
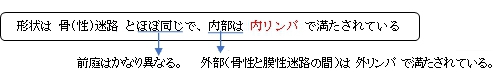
・「膜迷路の太さは、骨迷路のそれに比べてはなはだ細く、その壁の一部分は骨迷路壁に接着するが、大部分は骨壁から離れ、その間に外リンパを容れる広い空洞がある。」(日本人体解剖学)
・「In certain places, it (membranous labyrinth) is fixed to the walls of the cavity.」(Wikipedia)

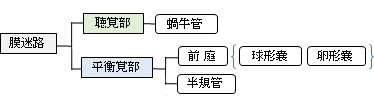
膜迷路の主な構造として聴覚部の蝸牛管と平衡覚部の前庭および半規管が挙げられる。
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The membranous labyrinth is a collection of fluid filled tubes and chambers which contain the receptors for the senses of equilibrium and hearing. It is lodged within the bony labyrinth in the inner ear and has the same general form; it is, however, considerably smaller and is partly separated from the bony walls by a quantity of fluid, the perilymph.
In certain places, it is fixed to the walls of the cavity.
The membranous labyrinth contains fluid called endolymph. The walls of the membranous labyrinth are lined with distributions of the cochlear nerve, one of the two branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The other branch is the vestibular nerve.
Within the vestibule, the membranous labyrinth does not quite preserve the form of the bony labyrinth, but consists of two membranous sacs, the utricle, and the saccule.
The membranous labyrinth is also the location for the receptor cells found in the inner ear.
【 語 句 】
・receptor:受容体 ・equilibrium:平行 ・bony labyrinth:骨(性)迷路 ・inner ear:内耳 ・perilymph:外リンパ ・endolymph:内リンパ ・distribution:分布 ・cochlear nerve:蝸牛神経 ・vestibulocochlear nerve:前庭蝸牛神経(内耳神経) ・vestibular nerve:前庭神経 ・utricle:卵形嚢 ・saccule:球形嚢 ・receptor cell:受容器細胞
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
