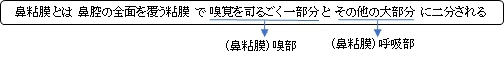

 |
 |
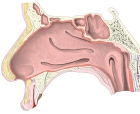
外側壁の粘膜 |
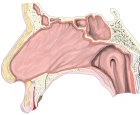
鼻中隔の粘膜 |

【特 徴】 参考)Wikipedia、日本人体解剖学
1. 血管に富み淡紅色を呈する。
2. 下鼻甲介および中鼻甲介では静脈叢(鼻甲介海綿叢)を形成する。
3. 粘膜固有層中にはリンパ球、リンパ小節、そして多くの鼻腺(鼻汁を分泌)を含んでいる。
4. 鼻中隔の前下部は出血の多発地帯でキーセルバッハ部位と呼ばれる。
5. 上皮細胞は円柱状で絨毛が見られる。また、基底細胞は錐体状となる。
6. 円柱細胞間に杯細胞・ムチン細胞?(mucin cell)が散在している。
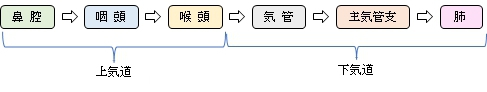
・呼吸部の構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイト-1
・呼吸部の構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイト-2
【特 徴】 参考)Wikipedia、日本人体解剖学、その他のサイト
1. 上皮細胞は円柱状で絨毛は見られない。
2. 上皮層の主な細胞としては嗅細胞と支持細胞(楕円形の核を有する)となる。
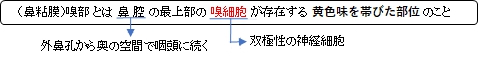
3. 上皮層の表層部には黄色い色素を含んだ小粒が見られる。(Wikipedia)
4. 粘膜固有層には粘液を分泌するボーマン腺(/嗅腺)が見られる。
・嗅部の構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイト-1
・嗅部の構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイト-2
・嗅部の構造が分かるイラストを掲載しているサイト-3
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The nasal mucosa lines the nasal cavity. It is part of the respiratory mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract. The nasal mucosa is intimately adherent to the periosteum or perichondrium of the nasal conchae. It is continuous with the skin through the nostrils, and with the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx through the choanae. From the nasal cavity its continuity with the conjunctiva may be traced, through the nasolacrimal and lacrimal ducts; and with the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, through the several openings in the nasal meatuses.
【 語 句 】
・nasal cavity:鼻腔 ・respiratory mucosa:呼吸/気道粘膜 ・mucous membrane:粘膜 ・respiratory tract:気道/呼吸器 ・intimately:密接に ・adherent:付着した ・periosteum:骨膜 ・perichondrium:軟骨膜 ・nasal conchae:鼻甲介 ・nostril:鼻孔 ・pharynx:咽頭 ・choanae:後鼻孔 ・cpmkimctiva: ・frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses:前頭洞、篩骨洞、蝶形骨洞、そして上顎洞 ・nasal meatus:鼻道
The mucous membrane is thickest, and most vascular, over the nasal conchae. It is also thick over the nasal septum where increased numbers of goblet cells produce a greater amount of nasal mucus. It is very thin in the meatuses on the floor of the nasal cavities, and in the various sinuses. It is one of the most commonly infected tissues in adults and children. Inflammation of this tissue may cause significant impairment of daily activities, with symptoms such as stuffy nose, headache, mouth breathing, etc.
Owing to the thickness of the greater part of this membrane, the nasal cavities are much narrower, and the middle and inferior nasal conchæ appear larger and more prominent than in the skeleton; also the various apertures communicating with the meatuses are considerably narrowed.
【 語 句 】
・nasal septum:鼻中隔 ・goblet cell:杯細胞 ・nasal mucus:鼻粘液 ・inflammation:炎症 ・impairment:障害 ・stuffy nose:鼻詰まり ・prominent:突出した ・aperture:穴
Structure
The epithelium of the nasal mucosa is of two types – respiratory epithelium, and olfactory epithelium differing according to its functions.
In the respiratory region it is columnar and ciliated. Interspersed among the columnar cells are goblet or mucin cells, while between their bases are found smaller pyramidal cells. Beneath the epithelium and its basement membrane is a fibrous layer infiltrated with lymph corpuscles, so as to form in many parts a diffuse adenoid tissue, and under this a nearly continuous layer of small and larger glands, some mucous and some serous, the ducts of which open upon the surface.
【 語 句 】
・epithelium:上皮 ・respiratory epithelium:呼吸上皮 ・olfactory epithelium:嗅上皮 ・columnar:円柱の ・ciliated:繊毛性の ・interspersed:散在して ・goblet cell:杯細胞 ・mucin cell:ムチン細胞? ・pyramidal cells:錐体細胞 ・infiltrate:浸透する ・lymph corpuscle:リンパ球 ・diffuse:拡散させる ・adenoid tissue:腺様組織 ・serous:漿液(性)の
In the olfactory region the mucous membrane is yellowish in color and the epithelial cells are columnar and non-ciliated; they are of two kinds, supporting cells and olfactory cells. The supporting cells contain oval nuclei, which are situated in the deeper parts of the cells and constitute the zone of oval nuclei; the superficial part of each cell is columnar, and contains granules of yellow pigment, while its deep part is prolonged as a delicate process which ramifies and communicates with similar processes from neighboring cells, so as to form a net-work in the mucous membrane.
【 語 句 】
・olfactory cell:嗅細胞 ・oval:楕円形の ・constitute:構成する ・pigment:色素 ・delicate:繊細な ・ramify:分岐する
Lying between the deep processes of the supporting cells are a number of bipolar nerve cells, the olfactory cells, each consisting of a small amount of granular protoplasm with a large spherical nucleus, and possessing two processes—a superficial one which runs between the columnar epithelial cells, and projects on the surface of the mucous membrane as a fine, hair-like process, the olfactory hair; the other or deep process runs inward, is frequently beaded, and is continued as the axon of an olfactory nerve fiber. Beneath the epithelium, and extending through the thickness of the mucous membrane, is a layer of tubular, often branched, glands, the glands of Bowman, identical in structure with serous glands. The epithelial cells of the nose, fauces and respiratory passages play an important role in the maintenance of an equable temperature, by the moisture with which they keep the surface always slightly lubricated.
【 語 句 】
・bipolar nerve cell:双極神経細胞 ・protoplasm:原形質 ・spherical:球形の ・bead:玉のようにつく ・axon:軸索 ・tubular:管状の ・identical:同一の ・serous gland:漿液腺 ・fauces:口峡 ・lubricated:滑らかにされて
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
