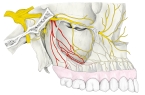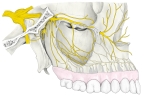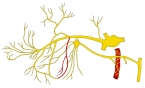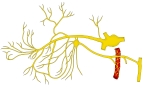

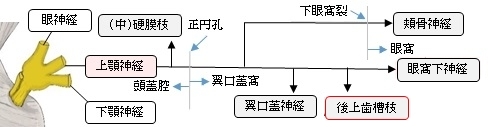
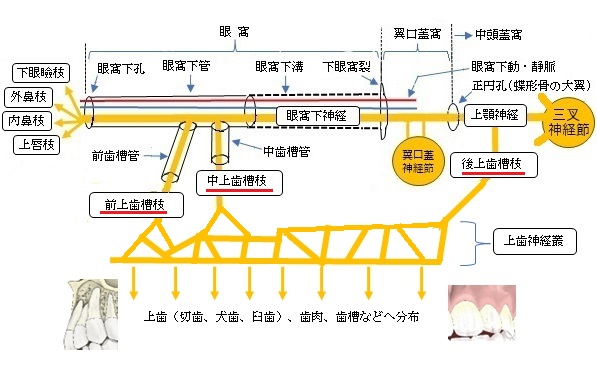
以下が上顎神経の枝を表す図となる。
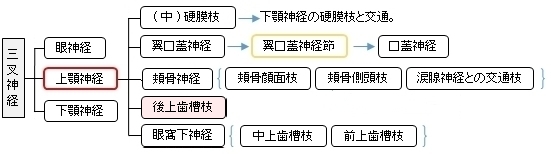
※「Rauber-Kopsch解剖学」では、この後上歯槽枝を眼窩下神経の枝の1つとして解説している。
「上顎結節に沿って下り、歯肉および口腔粘膜後部に分布するほか、後上歯槽動脈とともに上顎骨の歯槽孔を通り、歯槽管を経て上顎洞の外側壁に分布する。」(日本人体解剖学 (上巻) ) )

また、以下は「Rauber-Kopsch解剖学」の解説文となる。
「眼窩下神経が眼窩に入る前にすでに幹から分かれて,同名動脈に伴って上顎結節のところを下行する.後方の1枝はその線維の一部が上顎骨の外面Außenzvandにとどまって,大臼歯の範囲の歯肉と頬粘膜のこれに隣接する部分とに分布する.そのほかの諸枝は歯槽孔を通って上顎洞の後外側壁に達する.ここでは骨壁にある不完全な管のなかを前方に走り,中上歯槽枝と神経叢の状態をなして結合し,その細い枝を上顎洞の粘膜にだし,また上歯枝Rami dentales maxillaresを3本の大臼歯に送っている.」
「Wikipedia」では以下のように解説している。
The posterior superior alveolar nerves (also posterior superior dental nerves or posterior superior alveolar branches) are sensory branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). They arise within the pterygopalatine fossa as a single trunk. They run on or in the maxilla. They provide sensory innervation to the upper molar teeth and adjacent gum, and the maxillary sinus.
■Anatomy■
【Origin】
The nerves arise from the trunk of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) within the pterygopalatine fossa just before it enters the infraorbital groove
The nerve arises as a single trunk which split into 2-3 nerves within the pterygopalatine fossa.
【 語 句 】
・maxillary nerve:上顎神経 ・pterygopalatine fossa:翼口蓋窩 ・molar teeth:大臼歯 ・adjacent :隣接する ・gum:歯肉 ・maxillary sinus:上顎洞 ・infraorbital groove:眼窩下溝
【Course】
The nerves exit the pterygopalatine fossa through the pterygomaxillary fissure. They pass within or upon the posterior wall of the maxilla.
They descend on the tuberosity of the maxilla and give off several twigs to the gums and neighboring parts of the mucous membrane of the cheek
They then enter the alveolar canals on the infratemporal surface of the maxilla, and, passing from behind forward in the substance of the bone, communicate with the middle superior alveolar nerve, and give off branches to the lining membrane of the maxillary sinus and gingival and dental branches to each molar tooth from a superior dental plexus; these branches enter the apical foramina at the roots of the teeth.
【Distribution】
The nerves provide sensory innervation to the upper/maxillary molar teeth and the associated gingiva of the vestibule, and the maxillary sinus.
【Teeth】
The nerve innervates the second and third maxillary/upper molar teeth, and two of the three roots of the maxillary/upper first molar tooth (all but the mesiobuccal root).
【 語 句 】
・:翼上顎裂 ・tuberosity:結節 ・twig:小枝 ・mucous membrane:粘膜 ・alveolar canals:歯槽管 ・gingival:歯肉の ・superior dental plexus:上歯神経叢 ・apical foramina:根尖孔 ・vestibule:前庭 ・mesiobuccal root:近心頬側根
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|