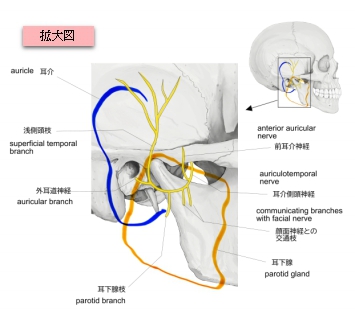
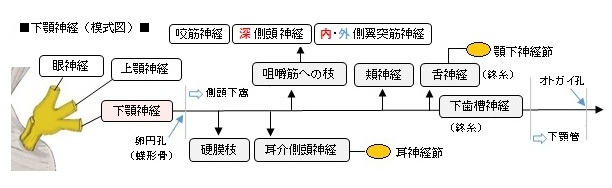
以下は下顎神経の枝を表した簡単な図となる。
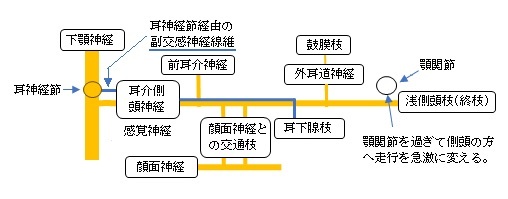
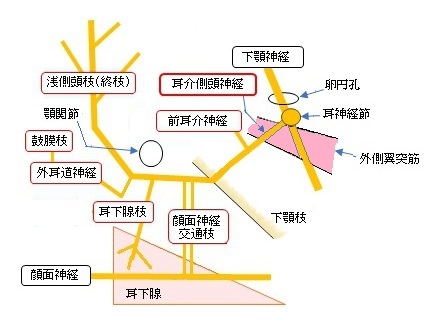
以下、耳介側頭神経の幹の神経線維の走行を解説したものになる。
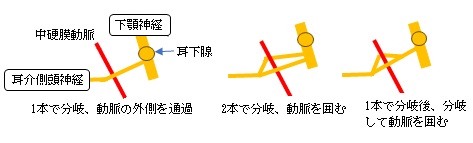
1. 卵円孔から10~13㎜前後の部位で下顎神経から分岐する。
(だいたい耳神経節の直下にあたり、2本で分岐する場合と1本の場合がある。)
2. 分岐後、後下方に向かい、外側翼突筋、中硬膜動脈を通り過ぎる。
(2本で分岐する場合は中硬膜動脈を挟んだのちに1本になる。
また、1本で分岐しても中硬膜動脈の前で二分岐し、動脈を挟んで通過したのちに再び1本になるケースもある。)
3. 後下方に走行を続け顎関節を通り過ぎた辺りから急激に走行方向を上方に変える。
4. 耳介の前方を上方に向かい浅側頭枝(終枝)となって側頭前部の皮膚に分布する。
「日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では耳介側頭神経の枝として、外耳道神経、耳下腺枝、顔面神経との交通枝、前耳介神経、および浅側頭枝の5つを挙げているが、「船戸和弥のホームページ」では、その5枝に加えて「鼓膜枝」の名称が見られる。以下が耳介側頭神経の枝とその分布の簡単な図になる。 」では耳介側頭神経の枝として、外耳道神経、耳下腺枝、顔面神経との交通枝、前耳介神経、および浅側頭枝の5つを挙げているが、「船戸和弥のホームページ」では、その5枝に加えて「鼓膜枝」の名称が見られる。以下が耳介側頭神経の枝とその分布の簡単な図になる。

Q.「分布は枝によるものと考えてよいか?それとも幹からも神経線維出るのか?」
A.「耳介側頭神経の分布について整理して説明します。
1. 基本構造
-
耳介側頭神経は 下顎神経(V3)から分岐 します。
-
下顎神経の運動根・感覚根のうち、感覚神経線維が主体です。
-
分岐後、神経幹(main trunk)から複数の枝(branches)が出て、側頭部や耳介などに分布します。
2. 分布の単位
- 枝を通じて分布
- 神経幹から直接出る微細線維
-
耳介側頭神経幹自体からも、名称を持たない細かい末梢線維が出る場合があります。
-
これらは周囲の皮膚や耳の軟骨部に直接分布することがあります。
-
ただし、解剖学的には 主要な知覚分布は枝単位で整理される ことが多く、実務的には「枝の分布=耳介側頭神経の分布」と考えて差し支えありません。
3. まとめ
-
耳介側頭神経の分布は 基本的には枝による分布 で理解してよい。
-
ただし、神経幹からも微細な無名線維が出て周囲の皮膚に分布することがあり得る。
-
解剖学的・臨床的には、分布を把握する上で 枝を基準にする方が実用的 です。
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
「The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve (V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head.
【 Origin 】
The auriculotemporal nerve arises as two roots from the posterior division of the mandibular nerve. The mandibular nerve is a branch of the trigeminal nerve, and the mandibular nerve exits the skull through the foramen ovale.[1] These roots encircle the middle meningeal artery (a branch of the mandibular part of the maxillary artery, which is in turn a terminal branch of the external carotid artery). The roots encompass the middle meningeal artery then converge to form a single nerve.
【 Course 】
The auriculotemporal nerve passes between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, gives off parotid branches and then turns superiorly, posterior to its head and moving anteriorly, gives off anterior branches to the auricle. It then crosses over the root of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone, deep to the superficial temporal artery.
【 Innervation 】
The somatosensory root (superior) originates from branches of the mandibular nerve (cranial nerve V), which pass through the otic ganglion without synapsing. Then they form the somatosensory (superior) root of the auriculotemporal nerve. The two roots re-unite, and shortly after the branching of secretomotor fibers to the parotid gland (parotid branches), the auriculotemporal nerve comprises exclusively somatosensory fibers, which ascend to the superficial temporal region. There, it supplies the auricle, external acoustic meatus, outer side of the tympanic membrane and the skin in the temporal region (superficial temporal branches). It also carries a few articular branches that go on to supply the temporomandibular joint.
The parasympathetic root (inferior) carries postganglionic fibers to the parotid gland. These parasympathetic, preganglionic secretomotor fibers originate from the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) as one of its branches, the tympanic nerve, which enters the tympanic cavity through the inferior tympanic canaliculus. The tympanic nerve and postganglionic sympathetic fibers, which come with the arteries-related head, make the tympanic plexus on the promontorium. This plexus gives off a branch lesser petrosal nerve. This nerve synapses in the otic ganglion and its postganglionic fibers form the inferior, parasympathetic root of the auriculotemporal nerve. The two roots re-unite and shortly after the "united" auriculotemporal branch gives off parotid branches, which serve as secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland.」
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|