【概 要】

・「ウィキペディア」には「蝶形口蓋神経節またはメッケル神経節とも呼ばれる」とあるが、「ChatGP」では「≠メッケル神経節」としている。

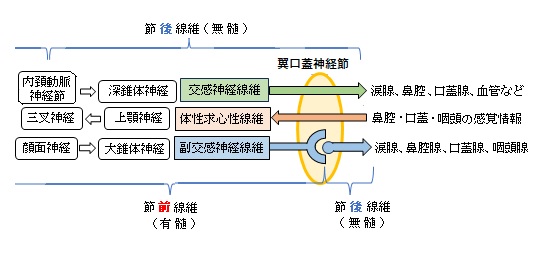
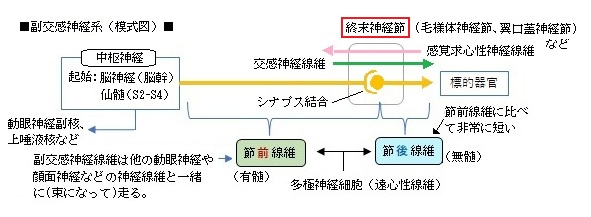
■ 入る神経 / 出る神経 ■
翼口蓋神経節には由来の異なる3つの神経線維の枝(/根)が入り、また、翼口蓋神経節からは以下の図にある複数の数枝が出る。
「(翼口蓋神経節から出る枝は)翼口蓋神経節に入る a)翼口蓋神経、b)大錐体神経、および c)深錐体神経の3つの根からの神経線維で、a)からの知覚性、b)からの副交感性と運動性、およびc)からの交感線維を種々の割合で含む。」「日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」
」
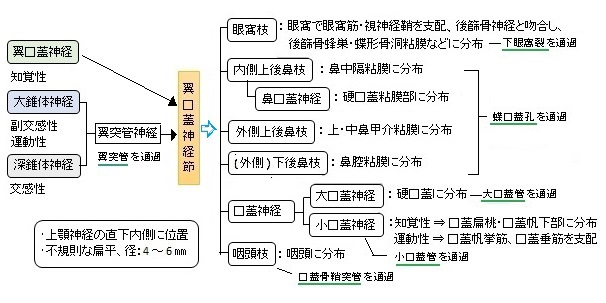
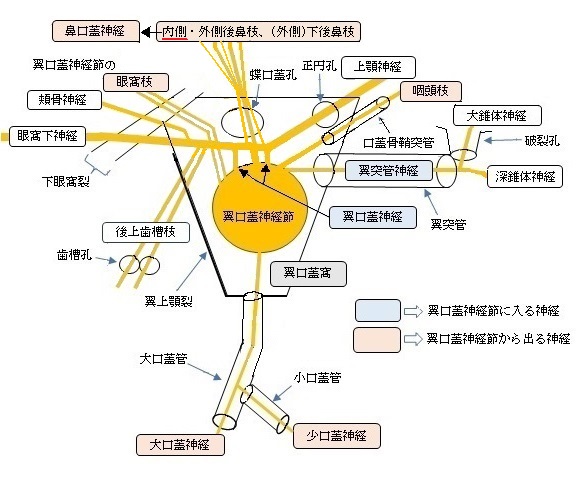
【参考になるサイト】
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
「The pterygopalatine ganglion (Meckel's ganglion, nasal ganglion or sphenopalatine ganglion) is a parasympathetic ganglion found in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is largely innervated by the greater petrosal nerve (a branch of the facial nerve); and its axons project to the lacrimal glands and nasal mucosa. The flow of blood to the nasal mucosa, in particular the venous plexus of the conchae, is regulated by the pterygopalatine ganglion and heats or cools the air in the nose. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck, the others being the submandibular ganglion, otic ganglion, and ciliary ganglion.
【 Structure 】The pterygopalatine ganglion (of Meckel), the largest of the parasympathetic ganglia associated with the branches of the maxillary nerve, is deeply placed in the pterygopalatine fossa, close to the sphenopalatine foramen. It is triangular or heart-shaped, of a reddish-gray color, and is situated just below the maxillary nerve as it crosses the fossa.
The pterygopalatine ganglion supplies the lacrimal gland, paranasal sinuses, glands of the mucosa of the nasal cavity and pharynx, the gingiva, and the mucous membrane and glands of the hard palate. It communicates anteriorly with the nasopalatine nerve.
Roots : It receives a sensory, a parasympathetic, and a sympathetic root.
【 Sensory root 】Its sensory root is derived from two sphenopalatine branches of the maxillary nerve; their fibers, for the most part, pass directly into the palatine nerves; a few, however, enter the ganglion, constituting its sensory root.
【 Parasympathetic root 】Its parasympathetic root is derived from the nervus intermedius (a part of the facial nerve) through the greater petrosal nerve.
In the pterygopalatine ganglion, the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the greater petrosal branch of the facial nerve synapse with neurons whose postganglionic axons, vasodilator, and secretory fibers are distributed with the deep branches of the trigeminal nerve to the mucous membrane of the nose, soft palate, tonsils, uvula, roof of the mouth, upper lip and gums, and upper part of the pharynx. It also sends postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the lacrimal nerve (a branch of the Ophthalmic nerve, also part of the trigeminal nerve) via the zygomatic nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve (from the trigeminal nerve), which then arrives at the lacrimal gland.
The nasal glands are innervated with secretomotor from the greater petrosal nerve. Likewise, the palatine glands are innervated by the nasopalatine, greater palatine nerve and lesser palatine nerves. The pharyngeal nerve innervates pharyngeal glands. These are all branches of maxillary nerve.
【 Sympathetic root 】The ganglion also consists of sympathetic efferent (postganglionic) fibers from the superior cervical ganglion. These fibers, from the superior cervical ganglion, travel through the carotid plexus, and then through the deep petrosal nerve. The deep petrosal nerve (carrying postganglionic sympathetics) joins with the greater petrosal nerve (carrying preganglionic parasympathetics) to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal, which passes through the pterygoid canal before entering the ganglion.
【 Branches 】
【イラスト掲載サイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
