


【上顎洞の各壁の特徴】
以下は「 日本人体解剖学 」の解説文となる。
「上顎体中にある大きな空洞で、副鼻腔の一つである。その形状はほぼ上顎体の形に一致し、尖端を上外側すなわち頬骨突起の方に向けた錐体状で、その底は鼻腔面に向き、ここに大きな不正形の上顎洞裂孔がある。」」
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the ostiomeatal complex.
【Structure】
It is the largest air sinus in the body. Found in the body of the maxilla, this sinus has three recesses: an alveolar recess pointed inferiorly, bounded by the alveolar process of the maxilla; a zygomatic recess pointed laterally, bounded by the zygomatic bone; and an infraorbital recess pointed superiorly, bounded by the inferior orbital surface of the maxilla. The medial wall is composed primarily of cartilage. The ostia for drainage are located high on the medial wall and open into the semilunar hiatus of the lateral nasal cavity; because of the position of the ostia, gravity cannot drain the maxillary sinus contents when the head is erect (see pathology). The ostium of the maxillary sinus is high up on the medial wall and on average is 2.4 mm in diameter; with a mean volume of about 10 ml.
The sinus is lined with mucoperiosteum, with cilia that beat toward the ostia. This membranous lining is also referred to as the Schneiderian membrane, which is histologically a bilaminar membrane with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells on the internal (or cavernous) side and periosteum on the osseous side. The size of the sinuses varies in different skulls, and even on the two sides of the same skull.
The infraorbital canal usually projects into the cavity as a well-marked ridge extending from the roof to the anterior wall; additional ridges are sometimes seen in the posterior wall of the cavity and are caused by the alveolar canals.
The mucous membranes receive their postganglionic parasympathetic nerve fibres for mucous secretion from the pterygopalatine ganglion. The preganglionic parasympathetic fibres are coming to this ganglion through the greater petrosal nerve (a branch of the facial nerve) and the nerve of the pterygoid canal. The superior alveolar (anterior, middle, and posterior) nerves, branches of the maxillary nerve provide sensory innervation.
【 語 句 】
・paranasal sinuses:副鼻腔 ・middle meatus:中鼻道 ・ostiomeatal complex:中鼻道自然口ルート ・air sinus:含気腔 ・recess:凹んだ部分 ・alveolar:歯槽の ・zygomatic:頬骨の ・infraorbital:眼窩窩の ・cartilage:軟骨 ・ostia:心門 ・drainage:排水 ・semilunar hiatus:半月裂孔 ・nasal cavity:鼻腔 ・ostium:小孔 ・mean:平均? ・mucoperiosteum:粘膜骨膜 ・cilia:細毛 ・membranous:膜状の ・Schneiderian membrane:シュナイデル膜(=鼻粘膜?) ・bilaminar: 二層の ・pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells:多列円柱上皮細胞 ・periosteum:骨膜 ・osseous:骨の ・infraorbital canal:眼窩管 ・ridge:隆起線 ・alveolar canal:歯槽管 ・postganglionic:節後の ・parasympathetic:副交感神経の ・secretion:分泌物 ・greater petrosal nerve:大錐体神経 ・pterygoid canal:翼突管 ・sensory innervation:知覚神経支配
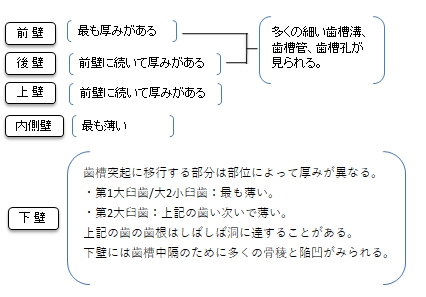
【Walls】
The nasal wall of the maxillary sinus, or base, presents, in the disarticulated bone, a large, irregular aperture, communicating with the nasal cavity. In the articulated skull this aperture is much reduced in size by the following bones:
The sinus communicates through an opening into the semilunar hiatus on the lateral nasal wall.
On the posterior wall are the alveolar canals, transmitting the posterior superior alveolar vessels and nerves to the molar teeth
The floor is formed by the alveolar process, and, if the sinus is of an average size, is on a level with the floor of the nose; if the sinus is large it reaches below this level. Projecting into the floor of the antrum are several conical processes, corresponding to the roots of the first and second maxillary molar teeth; in some cases the floor can be perforated by the apices of the teeth.
The roof is formed by floor of the orbit. It is traversed by infraorbital nerves and vessels.
【Development】
It is the first sinus to appear as a shallow groove. At birth it measures about 7*4*4mm. It continues to develops throughout childhood at an annual rate of 2mm vertically and 3mm anteroposteriorly. It reaches its final size in the seventeenth to eighteenth year of life.
【 語 句 】
・disarticulate:関節で離れる ・aperture:穴 ・semilunar hiatus:半月裂孔 ・molar teeth:大臼歯 ・alveolar process:歯槽突起 ・antrum:上顎洞 ・conical:円錐の ・perforate:貫通する ・apice:apex(頂点)の複数
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
