【概 要】

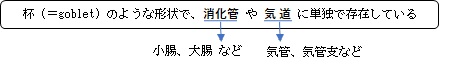

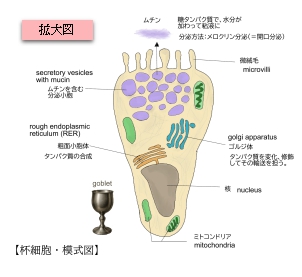

以下の図は外分泌細胞を導管および腺房の有無によって分類したものとなる。

【分泌方法】

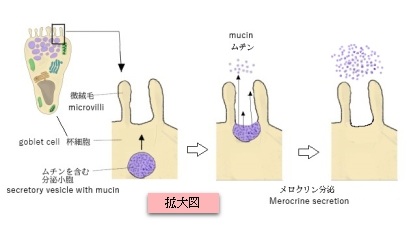
以下は外分泌細胞の分泌方法を簡単に表したものとなる。
|
分泌様式 |
説 明 |
例 |
1 |
メロクリン分泌
=開口分泌 |
分泌物だけを小胞で放出し、細胞自体は損傷しない。 |
膵腺房細胞、唾液腺(耳下腺など) 、杯細胞 |
2 |
アポクリン分泌
=離出分泌 |
細胞の一部(細胞質と膜)がちぎれて分泌される。 |
乳腺、腋下汗腺 |
3 |
ホロクリン分泌
=全分泌、 |
細胞全体が崩壊して分泌物となる。 |
皮脂腺 |
【部位別の割合】 参考:「ChatGPT」

杯細胞は部位によりその上皮細胞に占める割合が異なる。
| |
部 位 |
上皮細胞に占める割合 |
備 考 |
1 |
小腸(特に空腸・回腸) |
約 10~25% 程度 |
回腸に向かうにつれて増加 |
2 |
大腸(結腸・直腸) |
約 30~40%(以上) |
特に直腸では割合がさらに増す |
3 |
呼吸器(気管・気管支などの気道上皮) |
約 10~20% |
偽重層繊毛上皮の中に点在 |
【参考になるサイト】
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 5AC.[1] The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their secretions, when under stress.[2] The term goblet refers to the cell's goblet-like shape. The apical portion is shaped like a cup, as it is distended by abundant mucus laden granules; its basal portion lacks these granules and is shaped like a stem.
The goblet cell is highly polarized with the nucleus and other organelles concentrated at the base of the cell and secretory granules containing mucin, at the apical surface.[1] The apical plasma membrane projects short microvilli to give an increased surface area for secretion.[3]
Goblet cells are typically found in the respiratory, reproductive and gastrointestinal tracts and are surrounded by other columnar cells.[1] Biased differentiation of airway basal cells in the respiratory epithelium, into goblet cells plays a key role in the excessive mucus production, known as mucus hypersecretion seen in many respiratory diseases, including chronic bronchitis, and asthma.[4][5]
Goblet cells are found scattered among the epithelial lining of organs, such as the intestinal and respiratory tracts.[6] They are found inside the trachea, bronchi, and larger bronchioles in the respiratory tract, small intestines, the large intestine, and conjunctiva in the upper eyelid. In the conjunctiva goblet cells are a source of mucin in tears and they also secrete different types of mucins onto the ocular surface. In the lacrimal glands, mucus is synthesized by acinar cells instead.[7]
Microanatomy[edit]
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells, having a height of four times that of their width. The cytoplasm of goblet cells tends to be displaced toward the basal end of the cell body by the large mucin granules, which accumulate near the apical surface of the cell along the Golgi apparatus, which lies between the granules and the nucleus. This gives the basal part of the cell a basophilic staining because of nucleic acids within the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum staining with hematoxylin. Mucin within the granules stains pale in routine histology sections, primarily because these carbohydrate-rich proteins are washed out in the preparation of microscopy samples. However, they stain easily with the PAS staining method, which colours them magenta.[8][9]
In mucicarmine stains, deep red mucin is found within goblet cell bodies. Goblet cells can be seen in the examples below as the larger, more pale cells.
The main role of goblet cells is to secrete mucus in order to protect the mucous membranes where they are found. Goblet cells accomplish this by secreting mucins, large glycoproteins formed mostly by carbohydrates. The gel-like properties of mucins are given by its glycans (bound carbohydrates) attracting relatively large quantities of water.[10] On the inner surface of the human intestine, it forms a 200 µm thick layer (less in other animals) that lubricates and protects the wall of the organ.[11]
Distinct forms of mucin are produced in different organs: while MUC2 is prevalent in the intestine, MUC5AC and MUC5B are the main forms found in the human airway.[12] In the airway, mucus is swept by the cilia of the respiratory epithelium, in a process called mucociliary clearance, and propelled out of the lungs and into the pharynx, which results in the removal of debris and pathogens from the airway.[13] MUC5AC is overexpressed in allergic lung inflammation.[13]
Mucins are continuously made and secreted by goblet cells in order to repair and replace the existing mucus layer.[13] Mucins are stored in granules inside the goblet cells before being released to the lumen of the organ.[10] Mucin secretion in the airway may occur via regulated secretion.[14] Secretion may be stimulated by irritants such as dust and smoke, especially in the airway.[12] Other stimuli are microbes such as viruses and bacteria.
Anomalies in the number of goblet cells are associated with changes in the secretion of mucins, which can result in many of the abnormalities seen in asthma patients, such as clogged airways due to mucus hypersecretion, and eventual loss of lung function.[13] Overexpression of MUC5AC alone does not result in the pathophysiology seen in asthma patients; it is the excessive production along with the speed of secretion that leads to the formation of thick mucus that cannot be removed by cilia or coughing action.[13] This, in addition to airway narrowing leads to the clogging of the airways, which can be detrimental to health if not treated.[13]
There are other cells that secrete mucus (such as the foveolar cells of the stomach)[15] but these are distinguished histologically from goblet cells.
Role in oral tolerance[edit]
Oral tolerance is the process by which the immune system is prevented from responding to antigen derived from food products, as peptides from food may pass into the bloodstream via the gut, which would in theory lead to an immune response. A paper published in Nature in 2012 has shed some light on the process and implicated goblet cells as having a role in the process.[16] It was known that CD103-expressing dendritic cells of the lamina propria had a role to play in the induction of oral tolerance (potentially by inducing the differentiation of regulatory T cells), and this paper suggests that the goblet cells act to preferentially deliver antigen to these CD103+ dendritic cells.[16]
【 語 句 】
・: ・:・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・:
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
