【概 要】

・「発生学的には中胚葉性歯乳頭の発達したものである。」(日本人体解剖学)
・「外形は象牙質の外形にほぼ一致」(ウィキペディア)

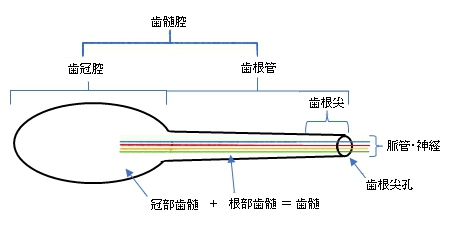
【区 分】

・「特に、髄室角を満たす歯髄を髄角と呼称する。」(ウィキペディア)
・「髄角は歯髄のなかでも血管と神経の両方がよく発達している。」(ウィキペディア)
【構 造】
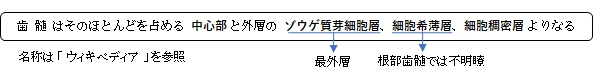

「ウィキペディア」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
象牙芽細胞層から細胞希薄層にかけては血管が豊富で、細胞希薄層から細胞稠密層にかけてはRaschkow神経叢が発達している。このRaschkow神経叢から枝分かれしたものの一部が象牙細管内に侵入し、象牙芽細胞の突起に結合している。
歯髄は多種多様な細胞成分を含んでおり、象牙質を髄側から形成する象牙芽細胞、コラーゲン線維の形成と分解を行う線維芽細胞(歯髄細胞)、血管の周りに存在し象牙芽細胞や線維芽細胞へと分化する未分化間葉細胞(歯髄幹細胞)が存在する。また免疫細胞としてマクロファージやリンパ球、樹状細胞が存在しており、化膿性歯髄炎の際は好中球などもみられる。
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文の一部となる。
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth.[1] The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour.
【Anatomy】
The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.[2] Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls.
Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are continuous with the periapical tissues through the apical foramen or foramina.
The total volume of all the permanent teeth organs is 0.38cc, and the mean volume of a single adult human pulp is 0.02cc.[citation needed]
Accessory canals are pathways from the radicular pulp. These canals, which extend laterally through the dentin to the periodontal tissue, are seen especially in the apical third of the root. Accessory canals are also called lateral canals because they are usually located on the lateral surface of the roots of the teeth.
【語句】
・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・: ・:
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
