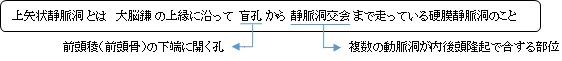
・「 上矢状静脈洞は尾側にいくに従い大きさを増す。」( 船戸和也のHP )
「 Wikipedia 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 It is triangular in section, narrow in front, and gradually increases in size as it passes backward. 」 ※ in section : 断面



以下は「 船戸和弥のHP 」をベースにして作成した硬膜静脈洞の一覧となる。資料によってそれぞれのグループに属する静脈洞には若干の違いが見られる。

以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
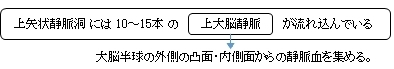
「 The superior sagittal sinus ( also known as the superior longitudinal sinus ), within the human head, is an unpaired area along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses. Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to venous circulation.
【 語 句 】
・ falx cerebri : 大脳鎌 ・ cerebral hemispheres : 大脳半球 ・ confluence : 合流 ・ Cerebrospinal fluid : 脳脊髄液 ・ arachnoid granulations : クモ膜顆粒
【 Structure 】
Commencing at the foramen cecum, through which it receives emissary veins from the nasal cavity, it runs from anterior to posterior, grooving the inner surface of the frontal, the adjacent margins of the two parietal lobes, and the superior division of the cruciate eminence of the occipital lobe. Near the internal occipital protuberance, it drains into the confluence of sinuses and deviates to either side (usually the right[1][2]).
At this point it is continued as the corresponding transverse sinus. The superior sagittal sinus is usually divided into three parts : anterior ( foramen cecum to bregma ), middle (bregma to lambda), posterior (lambda to confluence).[3]
It is triangular in section, narrow in front, and gradually increases in size as it passes backward.
【 語 句 】
・ foramen cecum : 盲孔 ・ emissary veins : 導出静脈 ・ parietal lobe : 頭頂葉 ・ cruciate eminence : 十字隆起 ・ occipital lobe : 後頭葉 ・ internal occipital protuberance : 内後頭隆起 ・ confluence of sinuses : 静脈洞交会 ・ deviate : それる ・ transverse sinus :横静脈洞 ・ bregma : 十字縫合 ・ lambda : ラムダ縫合? ・ in section : 断面
Its inner surface presents the openings of the superior cerebral veins, which run, for the most part, obliquely forward, and open chiefly at the back part of the sinus, their orifices being concealed by fibrous folds ; numerous fibrous bands (chordae Willisii) extend transversely across the inferior angle of the sinus ; and, lastly, small openings communicate with irregularly shaped venous spaces ( venous lacunae ) in the dura mater near the sinus.
There are usually three lacunae on either side of the sinus: a small frontal, a large parietal, and an occipital, intermediate in size between the other two.
Most of the cerebral veins from the outer surface of the hemisphere open into these lacunæ, and numerous arachnoid granulations ( Pacchionian bodies ) project into them from below.
The superior sagittal sinus receives the superior cerebral veins, veins from the diploë and dura mater, and, near the posterior extremity of the sagittal suture, veins from the pericranium, which pass through the parietal foramina.
Further information: Dural venous sinuses
Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to venous circulation.」
【 語 句 】
・ superior cerebral veins : 脳大脳静脈 ・ orifice : 開口部 ・conceale : 隠す ・ venous lacunae : 外側裂孔 ・ dura mater : 硬膜 ・ lacunae : 裂孔、空隙 ・ diploë : 板間層 ・ sagittal suture : 矢状縫合 ・ pericranium:頭蓋骨膜 ・ parietal foramina : 頭頂孔?
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|