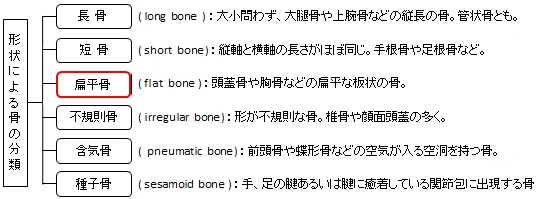
扁平骨とは

 以下は「船戸和弥のホームページ」の解説文となる。 以下は「船戸和弥のホームページ」の解説文となる。
「扁平骨は扁平な骨である。2層の硬い緻密質に挟まれて、薄い海綿質が存在する。頭蓋骨のほかに、胸骨、肋骨、肩甲骨、腸骨などが扁平骨に属する。偏平骨は頭蓋冠をつくる前頭骨や頭頂骨のように内腔を囲み保護するとともに、その広い表面は筋の付着面ともなる。」
以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
「Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates,[1] as in the cranium (skull), the ilium (pelvis), sternum and the rib cage. The flat bones are: the occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, hip bone (coxal bone), sternum, ribs, and scapulae.[1] In the cranial bones, the layers of compact tissue are familiarly known as the tables of the skull; the outer one is thick and tough; the inner is thin, dense, and brittle, and hence is termed the vitreous (glass-like) table.[1]
These bones are composed of two thin layers of compact bone enclosing between them a variable quantity of cancellous bone,[1] which is the location of red bone marrow. In an adult, most red blood cells are formed in flat bones. The intervening cancellous tissue is called the diploë, and this, in the nasal region of the skull, becomes absorbed so as to leave spaces filled with air–the paranasal sinuses between the two tables.[1]」
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ(構造が分かるイラスト)
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ

|