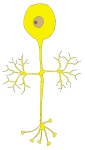
【概 要】
・「発生期には細胞体から複数の突起を出すが,やがてそれらの突起は整理されて,1本の突起となる.」(南山堂医学大辞典)
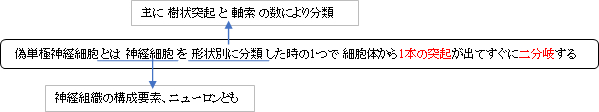
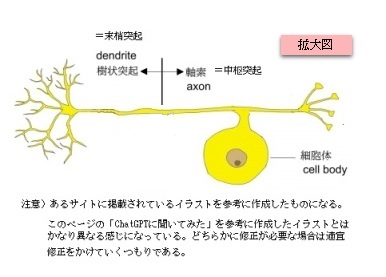
・細胞体から出てすぐに二分岐する突起の一方は末梢突起、そしてもう一方を中枢突起と呼ぶ。



|
|
|
|
|
| 単極ニューロン |
双極ニューロン |
多極ニューロン |
偽単極ニューロン |
【ChatGPTに聞いてみた】
A-1:「偽単極神経細胞にも有髄、無髄の区別はあるのか?」
Q:「はい、あります。太いAβ線維(触覚・圧覚)は有髄、細いC線維(痛み・温度・かゆみなど)は無髄」
感覚の種類 |
末梢突起 |
線維分類 |
例 |
触覚(精細な触覚・振動・
圧覚・皮膚の位置感覚) |
有 髄 |
Aβ線維 |
マイスナー小体、メルケル盤、パチニ小体、ルフィニ終末 |
筋肉の伸張や張力感知
(深部感覚) |
有 髄 |
Aα(Ⅰa, Ib)・
Aβ線維 |
筋紡錘、ゴルジ腱器官 |
| 痛覚(鋭い痛み)、冷覚 |
有 髄 |
Aδ線維 |
自由神経終末 |
| 痛覚(鈍い痛み)、温覚 |
無 髄 |
C線維 |
自由神経終末 |

A-2:「有髄と無髄の細胞が混在(同じ神経節内に存在)することもあるのか?」
Q:「はい、あります。例として腰神経節内にはAβ線維を持つ有髄細胞(触覚)とC線維を持つ無髄細胞(鈍痛)が混在している。」
A-3:「末梢突起と中枢突起は形態的に区別が容易につくのか?」
Q:「いいえ、両者はほぼ同じ形状で区別をつけるのは難しい。」
A-4:「末梢突起で感覚器からの情報を受け取っているのだから、末梢突起は軸索と考えてよいのでは?」
Q:「「情報を受け取る=樹状突起」と考えがちだが「軸索=活動電位を発生する・伝導する」が正しい考え方」

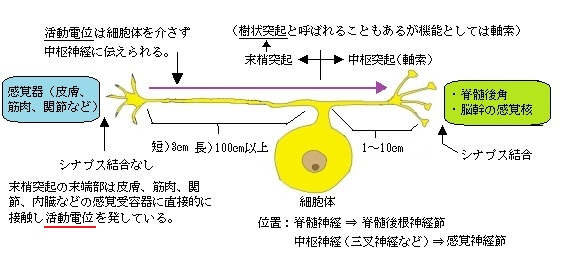
・末梢突起では感覚器の刺激によって直接活動電位が発生する ⇒ 軸索の特徴
通常の軸索では受け取った情報を電位変化に返還するだけで活動電位は起こさない。
・末梢突起はときおり髄鞘(=ミエリン鞘)を伴う。⇒ 軸索の特徴
樹状突起は髄鞘は持たない。
・末梢突起はシナプスがなく物理的・化学的刺激を直接感知し、興奮を発生 ⇒ 樹状突起の特徴ではない
通常の樹状突起は他のニューロンからのシナプス入力を受ける。
A-5:「末梢突起と中枢突起の長さの違いは?」
Q:「明確な長さの違いが存在し末梢突起の方が圧倒的に長く中枢突起は短いのが普通
末梢突起 : 感覚受容器(皮膚、筋肉など)~脊髄の後根神経節まで ⇒ 数㎝ ~ 数十㎝
中枢神経 : 後根神経節から脊髄後角 ⇒ 数㎜ ~ 数㎝ 」
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
A pseudounipolar neuron is a type of neuron which has one extension from its cell body. This type of neuron contains an axon that has split into two branches. A single process arises from the cell body and then divides into an axon and a dendrite. They develop embryologically as bipolar in shape, and are thus termed pseudounipolar instead of unipolar.
【Structure】
A pseudounipolar neuron has one axon that projects from the cell body for relatively a very short distance, before splitting into two branches. Pseudounipolar neurons are sensory neurons that have no dendrites, the branched axon serving both functions. The peripheral branch extends from the cell body to organs in the periphery including skin, joints and muscles, and the central branch extends from the cell body to the spinal cord.
【 語 句 】
・axon:軸索 ・dendrite:樹状突起 ・embryologically:発生学的に ・bipolar:双極神経細胞 ・sensory neuron:知覚神経 ・peripheral:末梢の ・spinal cord:脊髄
In the dorsal root ganglia
The cell body of a pseudounipolar neuron is located within a dorsal root ganglion. The axon leaves the cell body (and out of the dorsal root ganglion) into the dorsal root, where it splits into two branches. The central branch goes to the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, where it forms synapses with other neurons. The peripheral branch travels through the distal dorsal root into the spinal nerve all the way until skin, joint, and muscle.
In most sensory ganglia of cranial nerves
Pseudounipolar neurons are found in the sensory ganglia of most cranial nerves.
Specifically the:
【 語 句 】
・dorsal root ganglion:後根神経節 ・dorsal column:脊髄後柱 ・distal:末端の
Pseudounipolar neurons in cranial nerve sensory ganglia synapse in the main sensory trigeminal nucleus, spinal trigeminal nucleus or solitary nucleus.
While the vestibulocochlear nerve has two ganglia associated with it (spiral ganglion and vestibular ganglion), both contain bipolar neurons, not pseudounipolar.
In the mesencephalic nucleus
Main article: mesencephalic nucleus
The mesencephalic nucleus is made up of pseudounipolar neurons which migrated into the brainstem during embryological development. It is the only location in the central nervous system where the cell bodies of pseudounipolar neurons are found.
【 語 句 】
・cranial nerve:脳神経 ・trigeminal nucleus:三叉神経核 ・spinal trigeminal nucleus:三叉神経脊髄路核 ・solitary nucleus:孤束核 ・vestibulocochlear nerve:内耳神経 ・spiral ganglion:ラセン神経節 ・vestibular ganglion:前庭神経節 ・mesencephalic:中脳の ・migrate:移動する ・brainstem:脳幹 ・embryological:発生学の
【Function】
All pseudounipolar neurons are sensory neurons. The ones found in the dorsal root ganglia, and majority of those in cranial nerve sensory ganglia carry information about touch, vibration, proprioception, pain and temperature.
Pseudounipolar neurons in the geniculate ganglion, inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve and inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve also carry information about taste from taste buds.
Some of the pseudounipolar neurons in the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve carry information from the carotid body and carotid sinus.
The pseudounipolar neurons in the mesencephalic nucleus carry proprioceptive information from the muscle of mastication.
【 語 句 】
・proprioception:固有受容性感覚 ・geniculate ganglion:膝神経節 ・taste bud:味蕾 ・carotid body:頚動脈小体 ・carotid sinus:頚動脈洞 ・mastication:咀嚼
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ