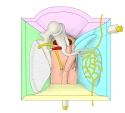
鼓膜張筋 ( こまくちょうきん、 英 : tensor tympani muscle )
・ 概 要 |
・ 作 用 |
・ イラスト掲載サイ |
|
・ イラスト |
・ 神経 / 脈管 |
||
・ 起始 / 停止 |
・ Wikipedia |


・ 紡錘状で、長さが約1㎜の アブミ骨筋 (stapedius) よりは長い。
その長さに関して言及している資料は見つからないのだが、インターネットで画像検索をかけてアブミ骨筋と比較してみると、その長さは1㎝から2㎝ほどあるように思われる。
|
 |
 |
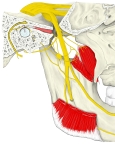
|
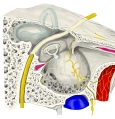
【 起 始 】: 「 管の内壁および耳管ならびに蝶錐体裂の付近から起こって、半管中を後外側方に走り、その小さな腱は
サジ状突起の溝を通って外側方に曲がり、鼓室内に出る。」 ( 日本人体解剖学 )
【 停 止 】: 「 ツチ骨柄の基部内側 」 ( 日本人体解剖学 )
「 ツチ骨柄を鼓室のほうに引いて鼓膜を緊張させ、伝音感度を高める。 」 ( 日本人体解剖学 )
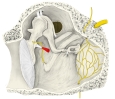
・ 神 経 : 鼓膜張筋神経 ( 三叉神経の運動根から )
・ 動 脈 : ?
・ 静 脈 : ?

|
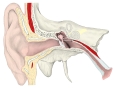
The tensor tympani is a muscle within the ear. It is contained in the bony canal above the osseous portion of the auditory tube. Its role is to dampen sounds, such as those produced from chewing.
【 Structure 】
Insertion of the tensor tympani muscle onto the malleus. . AA’ ( two fibrous collagenic layers) ; B épidermis ; C mucous membrane ; D head of malleus ; E uncus ; F stapes ; G tensor tympani ; H lateral process of malleus ; I Manubrium of malleus ; J stapes muscle.
The tensor tympani arises from the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube, and the adjoining part of the great wing of the sphenoid, as well as from the osseous canal in which it is contained. Passing backward through the canal, it ends in a slender tendon which enters the tympanic cavity, makes a sharp bend around the extremity of the septum, known as the processus cochleariformis, and is inserted into the neck of the malleus, near its root.[1]
The tensor tympani is the larger of the two muscles of the tympanic cavity, the other being the stapedius.
【 Innervation 】
Innervation of the tensor tympani is from the tensor tympani nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.[1] As the tensor tympani is innervated by motor fibers of the trigeminal nerve, it does not receive fibers from the trigeminal ganglion, which has sensory fibers only.
【 Development 】
The tensor tympani muscle develops from mesodermal tissue in the 1st pharyngeal arch.[2]
【 Function 】
The tensor tympani acts to dampen the noise produced by chewing. When tensed, the muscle pulls the malleus medially, tensing the tympanic membrane and damping vibration in the ear ossicles and thereby reducing the perceived amplitude of sounds.[1]
【 語 句 】
・ osseous : 骨の ・ auditory tube : 耳管 ・ dampen : 減らす? ・ malleus : ツチ骨 ・ mucous membrane : 粘膜 ・ uncus : 鈎 ・ great wing of the sphenoid : 蝶形骨大翼 ・tympanic cavity : 鼓室 ・ septum : 隔膜、隔壁 ・ processus cochleariformis : 匙状突起 ・ mandibular : 下顎骨の
・ stapedius : アブミ骨筋 ・ tensor tympani nerve : 鼓膜張筋神経 ・ trigeminal nerve : 三叉神経 ・ motor fibers : 運動神経 ・ trigeminal ganglion : 三叉神経節 ・ sensory fibers : 知覚神経線維 ・ mesodermal tissue : 中胚葉組織 ・ pharyngeal arch : 鰓弓 ・ tympanic membrane : 鼓膜 ・ ossicle : 小骨 ・ perceived : 知覚された ・ amplitude : 振幅