肺動脈 とは


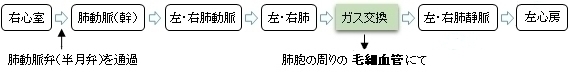
以下は心血管系の循環を簡単に表したものとなる。

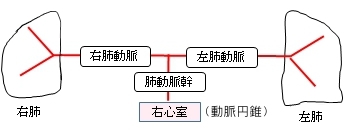
また、以下は肺動脈の構成を簡単に表したものとなる。

以下は肺循環を簡単に表した図となる。

2019年12月この肺動脈のページを8年振りに再作成している。イラストも数種類新たに作成しているが、初期のころに作成したイラストを確認してみて「そうか、初期のころに作成したイラストは肺動脈を青で描いていたんだ~」ということを再認識してしまった。つまり、同じ肺動脈でも、青で描いているイラストと赤で描いているものがあるので、その点はご了解いただきたい。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.
【 語 句 】
・ pulmonary circulation : 肺循環 ・ deoxygenated : 脱酸素化した ・ pulmonary trunk : 肺動脈幹 ・ arterioles (arterioleの複数): 小動脈 ・ capillaries (capillaryの複数): 毛細血管 ・ pulmonary alveoli : 肺胞
【 Pulmonary arterial tree 】
In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk or main pulmonary artery. The main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short and wide—approximately 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in length and 3 centimetres (1.2 in) in diameter.
The main pulmonary artery splits into the right and the left main pulmonary artery.[1] The left main pulmonary artery is shorter and somewhat smaller than the right, passes horizontally in front of the descending aorta and left bronchus to the root of the left lung. Above, the left main pulmonary artery is connected to the concavity of the proximal descending aorta by the ligamentum arteriosum.[2] It then divides into two lobar arteries, one for each lobe of the left lung. The right main pulmonary artery follows a longer and more horizontal course as it crosses the mediastinum. It passes underneath the aortic arch, behind the ascending aorta, and in front of the descending aorta. It courses posterior to the superior vena cava and in front of the right bronchus. Upon reaching the hilum of the right lung the right main pulmonary artery divides into two branches:
- ・ truncus anterior — supplies blood to the right upper lobe
- ・ interlobar artery — inferior and larger branch, supplies blood to the middle and inferior lobes of the lung
The right and left main pulmonary arteries give off branches that roughly correspond to the lung lobes and can in such cases be termed lobar arteries. The lobar arteries branch into segmental arteries (roughly 1 for each lobe segment), which in turn branch into subsegmental pulmonary arteries.[3] These eventually form intralobular arteries.[4]
【 語 句 】
・ right ventricle : 右心室 ・ descending aorta : 下行大動脈 ・ bronchus : 気管支 ・ concavity : くぼみ ・ ligamentum arteriosum : 動脈管索 ・ mediastinum : 縦隔 ・ superior vena cava : 上大静脈 ・ the hilum of the right lung : 右肺門 ・ upper lobe : 上葉 ・ lobar arteries : 葉動脈? ・ segmental arteries : 区(域)動脈?
【 Development 】
The pulmonary arteries originate from the truncus arteriosus and the sixth pharyngeal arch. The truncus arteriosis is a structure that forms during the development of the heart as a successor to the conus arteriosus. [5]
By the third week of development, the endocardial tubes have developed a swelling in the part closest to the heart. The swelling is known as the bulbus cordis and the upper part of this swelling develops into the truncus arteriosus [6] The structure is ultimately mesodermal in origin.[5] During development of the heart, the heart tissues undergo folding, and the truncus arteriosus is exposed to what will eventually be both the left and right ventricles. As a septum develops between the two ventricles of the heart, two bulges form on either side of the truncus arteriosus. These progressively enlarge until the trunk splits into the aorta and pulmonary arteries. [7]
During early development, the ductus arteriosis connects the pulmonary trunk and the aortic arch, allowing blood to bypass the lungs.[8]
【 語 句 】
・ truncus arteriosus : 動脈幹 ・ pharyngeal arch : 鰓弓 ・ successor : 後にくるもの ・ conus arteriosus : 動脈円錐 ・ endocardial tubes : 心内膜筒 ・ swelling : 隆起部 ・ bulbus cordis : 心臓球 ・ ultimately : 最後に ・ mesoderma : 中胚葉の ・ undergo : 受ける、経験する ・ eventually : やがては ・ bulge : 膨らみ ・ progressively : 次第に ・ ductus arteriosis : 動脈管?
【 Function 】
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.[9] The blood here passes through capillaries adjacent to alveoli and becomes oxygenated as part of the process of respiration.[10]
In contrast to the pulmonary arteries, the bronchial arteries supply nutrition to the lungs themselves.[11]
【 Pressure 】
The pulmonary artery pressure ( PA pressure ) is a measure of the blood pressure found in the main pulmonary artery. This is measured by inserting a catheter into the main pulmonary artery.[12] :190–191 The mean pressure is typically 9 - 18 mmHg,[13] and the wedge pressure measured in the left atrium may be 6-12mmHg. The wedge pressure may be elevated in left heart failure,[12]:190–191 mitral valve stenosis, and other conditions, such as sickle cell disease.[14]」
【 語 句 】
・ respiration : 呼吸 ・ measure : 尺度、基準 ・ catheter : カテーテル ・ wedge pressure : 楔入圧(せつにゅうあつ)カテーテルの先端にかかる圧力 ・ mitral valve stenosis : 僧帽弁狭窄症 ・ sickle cell disease : 鎌状赤血球症
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|