
以下は「ウィキペディア」の解説文からの抜粋を箇条書きにしたものとなる。
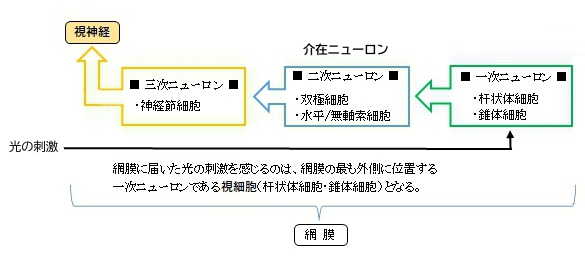
・ 網膜の視覚情報を視床、視床下部、中脳へ伝達する。(=脳へいたる長い軸索を持つ)
・ ヒト網膜には、おおよそ120万から150万個の神経節細胞が存在するとされる。
(視細胞の数は1億個程度であるので、1つの神経節細胞は平均して約100の錐体細胞と桿体細胞から入力を
受ける。)
(中心窩では、1つの視細胞が5つ程度の神経節細胞へ情報を伝達する。)
(網膜の端のような極度の周辺部では、1つの神経節細胞は、数千の視細胞から情報を受け取る。)
・ 静止状態であっても自発的に活動電位を生成している。
・ 神経投射のパターンや受容野特性から、神経節細胞には少なくとも5つの主要なタイプがあると考えられている。

以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain.
【 語 句 】
・retina:網膜 ・photoreceptor:光受容細胞(視細胞) ・bipolar cell:双極細胞 ・amacrine cell:無軸索細胞 ・collectively:合わせて ・action potential:活動電位 ・thalamus:視床 ・hypothalamus:視床下部 ・mesencephalon:中脳
Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract.
A small percentage of retinal ganglion cells contribute little or nothing to vision, but are themselves photosensitive; their axons form the retinohypothalamic tract and contribute to circadian rhythms and pupillary light reflex, the resizing of the pupil.
【 語 句 】
・significantly:かなり ・in terms of ~:~の点から ・stimulation:興奮、刺激 ・axon:軸索 ・optic nerve:視細胞 ・optic chiasm:視交叉 ・optic tract:視索 ・photosensitive:感光性の ・retinohypothalamic tract:網膜視床下部路 ・circadian rhythms:日周リズム ・pupillary light reflex:
対光反射 ・resize:大きさを変更する ・pupil:瞳孔
【
Function】
There are about 0.7 to 1.5 million retinal ganglion cells in the human retina. With about 4.6 million cone cells and 92 million rod cells, or 96.6 million photoreceptors per retina, on average each retinal ganglion cell receives inputs from about 100 rods and cones. However, these numbers vary greatly among individuals and as a function of retinal location. In the fovea (center of the retina), a single ganglion cell will communicate with as few as five photoreceptors. In the extreme periphery (edge of the retina), a single ganglion cell will receive information from many thousands of photoreceptors.
Retinal ganglion cells spontaneously fire action potentials at a base rate while at rest. Excitation of retinal ganglion cells results in an increased firing rate while inhibition results in a depressed rate of firing.
【 語 句 】
・cone cell:杆状体細胞 ・rod cell錐体細胞: ・fovea:中心窩 ・periphery:周辺部 ・spontaneously:自発的に ・excitation:興奮 ・inhibition:抑制
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
