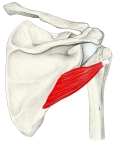
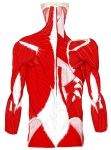
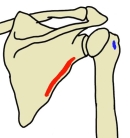
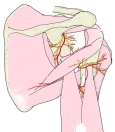
小円筋 ( しょうえんきん、英:teres minor muscle )筋
・ 概 要 |
・ 作 用 |
・ イラスト掲載サイト |
|
・ イラスト |
・ 神経 / 脈管 |
||
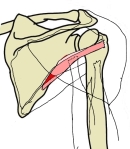
・ 起始 / 停止 |
・ Wikipedia |
![]()


![]()
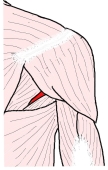
・ 皮下からは三角筋と大円筋に覆われて観察できない場合と、指ほどの太さのものが確認できる場合がある。
「Rauber-Kopsch解剖学」 には以下のような解説が見られる。
「 変異 : この筋と棘下筋との融合については,棘下筋の項を参照せよ.上腕骨の頚に停止する部分
はM. teres minimus (最小円筋) として独立することがある.(日本人における小円筋と棘下筋との分離
不全のものを古泉が集計している.古泉13/100(13%),小金井39/289(13.5%).足立3Ttns(20・3%).佐野
(アイヌ)0/10(0%).また完全癒合は古泉8/100(8.0%),小金井37/189(10.7%),足立13/128(7.1%),佐野
(アイヌ)0/10(0%).また保志場はこの問題についてさらに詳細に報告した(古泉光一:日本医科大学雑
誌,5巻,1063~1083,1934;保志場守一:金沢医科大学解剖学教室業績,27巻,73~97,1937).)」
![]()
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
![]()
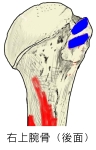
|
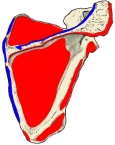
|
![]()
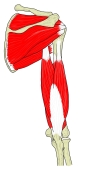
上腕骨を外旋させる。
![]()
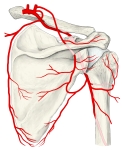
・ 神 経 : 腋窩神経(C5,C6)
・ 脈 管 : 肩甲回旋動脈
The teres minor (Latin teres meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.
The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve.[2]
【 Structure 】
It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle.
Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tubercle of the humerus; the lowest fibers are inserted directly into the humerus immediately below this impression.
【 語 句 】
・ elongate : 引き延ばす ・ rotator cuff : ローテーターカフ ・ adjacent : 近隣の ・ scapula : 肩甲骨 ・greater tubercle : 大結節 ・ joint capsule : 関節包 ・ modulate : 調節する ・ deltoid : 三角筋 ・ abduct : 外転させる ・ axillary nerve : 腋窩神経 ・ aponeurotic : 腱膜の ・ laminae : 薄板 ・ infraspinatus muscle : 棘下筋 ・ teres major muscle : 大円筋 ・ impressions : 跡
【 Relations 】
The teres minor originates at the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the scapula. It inserts at the greater tubercle of the humerus. The tendon of this muscle passes across, and is united with, the posterior part of the capsule of the shoulder-joint.
【 Innervation 】
The muscle is innervated by the posterior branch of axillary nerve where it forms a pseudoganglion. A pseudoganglion has no nerve cells but nerve fibres are present. Damage to the fibers innervating the teres minor is clinically significant.
【 Variation 】
Sometimes a group of muscle fibres from teres minor may be fused with infraspinatus.
【 Function 】
The infraspinatus and teres minor attach to head of the humerus; as part of the rotator cuff they help hold the humeral head in the glenoid cavity of the scapula. They work in tandem with the posterior deltoid to externally (laterally) rotate the humerus, as well as adduction. Teres Minor can produce only very small scapular plane adduction during maximal contraction (Hughes RE, An KN 1996) with adductor moment arm of approximately 0.2 cm at 45° of shoulder internal rotation and approximately 0.1 cm at 45° of shoulder external rotation.
【 語 句 】
・ pseudoganglion : 偽神経節 ・ fuse : 融合させる ・ infraspinatus : 棘下筋 ・ glenoid cavity : 関節窩 ・ posterior deltoid : 三角筋後部? ・ rotate :回転させる ・ adduction : 内転 ・ contraction : 収縮
![]()