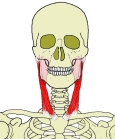
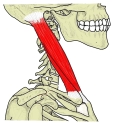
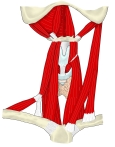
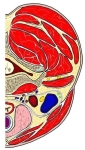
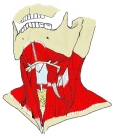
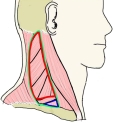
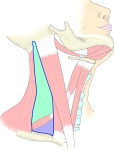
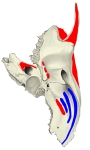
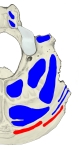
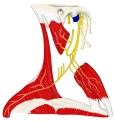
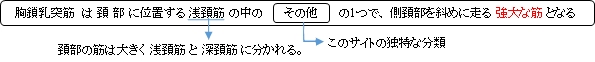
胸鎖乳突筋 ( きょうさにゅうとつきん、 英 : sternocleidomastoid muscle )
・ 概 要 |
・ 作 用 |
・ イラスト掲載サイト |
|
・ イラスト |
・ 神経 / 脈管 |
||
・ 起始 / 停止 |
・ Wikipedia |
![]()

・「 中央部は狭く厚みがあるが、両端はより広く薄くなっている。」( Wikipedia )
![]()
![]()
大鎖骨上窩 ( = 肩甲鎖骨三角 ): 鎖骨頭と僧帽筋の前縁、鎖骨の間の大きな窪み
![]()
![]()
![]()
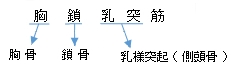
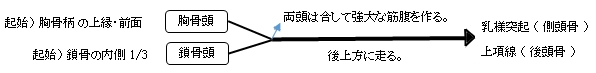
【 起 始 】 胸骨頭 : 胸骨柄 の上縁および前面
鎖骨頭 : 鎖骨 の内側1/3
両頭は合して強大な筋腹を構成し、後上方に走る。
【 停 止 】: 乳様突起( 側頭骨 )、 上項線( 後頭骨 )
![]()
「 頭を他側に回し、顔を上方に向かせる。左右が同時に働くと頭を前下方に引く、頭を固定させると、胸骨及び鎖骨を挙上させる。」(日本人体解剖学)
![]()
・ 神 経 : 副神経、 頚神経叢 の 筋枝 ( C2,C3 )
・ 動 脈 :
・ 静 脈 :
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve.
It is given the name sternocleidomastoid because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (sterno-) and the clavicle (cleido-), and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations : the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end.
The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the manubrium sterni. It travels superiorly, laterally, and posteriorly.
The clavicular head is composed of fleshy and aponeurotic fibers, arises from the upper, frontal surface of the medial third of the clavicle ; it is directed almost vertically upward.
The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval ( supraclavicular fossa ) but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin aponeurosis into the lateral half of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
【 語 句 】
・ cervical : 頚の ・ accessory nerve : 副神経 ・ manubrium : 胸骨柄 ・ sternum : 胸骨 ・ clavicle : 鎖骨 ・ mastoid process : 乳様突起 ・ temporal bone : 側頭骨 ・ fasciculus: 束 ・ fleshy : 多肉質の ・ manubrium sterni : 胸骨柄 ・ aponeurotic : 腱膜の ・ supraclavicular fossa : 鎖骨上窩 ・ nuchal line of the occipital bone : 後頭骨の上項線
【 Nerve supply 】
The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve of the same side. It supplies only motor fibres. The cervical plexus supplies sensation, including proprioception, from the ventral primary rami of C2 and C3.
【 Variation 】
The clavicular origin of the sternocleidomastoid varies greatly : in some cases the clavicular head may be as narrow as the sternal ; in others it may be as much as 7.5 millimetres (0.30 in) in breadth.
When the clavicular origin is broad, it is occasionally subdivided into several slips, separated by narrow intervals. More rarely, the adjoining margins of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius are in contact. This would leave no posterior triangle.
The supraclavicularis muscle arises from the manubrium behind the sternocleidomastoid and passes behind the sternocleidomastoid to the upper surface of the clavicle.
The function of this muscle is to rotate the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head. It also flexes the neck. When both sides of the muscle act together, it flexes the neck and extends the head. When one side acts alone, it causes the head to rotate to the opposite side and flexes laterally to the same side (ipsilaterally).
It also acts as an accessory muscle of respiration, along with the scalene muscles of the neck.
【 語 句 】
・ motor fibre : 運動線維 ・ cervical plexus : 頚神経叢 ・ proprioception : 固有受容(性感覚) ・ ventral primary rami : 頚神経前枝 ・ trapezius : 僧帽筋 ・ posterior triangle : 後頚三角 ・ supraclavicularis muscle : 鎖骨上筋 ・ respiration : 呼吸 ・ scalene muscles : 斜角筋
【 Contraction 】
The signaling process to contract or relax the sternocleidomastoid begins in Cranial Nerve XI, the accessory nerve. The accessory nerve nucleus is in the anterior horn of the spinal cord around C1-C3, where lower motor neuron fibers mark its origin. The fibers from the accessory nerve nucleus travel upward to enter the cranium via the foramen magnum. The internal carotid artery to reach both the sternocleidomastoid muscles and the trapezius. After a signal reaches the accessory nerve nucleus in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, the signal is conveyed to motor endplates on the muscle fibers located at the clavicle. Acetylcholine (ACH) is released from vesicles and is sent over the synaptic cleft to receptors on the postsynaptic bulb. The ACH causes the resting potential to increase above -55mV, thus initiating an action potential which travels along the muscle fiber. Along the muscle fibers are t-tubule openings which facilitate the spread of the action potential into the muscle fibers. The t-tubule meets with the sarcoplasmic reticulum at locations throughout the muscle fiber, at these locations the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions that results in the movement of troponin and tropomyosin on thin filaments. The movement of troponin and tropomyosin is key in facilitating the myosin head to move along the thin filament, resulting in a contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.[3]
【 Anatomical landmark 】
The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the trapezius muscle, with which it shares its nerve supply (the accessory nerve). It is thick and thus serves as a primary landmark of the neck, as it divides the neck into anterior and posterior cervical triangles (in front and behind the muscle, respectively) which helps define the location of structures, such as the lymph nodes for the head and neck.[4]
Many important structures relate to the sternocleidomastoid, including the common carotid artery, accessory nerve, and brachial plexus.
【 語 句 】
・anterior horn of the spinal cord : 髄前角 ・ foramen magnum : 大後頭孔 ・ internal carotid artery : 内頚動脈 ・ motor endplates : 運動終板 ・ Acetylcholine : アセチルコリン ・vesicle : 小脳 ・ synaptic cleft : シナプス間隙 ・ postsynaptic : シナプス後の ・ facilitate : 促進する ・ sarcoplasmic reticulum : 筋小胞体 ・ troponin : トロポニン ・ tropomyosin : トロポミオシン ・ myosin head : ミオシン頭部 ・ define : 明らかにする ・ ymph nodes : リンパ節 ・ common carotid artery : 総頚動脈 ・ brachial plexus : 腕神経叢
![]()