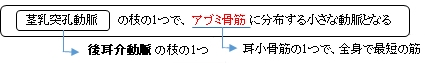
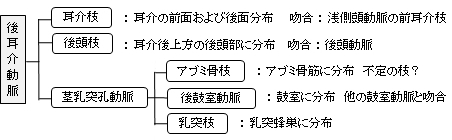
以下は後耳介動脈の枝を表した簡単な図になる。
・「 日本人体解剖学 」の解説には「不定」も文字見られ、「Wikipedia」では「胎児のときに見られる動脈で、成人では5000人に1の割合で見られる」というような解説が見られる。
「 In humans, the stapedial artery is normally present in the fetus …. it has been estimated to be present in 1 of 5,000 people. 」
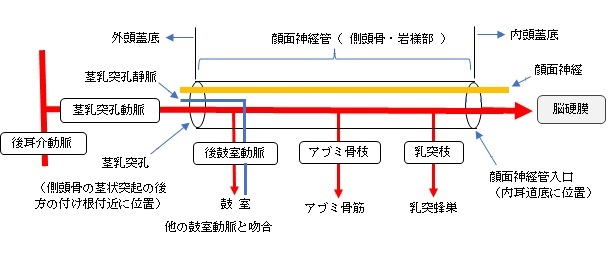
・「アブミ骨枝は直接、茎乳突孔動脈から、もしくはその枝である後鼓室動脈から出てアブミ骨筋に分布する。」(船戸和弥のホームページ )
「 Wikipedia 」では以下のように解説している。
「 In human anatomy, the stapedial branch of posterior auricular artery, or stapedial artery for short, is a small artery supplying the stapedius muscle in the inner ear.
【 structure 】
In humans, the stapedial artery is normally present in the fetus where it connects what is to become the external and internal carotid arteries.[1] Part of the carotid artery system, it originates from the dorsal branch of aortic arch. Its superior supraorbital branch becomes the middle meningeal artery, while its infraorbital and mandibular branches fuses with the external carotid artery and later become the internal maxillary artery. Its trunk atrophies and is replaced by branches from the external carotid artery.[2]
In rare cases, the embryonic structure is still present after birth in which case it is referred to as a persistent stapedial artery (PSA).[1] While the prevalence of this anomaly is unknown, it has been estimated to be present in 1 of 5,000 people.[3]」
【 語 句 】
・ fetus:胎児 ・atrophy:委縮する/機能が退化する ・persistent:頑固な、持続性の ・ prevalence:広く行き渡っている ・anomaly:例外
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ

|