

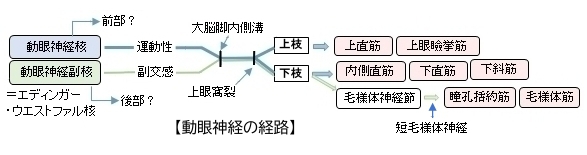
・毛様体筋は眼球内に存在する内眼筋の1つとなる。
・動眼神経(CNⅢ)からの副交感神経線維を毛様体神経節経由で短毛様体神経として支配を受ける。


以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文の序文となる。
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscle in the eye's middle layer, uvea (vascular layer). It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae.
【 語 句 】
・intrinsic muscle:内在筋 ・smooth muscle:平滑筋 ・uvea:眼球血管膜 ・vascular layer:血管層 ・accommodation:視力調節 ・regulate:調整する ・aqueous humor:房水 ・Schlemm's canal:シュレム管 ・pupil:瞳孔 ・sphincter pupillae muscle:瞳孔括約筋 ・dilator pupillae:瞳孔散大筋
【Structure】
【Development】
The ciliary muscle develops from mesenchyme within the choroid and is considered a cranial neural crest derivative.
【Nerve supply】
The ciliary muscle receives parasympathetic fibers from the short ciliary nerves that arise from the ciliary ganglion. The parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are part of cranial nerve V1 (Nasociliary nerve of the trigeminal), while presynaptic parasympathetic fibers to the ciliary ganglia travel with the oculomotor nerve. The postganglionic parasympathetic innervation arises from the ciliary ganglion.
Presynaptic parasympathetic signals that originate in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus are carried by cranial nerve III (the oculomotor nerve) and travel through the ciliary ganglion via the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers which travel in the short ciliary nerves and supply the ciliary body and iris. Parasympathetic activation of the M3 muscarinic receptors causes ciliary muscle contraction. The effect of contraction is to decrease the diameter of the ring of ciliary muscle causing relaxation of the zonule fibers, the lens becomes more spherical, increasing its power to refract light for near vision.
The parasympathetic tone is dominant when a higher degree of accommodation of the lens is required, such as reading a book.
【 語 句 】
・mesenchyme:間葉 ・choroid:脈絡膜 ・neural crest:神経堤 ・derivative:派生したもの? ・parasymphathetic:副交感神経の ・short ciliary nerves:短毛様体神経 ・ciliary ganglion:毛様体神経節 ・postganglionic fibers:節後繊維 ・presynaptic:シナプス前の ・oculomotor nerve:動眼神経 ・Edinger-Westphal nucleus:エディンガー・ウェストファル核 ・muscarinic receptors:ムスカリン受容体 ・contraction:収縮 ・zonule fibers:毛様体小帯 ・spherical:球状の ・dominant:優勢の
【Function】
■Accommodation■
The ciliary fibers have circular (Ivanoff), longitudinal (meridional) and radial orientations.
According to Hermann von Helmholtz's theory, the circular ciliary muscle fibers affect zonular fibers in the eye (fibers that suspend the lens in position during accommodation), enabling changes in lens shape for light focusing. When the ciliary muscle contracts, it pulls itself forward and moves the frontal region toward the axis of the eye. This releases the tension on the lens caused by the zonular fibers (fibers that hold or flatten the lens). This release of tension of the zonular fibers causes the lens to become more spherical, adapting to short range focus. Conversely, relaxation of the ciliary muscle causes the zonular fibers to become taut, flattening the lens, increasing the focal distance, increasing long range focus. Although Helmholtz's theory has been widely accepted since 1855, its mechanism still remains controversial. Alternative theories of accommodation have been proposed by others, including L. Johnson, M. Tscherning, and especially Ronald A. Schachar.
■Trabecular meshwork pore size■
Contraction and relaxation of the longitudinal fibers, which insert into the trabecular meshwork in the anterior chamber of the eye, cause an increase and decrease in the meshwork pore size, respectively, facilitating and impeding aqueous humour flow into the canal of Schlemm.
【 語 句 】
・longitudinal: ・meridional:子午線の ・radial:放射線状の ・orientation:方向 ・zonular fibers:小帯線維 ・suspend:宙に浮かせておく ・axis:軸 ・spherical:球状の ・conversely:逆に ・taut:ピンと張られた ・controversial:論争の的になる ・Trabecular meshwork:小柱網 ・pore:細穴 ・anterior chamber:前眼房 ・respectively:それぞれ ・facilitate:促進する ・impede:妨げる ・aqueous humour:房水
【参考になるサイト】
「船戸和也のHP」では以下のように解説している。
眼の遠近調節accommodation(ピント合わせ)はの仕組みは、近いものを見るときには、毛様体筋が収縮して毛様小体がゆるみ(毛様小体の付着部が前の方に引かれるため)、水晶体が自身の弾性によって膨らみ(球形に近付き)、屈折率を増す。長時間にわたって細かい字を読んだ時の眼の疲労は、主に毛様体筋の疲労である。)
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ

|