

|
|
|
|
|
側頭骨(外側面) |
側頭骨(下面) |
側頭骨の3部構成 |
側頭骨(外側面) |
側頭骨(下面)
|
【主な特徴】
外側面)
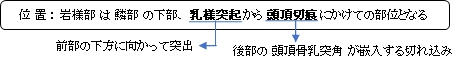
1.外側面は筋(胸鎖乳突筋、頭板状筋、頭最長筋)の停止部となり粗面を呈している。
2.前端(外耳孔の下部)の丸みを帯びた突起を乳様突起といい、耳介の後ろに位置し触察が容易となる。
外側面同様、筋の停止部でもある。
下面)
1.平行するように縦に走る2本の線が認められ、内側のものは後頭動脈を通す後頭動脈溝、そして外側の
ものは顎二腹筋の後腹の停止部となる乳突切痕となる。
2.乳突切痕の前後にはそれぞれ孔が認められ、前部のものを乳突孔(乳突導出静脈をS状洞溝に導く)、
そして、後部のものが茎乳突孔(顔面神経の通路)で顔面神経管の出口となっている。
「船戸和也のHP」では以下のように解説している。
「乳突部の外側面は筋の付着による粗面を有し、外耳孔の後方で下方へ延長した部分を乳様突起といい、胸鎖乳突筋の着くところである。乳様突起の後内側には乳突切痕があり、ここに顎二腹筋後腹が起こり、さらにその内側に後頭動脈溝が認められている。乳突部の内側面には深くて長い陥凹があり、ここにS状洞溝が走り、上方では後頭骨の横洞溝に、下方は頚静脈孔につづく。後縁にある乳突孔は乳突導出静脈を通し、S状洞溝に開く。
乳突部の後部は後頭鱗と結合する部分で後頭縁という。顔面神経管は顔面神経の通路で内耳道底の顔面神経野より骨内に入り、蝸牛の外側に沿って、ほとんど水平位で前外方へ進む。次いでほぼ直角をなして後外方へまがり、ここで顔面神経管膝を形成する。その後、鼓室壁の前庭窓の上部すなわち鼓室と骨半規管の間を走行し、外後方に進んだ後、弓状をなして下行し、茎乳突孔に開口する。鼓索神経小管は鼓索神経の通路で茎乳突孔の少し上方で顔面神経管から分かれて前上方へ延び、鼓室溝の後縁に極めて近いところで鼓室に開口する。次いで鼓室の外側壁の粘膜におおわれながら、ツチ骨柄とキヌタ骨長脚との間を前進し、鼓室の前上方を貫通し、錐体鼓室裂を経て、頭蓋外面に出る。 」
また、以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones.
【Etymology】
The word "mastoid" is derived from the Greek word for "breast", a reference to the shape of this bone.
【Surfaces】
【Outer surface】
Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles. It is perforated by numerous foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits a vein to the transverse sinus and a small branch of the occipital artery to the dura mater. The position and size of this foramen are very variable; it is not always present; sometimes it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal and the occipital.
【 語 句 】
・articulate with~:~と接合する ・etymology:語源学 ・occipitalis muscle:後頭骨 ・posterior auricular muscle:後耳介筋 ・perforate:貫通する ・mastoid foramen:乳突孔 ・transverse sinus:横静脈洞 ・transverse sinus後頭動脈 ・dura mater:硬膜
【Mastoid process】
The mastoid process is located posterior and inferior to the ear canal, lateral to the styloid process, and appears as a conical or pyramidal projection. It forms a bony prominence behind and below the ear. It has variable size and form (e.g. it is larger in the male than in the female). It is also filled with sinuses, or mastoid cells. The mastoid process serves for the attachment of the sternocleidomastoid, the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, splenius capitis, and longissimus capitis. On the medial side of the process is a deep groove, the mastoid notch, for the attachment of the digastric muscle; medial to this is a shallow furrow, the occipital groove, which lodges the occipital artery. The facial nerve passes close to the mastoid process.
【Inner surface】
The inner surface of the mastoid portion presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus; in it may be seen in the opening of the mastoid foramen.
The groove for the transverse sinus is separated from the innermost of the mastoid cells by a very thin lamina of bone, and even this may be partly deficient.
【Borders】
The superior border of the mastoid part is broad and serrated, for articulation with the mastoid angle of the parietal.
The posterior border, also serrated, articulates with the inferior border of the occipital between the lateral angle and jugular process.
Anteriorly, the mastoid portion is fused with the descending process of the squama above; below, it enters into the formation of the ear canal and the tympanic cavity.
【 語 句 】
・ear canal:外耳孔 ・styloid process:茎状突起 ・conical:円錐の ・sinus:洞 ・mastoid cell:乳突蜂巣 ・sternocleidomastoid (muscle):胸鎖乳突筋 ・digastric muscle:顎二腹筋 ・splenius capitis:頭板状筋 ・longissimus capitis:頭最長筋 ・mastoid notch:乳突切痕 ・furrow:溝 ・occipital groove:後頭動脈溝 ・occipital artery:後頭動脈 ・sigmoid sulcus:S状洞溝 ・lamina:薄板 ・deficient:不完全な ・serrated:鋸歯状の ・mastoid angle:乳突角 ・parietal (bone):頭頂骨 ・jugular process:頚静脈突起 ・squama:鱗(鱗部のこと?) ・ear canal:外耳道 ・tympanic cavity:鼓室
【Spaces】
A section of the mastoid process shows it to be hollowed out into a number of spaces, the mastoid cells, which exhibit the greatest possible variety as to their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process, they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part, they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequently quite small and contain marrow; occasionally, they are entirely absent, and the mastoid is then solid throughout.
In addition to these a large irregular cavity is situated at the upper and front part of the bone. It is called the tympanic antrum and must be distinguished from the mastoid cells, though it communicates with them. Like the mastoid cells, it is filled with air and lined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity, with which it communicates. The tympanic antrum is bounded above by a thin plate of bone, the tegmen tympani, which separates it from the middle fossa of the base of the skull, below by the mastoid process, laterally by the squama just below the temporal line, and medially by the lateral semicircular canal of the internal ear, which projects into its cavity. It opens in front into that portion of the tympanic cavity which is known as the attic or epitympanic recess. The tympanic antrum is a cavity of some considerable size at the time of birth; the mastoid air cells may be regarded as diverticula from the antrum and begin to appear at or before birth. By the fifth year, they are well-marked, but their development is not completed until toward puberty.
【Development】
The mastoid process is absent or rudimentary in the neonatal skull. It forms postnatally (starts to develop after 1 year old), as the sternocleidomastoid muscle develops and pulls on the bone. It usually finishes structural development by 2 years old.
【 語 句 】
・hollow out:えぐる ・mastoid cells:乳突蜂巣 ・marrow:骨髄 ・solid:中まで堅い ・throughout:終始 ・tympanic antrum:鼓室前庭 ・mucous membrane:粘膜 ・tegmen tympani:鼓室蓋 ・temporal line:側頭線 ・lateral semicircular canal:外側半規管 ・internal ear:内耳 ・epitympanic recess:鼓室上陥凹 ・diverticula:憩室 ・puberty:思春期 ・rudimentary:未発達の ・neonatal:新生児の
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
