頚動脈洞とは

・舌咽神経(頚動脈洞枝)によって支配される。
・「血圧の調整にあずかるといわれている。」(日本人体解剖学 (上巻) )
)
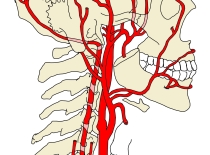
頚部の動脈
|
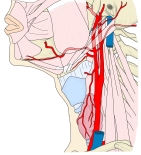
頚部の動脈
および筋
|

舌咽神経の模型図
|
以下は「日本人体解剖学 (上巻) 」の解説文となる。
」の解説文となる。
「総頚動脈の分岐部あるいは内頚動脈の基部は通常膨隆しており頚動脈洞と呼ばれ、一般に老人に著明である。頚動脈洞は舌咽神経の枝である頚動脈洞枝(洞神経)により支配され、血圧の調節にあずかるといわれる。 」
また、以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
「In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a dilated area at the base of the internal carotid artery just superior to the bifurcation of the internal carotid and external carotid at the level of the superior border of thyroid cartilage. The carotid sinus extends from the bifurcation to the "true" internal carotid artery[1]. The carotid sinus is sensitive to pressure changes in the arterial blood at this level. It is the major baroreception site in humans and most mammals.
【 Structure 】The carotid sinus is the reflex area of the carotid artery, consisting of various nerve receptors for baroregulation (pressure regulation of the body in sync to external conditions).
【 Function 】The carotid sinus contains numerous baroreceptors which function as a "sampling area" for many homeostaticmechanisms for maintaining blood pressure. The carotid sinus baroreceptors are innervated by the sinus nerve of Hering, which is a branch of cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal nerve). The glossopharyngeal nerve synapses in the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) located in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. The NTS indirectly modulates the activity of sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagal) neurons in the medulla and pons through the hypothalamus. These neurons then regulate the autonomic control of the heart and blood vessels. The aortic arch baroreceptors are innervated by the aortic nerve (Nerve of Cyon), which combines with CN X (vagus nerve) and travels to the NTS.」
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
