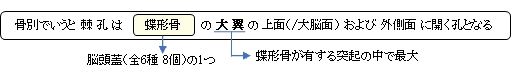
棘孔とは

【通過する神経、動・静脈】
以下が棘孔を通過する脈管および神経となる。 
1 |
神 経 |
・下顎神経( 三叉神経、第3枝 )の 硬膜枝 |
2 |
動 脈 |
|
3 |
静 脈 |
・中硬膜静脈 |

以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文の一部となる。
「 In the newborn, the foramen spinosum is about 2.25 mm long and in adults about 2.56 mm. The width of the foramen extends from 1.05 mm to about 2.1 mm in adults.[4] The average diameter of the foramen spinosum is 2.63 mm in adults. 」
・以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The foramen spinosum is one of two foramina located in the base of the human skull, on the sphenoid bone. It is situated just anterior to the spine of the sphenoid bone, and just lateral to the foramen ovale, The middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve pass through the foramen.
The foramen spinosum is often used as a landmark in neurosurgery, due to its close relations with other cranial foramina. It was first described by Jakob Benignus Winslow in the 18th century.
【 structure 】
The foramen spinosum is a foramen through the sphenoid bone situated in the middle cranial fossa.[1][2]:771It is one of two foramina in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of these two cranial foramina, situated directly anterior and medial to the foramen spinosum.[2]:776 The spine of sphenoid falls medial and posterior to the foramen. Lateral to the foramen is the mandibular fossa, [2]:873and posterior is the Eustachian tube.[1]
【 語 句 】
・ foramen ovale : 卵円孔 ・ middle meningeal artery : 中硬膜動脈 ・ eningeal branch of the mandibular nerve : 下顎神経の硬膜枝 ・ mandibular fossa : 下顎窩 ・ Eustachian tube : 耳管
【 variation 】
The foramen spinosum varies in size and location. The foramen is rarely absent, usually unilaterally, in which case the middle meningeal artery enters the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale.[3] It may be incomplete, which may occur in almost half of the population. Conversely, in a minority of cases (less than 1%), it may also be duplicated, particularly when the middle meningeal artery is also duplicated.[1][3]
The foramen may pass through the sphenoid bone at the apex of the spinous process, or along its medial surface.
【 語 句 】
・ unilaterally : 片側性に ・ Conversely : 反対に ・ duplicated : 重複の
【 vevelopment 】
In the newborn, the foramen spinosum is about 2.25 mm long and in adults about 2.56 mm. The width of the foramen extends from 1.05 mm to about 2.1 mm in adults.[4] The average diameter of the foramen spinosum is 2.63 mm in adults.[5]
The earliest perfect ring-shaped formation of the foramen spinosum was observed in the eighth month after birth and the latest seven years after birth in a developmental study of the
foramen rotundum,
foramen ovale and foramen spinosum. The majority of the foramina in the skull studies were round in shape.
[5] The
sphenomandibular ligament, derived from the first
pharyngeal arch and usually attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone, may be found attached to the rim of the foramen. 」
【 語 句 】
・ foramen rotundum : 正円孔 ・ sphenomandibular ligament : 蝶下顎靭帯 ・ pharyngeal arch : 咽頭弓
【 参考になるサイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
