
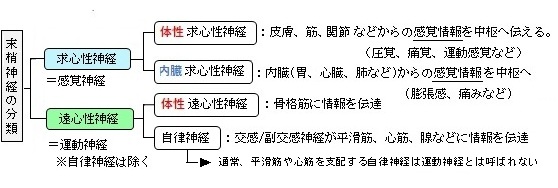
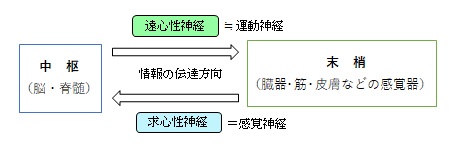
・遠心性神経はほぼ運動神経と同義になるが、正確には平滑筋や心筋を神経支配する自律神経も含めるため「遠心性神経=運動神経」とはならない。(通常、「運動神経」は骨格筋を神経支配する神経線維を指す。
【「ChatGPT」に聞いてみた】
Q.「中枢神経も求心性神経と遠心性神経に分けられるのか?」
脳や脊髄の内部の神経回路については、求心性・遠心性という表現は通常あまり使いません。
・中枢神経の内部は複雑にニューロンが連絡し合っているため、末梢のように「入力方向/出力方向」で単純に整理しにくいからです。
・中枢では「上行路」「下行路」「抑制性」「興奮性」といった用語の方がよく使われます。
【参考になるサイト】
「実験医学 online」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「自律神経系(交感神経と副交感神経)は,かつては遠心性の線維のみからなるとされていたが,求心性線維も多く含まれていることがわかってきた.迷走神経(副交感神経)構成線維の約75%,内臓神経(交感神経)の50%は求心性線維とされている。」
また、以下は「Wikipedia」の「efferent nerve fiber(遠心性神経線維)」の解説文となる。
「In the peripheral nervous system, an efferent nerve fiber is the nerve fiber (axon) of an efferent neuron (motor neuron). It is a long process (projection) extending far from the neuron's body that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system toward the peripheral effector organs (mainly muscles and glands). The opposite direction of neural activity is afferent conduction.[1][2][3]
In the nervous system there is a "closed loop" system of sensation, decision, and reactions. This process is carried out through the activity of afferent neurons (sensory neurons), interneurons, and efferent neurons (motor neurons).
The motor nerves are efferent nerves involved in muscular control. The cell body of the efferent neuron is connected to a single, long axon and several shorter dendrites projecting out of the cell body itself. This axon then forms a neuromuscular junction with the effectors. The cell body of the motor neuron is satellite-shaped. The motor neuron is present in the grey matter of the spinal cord and medulla oblongata, and forms an electrochemical pathway to the effector organ or muscle. Besides motor nerves, there are efferent sensory nerves that often serve to adjust the sensitivity of the signal relayed by the afferent sensory nerve.」
【参考になるサイト】
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
