陰部神経とは

つまり

・「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では仙骨神経叢の一部として解説している。 」では仙骨神経叢の一部として解説している。
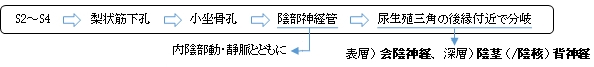
陰部神経は、会陰神経と陰茎(/ 陰核 )背神経に分岐するまでにおおよそ以下のような道程をたどる。
以下は 「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」 の解説文となる。 」 の解説文となる。
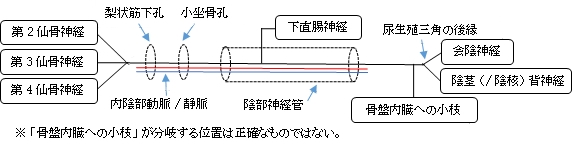
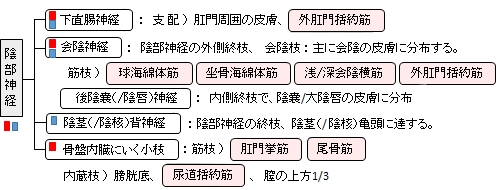
「 第2~第4仙骨神経から起こり、内陰部動・静脈とともに、大坐骨孔で梨状筋の下、すなわち梨状筋下孔を通り、骨盤腔を出て坐骨棘の後側を回り、小坐骨孔を通って坐骨直腸窩に向かい、陰部神経管を通り、下直腸神経を出し、尿生殖三角の後縁の近くで、表層の会陰神経と深層の陰茎背神経(♂)(あるいは陰核背神経(♀))とに分かれる。小枝は骨盤内臓に分布する。 」
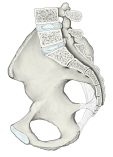
大坐骨孔/小坐骨孔
|
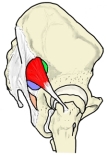
梨状筋上孔/下孔
|
|
|
|
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では陰部神経の枝として、下直腸神経、会陰神経、陰茎(/陰唇)背神経、そして「骨盤内臓にいく小枝」を挙げている。それぞれの枝の分布域はそれぞれの枝のページを参照のこと。そして、それらの枝を除く陰部神経の神経幹が分布する域は不明。 」では陰部神経の枝として、下直腸神経、会陰神経、陰茎(/陰唇)背神経、そして「骨盤内臓にいく小枝」を挙げている。それぞれの枝の分布域はそれぞれの枝のページを参照のこと。そして、それらの枝を除く陰部神経の神経幹が分布する域は不明。
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」では陰部神経の枝として、以下の下直腸神経、会陰神経、陰茎(/陰唇)背神経、そして「 骨盤内臓にいく小枝 」の4つを挙げている。 」では陰部神経の枝として、以下の下直腸神経、会陰神経、陰茎(/陰唇)背神経、そして「 骨盤内臓にいく小枝 」の4つを挙げている。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum.[1]:274 It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure.
The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836.
The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligamentand the coccygeus muscle.[2] The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to form the lower cord, and these in turn unite to form the pudendal nerve proper just proximal to the sacrospinous ligament.[3]The three roots are derived from the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth sacral spinal nerves, with the primary contribution coming from the fourth.[2][4]:215[5]:157
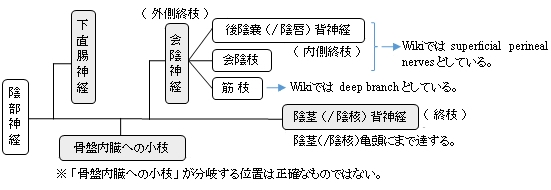
The pudendal nerve passes between the piriformis muscle and coccygeus(ischiococcygeus) muscles and leaves the pelvis through the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen.[2] It crosses over the lateral part of the sacrospinous ligament and reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen. After reentering the pelvis, it accompanies the internal pudendal artery and internal pudendal veinupwards and forwards along the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa, being contained in a sheath of the obturator fascia termed the pudendal canal, along with the internal pudendal blood vessels.[6]:8
Inside the pudendal canal, the nerve divides into branches, first giving off the inferior rectal nerve, then the perineal nerve, before continuing as the dorsal nerve of the penis (in males) or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris (in females).[6]:34
Nucleus[edit] 【】
The nerve is a major branch of the sacral plexus,[7]:950 with fibers originating in Onuf's nucleus in the sacral region of the spinal cord.[3]
Variation[edit] 【】
The pudendal nerve may vary in its origins. For example, the pudendal nerve may actually originate off of the sciatic nerve.[8] Consequently, damage to the sciatic nerve can affect the pudendal nerve as well. Sometimes dorsal rami of the first sacral nerve contribute fibers to the pudendal nerve, and even more rarely S5.[3]
The pudendal nerve has both motor and sensory functions. It does not carry parasympathetic fibers but does carry sympathetic fibers.[9]:1738
The pudendal nerve supplies sensation to the penis in males, and to the clitoris in females, which travels through the branches of both the dorsal nerve of the penis and the dorsal nerve of the clitoris.[10]:422 The posterior scrotum in males and the labia in females are also supplied, via the posterior scrotal nerves (males) or posterior labial nerves (females). The pudendal nerve is one of several nerves supplying sensation to these areas.[11] Branches also supply sensation to the anal canal.[6]:8 By providing sensation to the penis and the clitoris, the pudendal nerve is responsible for the afferentcomponent of penile erection and clitoral erection.[12] :147 It is also responsible for ejaculation.[13]
Branches also innervate muscles of the perineum and the pelvic floor; namely, the bulbospongiosus and the ischiocavernosus muscles respectively[11], the levator ani muscle (including the Iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus, puborectalis and either pubovaginalis in females or puboprostaticus in males)[10]:422[14] the external anal sphincter (via the inferior anal branch),[6]:7 and male or female external urethral sphincter.[10]:424–425
As it functions to innervate the external urethral sphincter it is responsible for the tone of the sphincter mediated via acetylcholine release. This means that during periods of increased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle in the external urethral sphincter contracts, causing urinary retention. Whereas in periods of decreased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle in the external urethral sphincter relaxes, allowing voiding of the bladder to occur.[15] (Clarification: Unlike the internal sphincter muscle, the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle, therefore it is under voluntary control of the somatic nervous system.)」
【 語 句 】
・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ :

|