
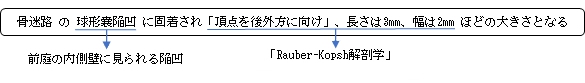
・「卵形嚢は長さ5~6mm, 球形嚢は長さ3mm,幅2mmである.」(Rauber-Kopsh解剖学)




以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The saccule is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear. It translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane. When the head moves vertically, the sensory cells of the saccule are disturbed and the neurons connected to them begin transmitting impulses to the brain. These impulses travel along the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve to the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem.
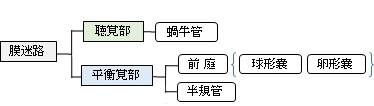
The vestibular system is important in maintaining balance, or equilibrium. The vestibular system includes the saccule, utricle, and the three semicircular canals. The vestibule is the name of the fluid-filled, membranous duct that contains these organs of balance. The vestibule is encased in the temporal bone of the skull.
【 語 句 】
・sensory cell:感覚細胞 ・inner ear:内耳 ・neural impulse:神経繊維に沿って進む放電 ・interpret:理解する ・detect:検出する ・linear acceleration:直線加速 ・head tilt:頭部後屈 ・vertical plane:垂直面 ・disturb:乱す、妨害する ・cranial nerve:脳神経 ・vestibular nuclei:前庭神経核 ・equilibrium:平衡 ・utricle:卵形嚢 ・semicircular canal:半規管 ・vestibule:前庭 ・encase:包む ・temporal bone:側頭骨
【Structure】
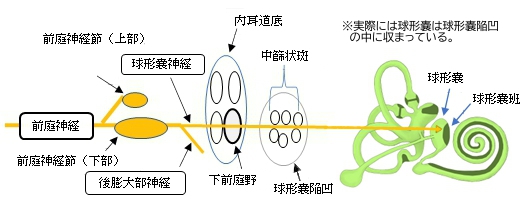
The saccule, or sacculus, is the smaller of the two vestibular sacs. It is globular in form and lies in the recessus sphæricus near the opening of the vestibular duct of the cochlea. Its cavity does not directly communicate with that of the utricle. The anterior part of the saccule exhibits an oval thickening, the macula acustica sacculi, or macula, to which are distributed the saccular filaments of the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve, also known as the statoacoustic nerve or cranial nerve VIII.
Within the macula are hair cells, each having a hair bundle on the apical aspect. The hair bundle is composed of a single kinocilium and many (at least 70) stereocilia. Stereocilia are connected to mechanically gated ion channels in the hair cell plasma membrane via tip links. Supporting cells interdigitate between hair cells and secrete the otolithic membrane, a thick, gelatinous layer of glycoprotein. Covering the surface of the otolithic membrane are otoliths, which are crystals of calcium carbonate. For this reason, the saccule is sometimes called an "otolithic organ."
【 語 句 】
・globular:球状の ・recessus sphaericus:球形嚢陥凹 ・vestibular duct:前庭階 ・cochlea:蝸牛 ・exhibit:示す、表す ・macula acustica sacculi:球形嚢斑 ・vestibulocochlear nerve:内耳神経 ・hair cell:有毛細胞 ・apical:頂上の ・kinocilium:動毛 ・stereocilia:不動毛 ・gated:門のある ・plasma membrane:細胞膜、形質膜、原形質膜 ・interdigitate:互いに組み合わせる ・secrete:分泌する ・otolithic membrane:耳石膜 ・gelatinous:ゼラチン状の ・glycoprotein:糖タンパク ・otolith:耳石 ・calcium carbonate:炭酸カルシウム ・otolithic organ:耳石器
From the posterior wall of the saccule is given off a canal, the ductus endolymphaticus (endolymphatic duct). This duct is joined by the ductus utriculosaccularis, and then passes along the aquæductus vestibuli and ends in a blind pouch saccus endolymphaticus (endolymphatic sac) on the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone, where it is in contact with the dura mater.
From the lower part of the saccule a short tube, the canalis reuniens of Hensen, passes downward and opens into the ductus cochlearis near its vestibular extremity.
Both the utricle and the saccule provide information about acceleration. The difference between them is that the utricle is more sensitive to horizontal acceleration, whereas the saccule is more sensitive to vertical acceleration.
【 語 句 】
・endolymphatic duct:内リンパ管 ・ductus utriculosaccularis:連嚢管 ・blind pouch:盲嚢 ・endolyphatic sac:内リンパ嚢 ・petrous portion:錐体部 ・dura mater:硬膜 ・canalis reuniens:結合管 ・extremity:末端 ・acceleration:加速
【Function】
The saccule gathers sensory information to orient the body in space. It primarily gathers information about linear movement in the vertical plane, including the force due to gravity. The saccule, like the utricle, provides information to the brain about head position when it is not moving. The structures that enable the saccule to gather this vestibular information are the hair cells. The 2 by 3 mm patch of hair cells and supporting cells are called a macula. Each hair cell of a macula has 40 to 70 stereocilia and one true cilium called a kinocilium. The stereocilia are oriented by the striola, a curved ridge that runs through the middle of the macula; in the saccule they are oriented away from the striola The tips of the stereocilia and kinocilium are embedded in a gelatinous otolithic membrane. This membrane is weighted with protein-calcium carbonate granules called otoliths, which add to the weight and inertia of the membrane and enhance the sense of gravity and motion.
Not much is known of how this organ is used in other species. Research has shown, like songbirds, females in some species of fish show seasonal variation in auditory processing and the sensitivity of the saccule of females peaks during the breeding season. This is due to an increase in the density of saccular hair cells, partly resulting from reduced apoptosis. The increase the hair cells make also increase the sensitivity to male mating calls. An example of this is seen in Porichthys notatus, or plainfin midshipman fish.
【 語 句 】
・orient:適応させる ・linear movement:直線移動 ・vertical plane:垂直面 ・macula:斑 ・cilium:絨毛 ・striola:平衡斑条, 細線条・orient:向きを合わせる? ・embed:はめ込む、埋める ・gelatinous:ゼラチン状の ・otolithic membrane:耳石膜 ・carbonate:炭酸塩 ・granule:粒 ・inertia:緩慢 ・enhance:高める ・songbird:鳴鳥 ・apoptosis:アポトーシス ・mating:交配、交尾 ・Porichthys notatus:イサリビガマアンコウ
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
