後大脳動脈とは

以下は脳底動脈の枝を簡単に表した図となる。



⇒ 分布範囲を表したイラスト-Ⅰ
⇒ 分布範囲を表したイラスト-Ⅱ
⇒ 分布範囲を表したイラスト-Ⅲ
「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 後大脳動脈は、脳底動脈が吻側端で左右に分岐して形成され、大脳脚上を外側方向へ走る。そして、後交通動脈と吻合した後、中脳の外側面に沿って迂回し、小脳テントの上面を通り、側頭葉と後頭葉の内側面と下面に広がる。」
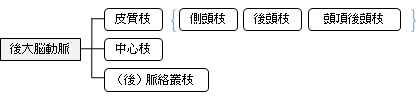
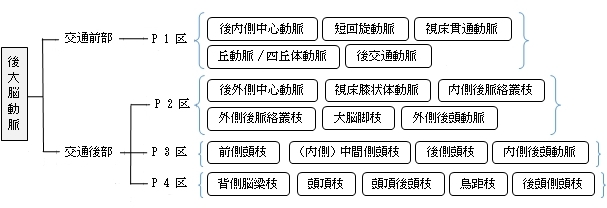
「 日本人体解剖学 」では後大脳動脈の枝として以下のような名称を挙げている。
それに対して、「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では全体を4区に分け、それぞれの区の枝の名称を詳しく記している。
「 プロメテウス解剖学アトラス 」ではP1区からP4区のそれぞれの範囲を以下のように解説しているが、上記の「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」の区分とは若干異なると思われる。
・ P1区 : 脳底動脈と後交通動脈の間の部分
・ P2区 : 後交通動脈と前側頭枝の間の部分
・ P3区 : 外側後頭動脈
・ P4区 : 内側後頭動脈
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. It begins near where the posterior communicating artery and the basilar artery join, and connects with the middle cerebral artery of the same side and internal carotid artery via the posterior communicating artery.
【 structure 】
The branches of the posterior cerebral artery are divided into two sets, ganglionic and cortical :
■ Central branches ■ See also: Artery of Percheron
Also known as the perforating branches :
■ (Posterior) choroidal branches ■
Not to be confused with the Anterior choroidal artery
The posterior choroidal branches of the posterior cerebral artery are sometimes referred to as a single posterior choroidal artery.
- ・ Medial posterior choroidal branches ( 内側後脈絡叢枝 )
- ・ Lateral posterior choroidal branches ( 外側後脈絡叢枝 )
-
【 語 句 】
・ choroidal : 脈絡叢の
■ Cortical branches(皮質枝)■
The cortical branches are:
- ・ Anterior temporal ( 前側頭枝 )
- ・ Posterior temporal ( 後側頭枝 )
- ・ Lateral occipital ( 外側後頭動脈 )
- ・ Medial occipital ( 内側後頭動脈 )
- which branches into the : Calcarine, to the cuneus and gyrus lingualisand the back part of the convex (凸状の)surface of the occipital lobe
- ・ Parieto-occipital ( 頭頂後頭枝 )
【 development 】
The development of the PCA in fetal brain comes relatively late and arises from the fusion of several embryonic vessels near the caudal end of the PCommA supplying the mesencephalon and diencephalon of the fetus.[2] The PCA begins as such, as a continuation of the PCommA in the fetus with only 10–30% of fetuses having a prominent basilar origin.[3]
The fetal carotid origin of the PCA usually regresses as the vertebral and basilar arteries develop with the PCommA reducing is size. In most adults, the PCA sources from the anterior portion of the basilar artery. Only about 19% of adults retain PCommA dominance of the PCA with 72% having dominant basilar origin, and the rest having either equal prominence between PCommA and basilar artery, or a single exclusive source.[3]」
【 語 句 】
・ Calcarine : 鳥距枝? ・ gyrus lingualis : 舌状回 ・ convex : 凸状の ・ fetal : 胎児の ・ fusion : 融合 ・ embryonic : 胎生の ・caudal : 尾部の ・ mesencephalon : 中脳 ・ diencephalon : 間脳 ・regress : 後戻りする ・ dominance : 優勢 ・ exclusive : 独占的な
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ

|