


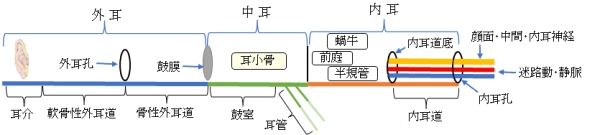


「 日本人体解剖学 」では以下のように解説している。
「内耳は、音波の受容器すなわち聴覚器であると同時に、身体の位置・方向および運動に伴う加速度などを知覚する平衡覚器であって、その構造がきわめて複雑なところから迷路とも呼ばれる。
内耳は、側頭骨の岩様部の中にあり、内耳を内耳道、骨迷路と膜迷路に分ける。骨迷路の内部を内リンパ隙といい、内リンパによって満たされ、膜迷路と骨迷路との間には外リンパ隙があって外リンパによって満たされる。 」
また、以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:
The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates.
【 語 句 】
・vertebrate:脊椎動物の ・detection:探知、検出 ・bony labyrinth:骨迷路 ・hollow:中空の ・temporal bone:側頭骨 ・comprise:構成する ・cochlea:蝸牛 ・auditory nerve:蝸牛神経 ・vestibular system:前庭系
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
