

・「 多くの結合組織性の線維束に貫かれて海綿状を呈する 」( 日本人体解剖学 )


「 船戸和弥のHP 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 静脈洞の外側壁には動眼神経、滑車神経、三叉神経の枝である眼神経と上顎神経が存在する。」
※ 海綿静脈洞を通過するものは下の「Wikipedia」でも詳しく解説が見られる。

⇒ 左右の海綿静脈洞は、前・後海綿間静脈洞を介して連絡しあっている。

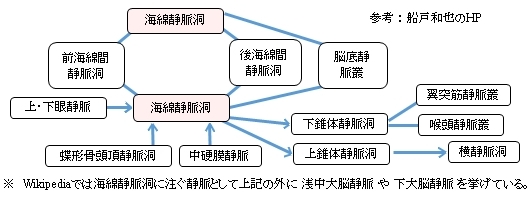
以下は「 船戸和弥のHP 」をベースにして作成した硬膜静脈洞の一覧となる。資料によってそれぞれのグループに属する静脈洞には若干の違いが見られる。


以下は「 日本人体解剖学 」の解説文となる。
「 海綿静脈洞の前方は、上眼静脈および蝶形(骨)頭頂静脈洞に連絡する。後方は上・下錐体静脈洞と連絡し、さらに下方は卵円孔静脈叢および頚動脈管静脈叢によって翼突筋静脈叢と連絡する。」
また「 船戸和弥のHP 」では以下のように解説している。
「 左右の海綿静脈洞は脳底静脈叢および下垂体前面にある前海綿間静脈叢と後面にある後海綿間静脈叢により対側の静脈洞と連絡する。眼静脈と蝶形骨頭頂静脈洞は、海綿静脈洞に注ぎ込む。海綿静脈洞は、後方に向かい上錐体静脈洞と下錐体静脈洞に入り、上錐体動脈洞は横静脈洞に、下垂体静脈洞は、短い静脈網によって翼突筋静脈叢や喉頭静脈叢とも連絡する。」
以下は海綿静脈洞に注ぐ、または連絡する静脈(洞)を簡単に表した図となる。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses[1] creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
【 Structure 】
The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity, approximately 1 x 2 cm in size in an adult.[2] The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space.
【 語 句 】
・ dural venous sinuses : 硬膜静脈洞 ・ cavity : 空洞 ・ temporal bone : 側頭骨 ・ sphenoid bone : 蝶形骨 ・ sella turcica : トルコ鞍
【 Nearby structures 】
【 Venous connections 】
The cavernous sinus receives blood from:[2]
Blood leaves the sinus via superior and inferior petrosal sinuses as well as via the emissary veins through the foramina of the skull (mostly through foramen ovale). There are also connections with the pterygoid plexus of veins via inferior ophthalmic vein, deep facial vein and emissary veins
【 語 句 】
・ superior and inferior petrosal sinuses: ・ emissary veins: ・ foramen ovale: ・foramina : ・ pterygoid plexus:
【 Contents 】
Apart from the blood which passes through a venous sinus, several anatomical structures, including some cranial nerves and their branches, also pass through the sinus.[2]
Structures within the outer (lateral) wall of the compartment from superior to inferior:[2]
Structures passing through the midline (medial) wall :[2]
These nerves, with the exception of CN V2, pass through the cavernous sinus to enter the orbital apex through the superior orbital fissure. The maxillary nerve, division V2 of the trigeminal nerve travels through the lower portion of the sinus and exits via the foramen rotundum. The maxillary branch passes external to, but immediately adjacent to, the lateral wall of the sinus)[1]
A mnemonic exists to remember the orientation of the vertical and horizontal content of the sinus :
OTOM CAT. ( OTOM are the lateral wall contents from superior to inferior ; CAT are the horizontal contents from medial to lateral )[3]
The optic nerve lies just above and outside the cavernous sinus, superior and lateral to the pituitary gland on each side, and enters the orbital apex via the optic canal.
【 Function 】
Venous drainage
As a venous sinus, the cavernous sinus receives blood from the superior and inferior opthalmic veins and from superficial veins, and is connected to the basilar plexus of veins posteriorly. The cavernous sinus drains by two larger channels, the superior and inferior petrosal sinuses, ultimately into the internal jugular vein via the sigmoid sinus, also draining with emissary vein to pterygoid plexus. 」
【 語 句 】
・ CN V2 : = maxillary nerve ・ orbital apex : 眼窩尖 ・ foramen rotundum : 正円孔 ・ mnemonic : 記憶術の ・ optic nerve : 視神経 ・ optic canal : 視神経管 ・ drainage : 排水 ・ cortical : 皮層の ・ basilar plexus : 脳底静脈叢 ・ pterygoid plexus : 翼突筋静脈叢
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|