【概 要】
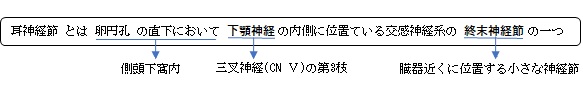
・「灰赤色扁平円形の3~4㎜大の神経節」(日本人体解剖学)
・下顎神経に付属する神経節の一つである。
・「」
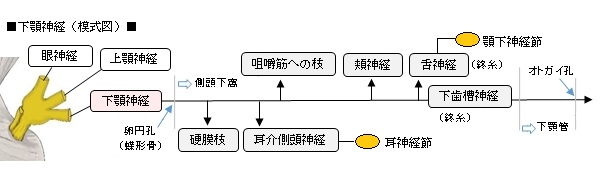

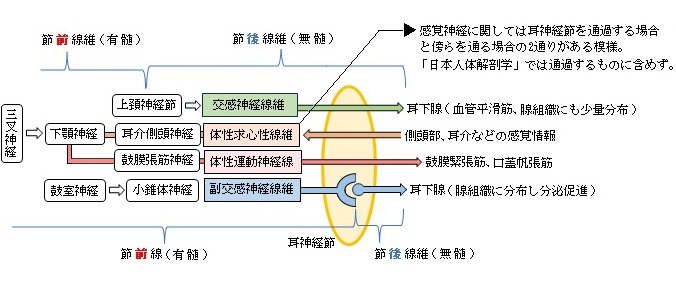
1. 副交感神経(線維): 節前線維、神経節でシナプスして節後線維に情報を伝える。
2. 交感神経(線維): 上頚神経節でシナプスした節後線維、神経節は通過するのみ。
3. 知覚神経(線維): 舌の前部2/3からの感覚情報を伝える線維は神経節を通過するのみ。
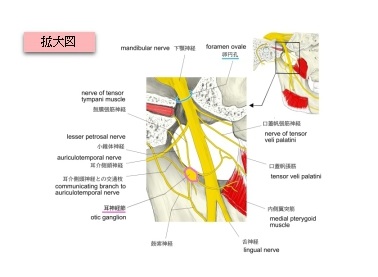
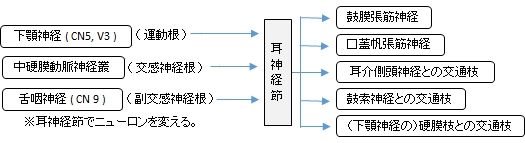
【入る神経線維】
「耳神経節には3つの由来を異にする神経線維の枝(根)が入る。
1.
2. 中硬膜動脈神経叢(中硬膜動脈を包む交感神経叢)からの交感神経根
3. 舌咽神経の枝(小錐体神経)からの副交感神経根(耳神経節でニューロンを変える)
【出る神経線維】
耳神経節からは、次の数枝が出る。これらの枝は、耳神経節に入る上記のa)~c)の3つの根からの神経線維で、a)からの運動性、b)からの交感性、およびc)からの副交感性線維の種々の割合で含む。
1. 鼓膜張筋神経 nerve of tensor tympani muscle:鼓膜張筋に分布する。
2. 口蓋帆張筋神経 nerve of tensor veli palatine muscle:口蓋帆張筋に分布する。
3. 耳介側頭神経との交通枝 communicating branch with auriculotemporal nerve:
舌咽神経の枝(小錐体神経)からくる副交感神経で、耳神経節でニューロンをかえ、節後線維となり
下顎神経の枝の耳介側頭神経と交通する。(耳下腺の分泌に関係する)
4. 鼓索神経との交通枝 communicating branch with chorda tympani:鼓索神経と交通する。
5.(下顎神経の)硬膜枝との交通枝 communicating branch with meningeal branch of mandibular nerve:(下顎神経の)硬膜枝と交通する。
⇒ 別の図
【ChatGPTに聞いてみた】
Q:「耳神経節は本当に灰赤色を呈するのか?」
A:「はい、耳神経節は解剖学書では 灰赤色(reddish-gray) と記載されることがあります。
🔹 理由と補足
- 構造的要因
- 耳神経節は神経細胞体が集まった小さな神経節で、肉眼では灰色が主体
- ただし、血流の影響で赤みが少し混ざって見えるため、「灰赤色」と表現される
- 大きさ・形態
- 小豆大(約3〜4 mm)、扁平
- 卵円孔の下、下顎神経(V3)内側に位置
- 観察条件による変化
- 標本の固定法や血流の有無によって色調は変化する
- 固定標本では灰色~淡褐色に見える場合もある
🔹 文献の記載例
“The otic ganglion is a small, flattened, reddish-gray structure about 3–4 mm in diameter.”
→ 「耳神経節は小さく扁平で、直径3〜4mmの灰赤色の構造である」
「耳神経節は卵円孔の直下に位置し、灰赤色の扁平な神経節である」
【参考となるサイト】
「Wikipedia」では以下のように解説している。
「The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.
It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. The others are the ciliary ganglion, the submandibular ganglion and the pterygopalatine ganglion.
【 語 句 】
・parasympathetic:副交感神経の ・foramen ovale:卵円孔 ・infratemporal fossa:側頭下窩 ・mandibular nerve:下顎神経 ・glossopharyngeal nerve:舌咽神経 ・innervate:神経支配する ・parotid gland:耳下腺 ・salivation:唾液の分泌 ・ciliary ganglion:毛様体神経節 ・submandibular ganglion:顎下神経節 ・pterygopalatine ganglion:翼口蓋神経節
【 Structure and Relations 】
The otic ganglion is a small (2-3 mm), oval shaped, flattened parasympathetic ganglion of a reddish-gray color, located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve.
It is in relation, laterally, with the trunk of the mandibular nerve at the point where the motor and sensory roots join; medially, with the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube , and the origin of the tensor veli palatini; posteriorly, with the middle meningeal artery. It surrounds the origin of the nerve to the medial pterygoid.
【 語 句 】
・reddish-gray color:灰赤色 ・motor and sensory roots:運動と知覚根・cartilaginous:軟骨性の ・auditory tube:耳管 ・tensor veli palatini: 口蓋帆張筋・middle meningeal artery:中硬膜動脈 ・medial pterygoid:内側翼突筋
【 Connections 】
The preganglionic parasympathetic fibres originate in the inferior salivatory nucleus of the glossopharyngeal nerve. They leave the glossopharngeal nerve by its tympanic branch and then pass via the tympanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve to the otic ganglion. Here, the fibres synapse, and the postganglionic fibers pass by communicating branches to the auriculotemporal nerve, which conveys them to the parotid gland. They produce vasodilator and secretomotor effects.
Its sympathetic root is derived from the plexus on the middle meningeal artery. It contains post-ganglionic fibers arising in the superior cervical ganglion. The fibers pass through the ganglion without relay and reach the parotid gland via the auriculotemporal nerve. They are vasomotor in function.
【 語 句 】
・preganglionic parasympathetic fibres:副交感神経節前線維 ・inferior salivatory nucleus:下唾液核 ・tympanic:鼓膜の ・lesser petrosal nerve:小錐体神経 ・postganglionic fibers:節後線維 ・auriculotemporal nerve:耳介側頭神経 ・convey:伝える、運ぶ ・vasodilator:血管拡張物質 ・secretomotor effects:分泌運動効果 ・superior cervical ganglion:上頚神経節 ・vasomotor:血管収縮・拡張を調節する
The sensory root comes from the auriculotemporal nerve and is sensory to the parotid gland.
The motor fibers supplying the medial pterygoid and the tensor palati and the tensor tympani pass through the ganglion without relay.
The ganglion is connected to the chorda tympani nerve and also to the nerve of the pterygoid canal. These pathways provide an alternate pathway of taste from the anterior two thirds of the tongue. These fibers do not pass through the middle ear.」
【 語 句 】
・tensor palati:口蓋帆張筋 ・tensor tympani:鼓膜張筋 ・:・without relay:シナプス無しで ・chorda tympani nerve:鼓索神経 ・nerve of the pterygoid canal:翼突管神経 ・middle ear:中耳
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
