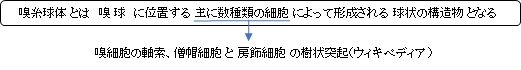
以下の解説は「Wikipedia」からの抜粋となる。
・直径:50~120μ(哺乳類)
・数:人で1100~1200個 加齢により減少し80才以上で欠損が生じる。
・構造:嗅細胞部とその他の細胞部に分けることができる。
・周囲の抑制性神経細胞により他の糸球体と連絡している。
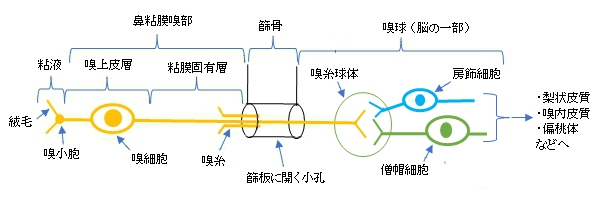
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a spherical structure located in the olfactory bulb of the brain where synapses form between the terminals of the olfactory nerve and the dendrites of mitral, periglomerular and tufted cells. Each glomerulus is surrounded by a heterogeneous population of juxtaglomerular neurons (that include periglomerular, short axon, and external tufted cells) and glial cells.
【語句】
・spherical:球状の ・olfactory bulb:嗅球 ・olfactory nerve:嗅神経 ・dendrite:樹状突起 ・mitral cell:僧帽細胞 ・periglomerular cell:傍糸球体細胞 ・tufted cell: ・heterogeneous population:異種集団 ・juxtaglomerular:房糸球体の ・glial cell:膠細胞
All glomeruli are located near the surface of the olfactory bulb. The olfactory bulb also includes a portion of the anterior olfactory nucleus, the cells of which contribute fibers to the olfactory tract. They are the initial sites for synaptic processing of odor information coming from the nose. A glomerulus is made up of a globular tangle of axons from the olfactory receptor neurons, and dendrites from the mitral and tufted cells, as well as, from cells that surround the glomerulus such as the external tufted cells, periglomerular cells, short axon cells, and astrocytes.
【語句】
・anterior olfactory nucleus:前嗅核 ・olfactory tract:嗅索 ・tanble:もつれ ・axon:軸索 ・dentrite:樹状突起 ・periglomerular cells:傍糸球体細胞 ・astrocyte:星状細胞
In mammals, glomeruli typically range between 50-120 µm in diameter and number between 1100 and 2400 depending on the species, with roughly between 1100 and 1200 in humans. The number of glomeruli in a human decreases with age; in humans that are over 80 they are nearly absent.
Each glomerulus is composed of two compartments, the olfactory nerve zone and the non-olfactory nerve zone. The olfactory nerve zone is composed of preterminals and terminals of the olfactory nerve and is where the olfactory receptor cells make synapses on their targets. The non-olfactory nerve zone is composed of the dendritic processes of intrinsic neurons and is where dendrodendritic interactions between intrinsic neurons occur.
【語句】
・intrinsic:固有の
Anatomy
Glomeruli are important waystations in the pathway from the nose to the olfactory cortex and have been found to be critical for odorant signal transduction. The olfactory receptor neurons (ORN), which originate in the nasal epithelium express only one type of olfactory receptor (OR). These ORNs then project their axons to the olfactory bulb. In the olfactory bulb, the ORNs synapse with termination in the glomeruli. Each glomerulus receives input from olfactory receptor neurons expressing only one type of olfactory receptor. The glomerular activation patterns within the olfactory bulb are thought to represent the quality of the odor being detected. These activation patterns of glomeruli can change due to changes in airflow rate and odor concentration in the mucus layer of the nasal cavity.A certain odorant can activate a glomeruli strongly whilst affecting others with less efficiency to very little at all. Linda Buck and Richard Axel were awarded a Nobel prize in 2004 for heavily influencing the working out of the genetic basis for this Olfactory coding.
【語句】
・waystation:中間駅 ・olfactory cortex: ・critical:重大な ・odorant:匂い物質 ・transduction:伝達 ・epithelium:上皮 ・detect:検出する ・concentration:濃度 ・mucus layer:粘膜層 ・whilst:~する一方、~の間に
The current dogma is that axons from all ORNs expressing the same receptor converge onto one or two glomeruli of a possible 1800 glomeruli in each olfactory bulb. As the axons of the ORNs migrate towards their specific glomeruli they often overshoot into neighboring glomeruli. Thus, a glomerulus representing a specific OR develops slowly and involves considerable axonal reorganization in order to achieve the highly topographical projection observed in adult mice.
【語句】
・dogma:独断的な意見 ・converge:集中する ・migrate:移動する ・overshot:飛び越える ・topographical:地形上の
Function
The glomerulus is the basic unit in the odor map of the olfactory bulb. Each odor activates a different pattern of glomeruli, such that, simply by analyzing the different sets of activated glomeruli, one could, in theory, decode the identity of the odor. This odor map, however, is modified by the circuitry within the olfactory bulb so that the spiking pattern of the second-order mitral cells is usually different from that of the olfactory sensory neurons.
【語句】
・odor map:嗅覚地図? ・activate:活発化する ・decode:解読する ・modify:変更する ・circuitry:電気回路構成 ・spike:?
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ(糸球体そのもののイラスト)
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
