
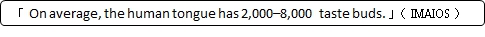
・「味蕾は、紡錘形の細胞の集団で、重層扁平上皮の中に埋もれたように存在している。」(日本人体解剖学)
・「胎児の舌、若年者には多いが、思春期以降では減少する。」(日本人体解剖学)
・「成人における有郭乳頭の断面では輪溝の上部から底部に至る味蕾の数は、10~12個を数えるが、味蕾の数は種々の条件で増減する。」(日本人体解剖学)
・未来の先端部(鼻腔に向く部分で味細胞の微絨毛が位置)の細くなった空間を味孔という。
・舌の表面に4種ある乳頭のうち糸状乳頭以外は味蕾を有する。


1 |
味細胞 |
「明調細胞で細胞の自由端には微絨毛である味毛(小茎)と呼ばれる小突起があり、味孔に突出する。味細胞は味を感じる感覚上皮細胞で、支持細胞の間に存在して、味蕾に分布する神経終末と典型的なシナプスをつくる細胞である(Type Ⅲ)。
」(日本人体解剖学) |
2 |
支持細胞 |
「2種が区別される。その1つは暗調細胞で、味蕾の周辺に主に見られ、分泌顆粒を持っている。(Type Ⅰ)他は明調細胞で、比較的内方に存在し、神経終末とは連絡があるといわれ、味細胞とみなす人もある(Type Ⅱ)これらの細胞は長い微絨毛をもつ。これらの細胞の働きについてはよく分かっていない。」(日本人体解剖学) |
3 |
基底細胞 |
「基底側にある丈の低い細胞(Type Ⅳ)で、味孔には達しない。味蕾中にある基底細胞の数は2~3個(まれに5~7個)であり、支持細胞から味蕾細胞に分化すると考えられている。」(日本人体解剖学) |
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
Taste buds contain the taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the cheek, and epiglottis. These structures are involved in detecting the five elements of taste perception: saltiness, sourness, bitterness, sweetness and savoriness (umami). A popular myth assigns these different tastes to different regions of the tongue; in fact, these tastes can be detected by any area of the tongue. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with the taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nerves.
On average, the human tongue has 2,000-8,000 taste buds. The average lifespan of these is estimated to be 10 days.
【語句】
・taste receptor:味覚受容体 ・gustatory cell: ・papillae:乳頭 ・soft palate: ・esophagus: ・epiglottis: ・detect: ・taste perception:味覚 ・savoriness:滋味 ・myth:神話、作り話 ・epithelium:上皮 ・taste pore:味孔 ・dissolve: ・saliva: ・constitute:構成する ・cluster: ・gustatory area:味覚野 ・cranial nerve:脳神経
【Types of papillae】
The taste buds on the tongue sit on raised protrusions of the tongue surface called papillae. There are four types of lingual papillae; all except one contain taste buds:
- Fungiform papillae (茸状乳頭)- as the name suggests, these are slightly mushroom-shaped if looked at in longitudinal section. These are present mostly at the dorsal surface of the tongue, as well as at the sides. Innervated by facial nerve.
- Foliate papillae(葉状乳頭) - these are ridges and grooves towards the posterior part of the tongue found at the lateral borders. Innervated by facial nerve (anterior papillae) and glossopharyngeal nerve (posterior papillae).
- Circumvallate papillae(有郭乳頭) - there are only about 10 to 14 of these papillae on most people, and they are present at the back of the oral part of the tongue. They are arranged in a circular-shaped row just in front of the sulcus terminalis of the tongue. They are associated with ducts of Von Ebner's glands, and are innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Filiform papillae(糸状乳頭) - the most numerous type but do not contain taste buds. They are characterized by increased keratinisation and are involved in the mechanical aspect of providing abrasion.
The bud is formed by two kinds of cells: supporting cells and gustatory cells. The supporting (sustentacular cells) are mostly arranged like the staves of a cask, and form an outer envelope for the bud. Some, however, are found in the interior of the bud between the gustatory cells. The gustatory (taste) cells, which are chemoreceptors, occupy the central portion of the bud; they are spindle-shaped, and each possesses a large spherical nucleus near the middle of the cell. The peripheral end of the cell terminates at the gustatory pore in a fine hair filament, the gustatory hair. The central process passes toward the deep extremity of the bud, and there ends in single or bifurcated varicosities. The nerve fibrils after losing their medullary sheaths enter the taste bud, and end in fine extremities between the gustatory cells; other nerve fibrils ramify between the supporting cells and terminate in fine extremities; these, however, are believed to be nerves of ordinary sensation and not gustatory.
Salt, sweet, sour and umami tastes causes depolarization of the taste cells, although different mechanisms are applied. Bitter causes an internal release of Ca2+, no external Ca2+ is required.
【語句】
・supporting cell: ・stave of a cask:樽の板? ・chemoreceptors:化学受容器 ・spindle-shaped:錘型 ・spherical:球形の ・peripheral:末梢の ・gustatory hair:味毛 ・bifurcated: ・varicosities: ・medullary sheath:ミエリン鞘 ・ramify:分岐する ・depolarization:脱分極、減極
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
