


前庭階を進む音の振動(進行波)は、周波数によって決まった特定の場所で前庭膜を
刺激し、その振動が蝸牛管に伝わり蓋膜を刺激して、最終的には有毛細胞によって電気
信号に変換される。
ただ、蝸牛管に伝わった刺激はすべて有毛細胞に伝わるわけではなく、そのうちのある
程度は基底板を刺激して鼓室階に達するようである。
インターネットで画像検索をしてみると、そのような感じのイラストを掲載しているサイトが
いくつか見受けられる。下の「音の伝達」のイラストもそのようなものを参考にして作成した
ものとなる。
|
|
|
|
|
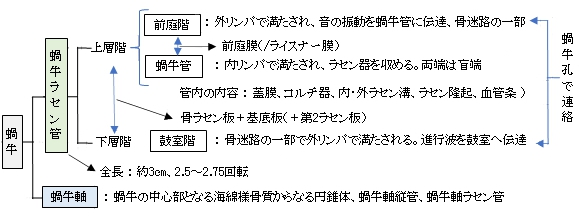
蝸牛ラセン管 |
蝸牛ラセン管 |
音の伝達
その他の名称 |
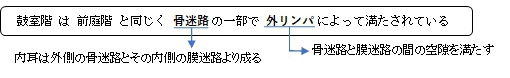
骨迷路・膜迷路 |
|
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The tympanic duct or scala tympani is one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of humans. It is separated from the cochlear duct by the basilar membrane, and it extends from the round window to the helicotrema, where it continues as vestibular duct.
The purpose of the perilymph-filled tympanic duct and vestibular duct is to transduce the movement of air that causes the tympanic membrane and the ossicles to vibrate, to movement of liquid and the basilar membrane. This movement is conveyed to the organ of Corti inside the cochlear duct, composed of hair cells attached to the basilar membrane and their stereocilia embedded in the tectorial membrane. The movement of the basilar membrane compared to the tectorial membrane causes the stereocilia to bend. They then depolarise and send impulses to the brain via the cochlear nerve. This produces the sensation of sound.
【 語 句 】
perilymph(外リンパ)、inner ear(内耳)、cochlear duct(蝸牛管)、basilar membrane(基底板)、round window(正円窓、蝸牛窓)、helicotrema(蝸牛孔)、vestibular duct(前庭階)、transduce(変換する)、tympanic membrane(鼓膜)、ossicles(耳小骨)、convey(伝達する)、organ of Corti(コルチ器)、hair cells(有毛細胞)、stereocilia(不動毛)、embed(はめ込む)、tectorial membrane(蓋膜)、depolarise(分極化を排除する)、cochlear nerve(蝸牛神経)
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
