【概 要】

・腹腔神経節は自立神経叢神経節の中で最大の交感神経節となる。
・「日本人体解剖学」ではこの腹腔神経節を「対性」ではなく、左右とその間にある神経線維(交通枝)などを合わせて1つの神経節としてみているようである。よって以下のような解説文が見られる。
「大きさ、形状など不定な数個の扁平神経節の集団であり、多数の交通枝によって連絡する。」
【通過するもの】
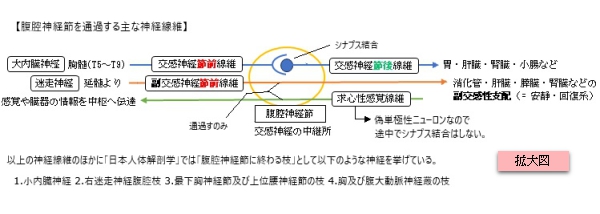

【「ChatGPT」に聞いてみた】
Q.「腹腔神経節を通過する交感神経線維は全てシナプス結合するか?」
A.「」
Q.「腹腔神経節を交感神経節後線維が通過することはある?」
A.「」
「 日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
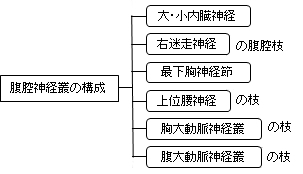
腹腔神経節は、腹腔動脈起始部の周囲にあって、大きさ、形状など不定な数個の扁平神経節の集団であり、多数の交通枝によって連絡する。腹腔神経節には腹腔神経叢を構成する上記の各神経(大・小内臓神経、右迷走神経腹腔枝、最下胸神経節および上位腰神経節の枝、胸および腹大動脈神経叢の枝など)の枝が終わる(副交感性の迷走神経の枝は例外)。さらに腹腔神経節から多数の枝が出て腹部内臓に分布する娘神経節に入る。
※ 上記の解説文で「上記」というのは、以下の図の神経や神経節となる。
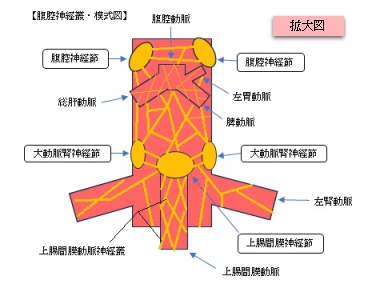
以下は腹腔神経叢を構成する神経を簡単に表した図となる。 参考:日本人体解剖学
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。 ※「語句」は加筆したもの。
「The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in the ANS, and they innervate most of the digestive tract.
They have the appearance of lymph glands and are placed on either side of the midline in front of the crura(脚)of the diaphragm, close to the suprarenal glands (also called adrenal glands). The ganglion on the right side is placed behind the inferior vena cava.
They are sometimes referred to as the semilunar ganglia or the solar ganglia.
【 語 句 】
・ digestive tract : 消化管 ・ suprarenal glands : 副腎 ・inferior vena cava : 下大静脈
Neurotransmission
The celiac ganglion is part of the sympathetic prevertebral chain possessing a great variety of specific receptors and neurotransmitters such as catecholamines, neuropeptides, and nitric oxide and constitutes a modulation center in the pathway of the afferent and efferent fibers between the central nervous system and the ovary.
The main preganglion neurotransmitter of the celiac ganglion is acetylcholine, yet the celiac ganglion-mesenteric complex also contain α and β adrenergic receptors and is innervated by fibers of adrenergic nature that come from other preaortic ganglia.
【 語 句 】
・ neurotransmission : 神経伝達 ・ catecholamines : カテコールアミン ・ neuropeptides : 神経ペプチド
・ nitric oxide : 一酸化窒素 ・ ovary : 卵巣
Path
The upper part of each ganglion is joined by the greater splanchnic nerve), while the lower part, which is segmented off and named the aorticorenal ganglion, receives the lesser splanchnic nerve and gives off the greater part of the renal plexus.
Innervation
These ganglia contain neurons whose postganglionic axons innervate the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, kidney, small intestine, and the ascending and transverse colon. They directly innervate the ovarian theca and secondary interstitial cells and exert an indirect action on the luteal cells.
Links to ovary
Modifications in the adrenergic activity of the celiac ganglion results in an altered capacity of the ovary of pregnant rats to produce progesterone, suggesting that the celiac ganglion-superior ovarian nerve-ovarian axis provides a direct link between the autonomic nervous system and the physiology of pregnancy.[1] It has also been shown that modifications in the cholinergic input at the celiac ganglion also led, via the superior ovarian nerve, to modifications in ovarian steroidogenesis.[1][2][3] Most of the fibers of the superior ovarian nerve come from the postganglionic sympathetic neurons of the celiac ganglion.」
【 語 句 】
・greater splanchnic nerve : 大内臓神経 ・aorticorenal ganglion : 大動脈腎神経節 ・renal plexus : 腎神経叢
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
