中大脳動脈とは


以下は「 日本人体解剖学 」の解説文となる。
「最大枝(内頚動脈の終枝)で、外側溝を後外側方に走り、これに接する葉を養う。すなわち、外側溝の壁、大脳半球外側面の大部分に分布し、かつ脳底部では前有孔質から内部にある大脳核および内包などに至る臨床上きわめて重要で、最もしばしば脳出血を起こす多数の小枝、皮質枝(眼窩枝、前頭枝、頭頂枝、側頭枝)および中心枝(線条体枝)を出す。」
また、「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では以下のように解説している。
「中大脳動脈は内頚動脈の続きであるが、前大脳動脈の分岐点を過ぎてからはじまる。この動脈は、前有孔質を越えて外側方向に走り、側頭葉と島の間にある大脳外側窩に入る。中大脳動脈は大脳動脈の中で最も大きく複雑であり、上方や後方に走る多数の大きな枝を分岐する。この多数の枝は、島の背側周縁に達すると外側溝に向かって方向を急に下方に変え彎曲して走る。 」
「 日本人体解剖学 」では中大脳動脈の区分に解説は見られないが、「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では以下のように解説している。
「 Fischerらは ( Fischer E : Lageabweichungen der vorderen Hirnarterie im Gefassbild. Zentralbl Neurochir 3: 300-312, 1938 ) 中大脳動脈を放射線学的に
・ M1 ( horizontal ) ・ M2 ( insular ) ・ M3 ( cortical ) 区域と分類した。
中大脳動脈皮質枝はSylvius裂より脳表に出る際に強く屈曲し、この屈強部を横に結んだ線と中大脳動脈本幹の最も前方の点の間で三角形が形成される。この三角形は、放射線学的にSylvian traiangleといわれ、脳血管撮影の重要な所見のひとつである。
微小外科解剖学的には各々
・ M1 ( sphenoidal ) ・ M2 ( insular ) ・ M3 ( opercular ) ・ M4 ( cortical segment or terminal segment )
となっている。
TAにおいては
・ M1 ( Pars sphenoidalis ) ・ M2 ( Pars insularis ) ・ M3 ( Rr. Terminales inferiores ) ・ M4 ( Rr. Terminales superiores )
となっているので注意する。)」
「 日本人体解剖学 」では中大脳動脈の枝に関しては以下のように簡単に解説しているだけで、具体的な枝の名称の言及は見られない。
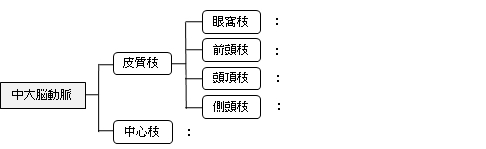
それに対して「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では以下のように区分ごとの枝の名称が見られる。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.
The left and right MCAs rise from trifurcations of the internal carotid arteries and thus are connected to the anterior cerebral arteries and the posterior communicating arteries, which connect to the posterior cerebral arteries. The MCAs are not considered a part of the Circle of Willis.[1]
【 Structure 】
The middle cerebral artery can be classified into 4 parts:[2]
- ・ M 1 : The sphenoidal segment, so named due to its origin and loose lateral tracking of the sphenoid bone. Although known also as the horizontal segment, this may be misleading since the segment may descend, remain flat, or extend posteriorly the anterior (dorsad) in different individuals. The M1 segment perforates the brain with numerous anterolateral central (lateral lenticulostriate) arteries, which irrigate the basal ganglia.
- ・ M 2 : Extending anteriorly on the insula, this segment in known as the insular segment. It is also known as the Sylvian segment when the opercular segments are included. The MCA branches may bifurcate or sometimes trifurcate into trunks in this segment which then extend into branches that terminate towards the cortex.
- ・ M 3 : The opercular segments and extends laterally exteriorly from the insula towards the cortex. This segment is sometimes grouped as part of M2.
- ・ M 4 : These finer terminal or cortical segments irrigate the cortex. They begin at the external of the Sylvian fissure and extend distally away on the cortex of the brain.
The M2 and M3 segments may each split into 2 or 3 main trunks (terminal branches) with an upper trunk, lower trunk and occasionally a middle trunk. Bifurcations and trifurcations occurs in 50% and 25% of the cases respectively. Other cases include duplication of the MCA at the internal carotid artery (ICA) or an accessory MCA (AccMCA) which arise not from the ICA but as a branch from the anterior cerebral artery.[3]The middle trunk that exist in parts of the population, when present provides the pre-Rolandic, Rolandic, anterior parietal, posterior parietal and the angular artery for irrigation instead of the upper and lower trunks.
The branches (ramus) of the MCA can be described by the areas that they irrigate.
【 語 句 】
・ insula : 島 ・ opercular : 鰓蓋の ・ irrigate : 灌漑する ・c ortex : 大脳皮質
【 Frontal lobe 】
- ・Lateral frontobasal (orbitiofrontal): This artery branches out anteriorly, superiorly and laterally to vascularize the inferior frontal gyrus. It "competes" in size with the frontal polar branch of the anterior cerebral artery
- ・Prefrontal arteries: These arteries fan out over the insula and exit to the cortex via the medial surface of the frontal operculum. The arteries fan superiorly over the pars triangularis and vascularize the inferior and middle frontal gyrus. Near the superior frontal gyrus these arteries anastamose with branches from the pericallosal artery of the anterior cerebral artery.
- ・Pre-Rolandic artery (precentral): The artery extends out on the medial surface of the operculum and supplies the posterior parts of the middle and inferior frontal gyri as well as the lower parts of the pre-central gyrus. This artery branches once or twice and is relatively invariant across anatomies.
- ・Rolandic arteries (central): The artery extends out and exits from the central portion of the operculum then passes inside the central sulcus. This artery bifurcates in 72% of individuals and irrigates the posterior pre-central gyrus and the inferior portion of the post-central gyrus.
【 Parietal lobe 】
- ・Anterior parietal: This artery usually originates from the anterior or middle MCA trunk. In some cases it branches from the rolandic artery or from the posterior parietal artery. It extends the length of interparietal sulcus and descends slightly posteriorly.
- ・Posterior parietal: Emerges from the posterior end of the Sylvian fissure and extends first posteriorly, and then anteriorly along the posterior of the parietal lobe. It also branches to the supramarginal gyrus.
- ・Angular: The angular artery is a significant terminal branch of the anterior or middle trunk of the MCA. It emerges from the Sylvian fissure and passes over the anterior transverse temporal gyrus and usually divides into two branches. One of the branches supplies the angular gyrus while the other supplies the supramarginal gyrus, posterior superior temporal gyrus, and the parietooccipital arcus (sulcus).
- ・Temporooccipital: The longest cortical artery, it runs posteriorly opposite to the center of the operculum. Upon its exit from the Sylvian fissure, it runs parallel to the superior temporal sulcus and supplies the superior and inferior occipital gyri. This vessel anastamoses with the posterior cerebral artery and may exist as one or two arteries, 67% or 33% of the time, respectively.
【 Temporal lobe 】
- ・Temporopolar: The artery extends from the sphenoidal segment of the MCA via the inferior surface of the operculum and supplies the polar and anterior lateral portions of the temporal lobe. The vessel can be identified in 52% of normal angiograms
- ・Anterior temporal: This artery extends in the similar fashion as the temporopolar artery and vascularizes the same regions.
- ・Middle temporal: This artery extends from the Sylvian fissure opposite to the inferior frontal gyrus and supplies superior and middle portions of the middle temporal lobe. It can be identified in 79% of angiograms.
- ・Posterior temporal: This artery extends out and away from the operculum and turns in a step-wise manner first inferiorly then posteriorly into the superior temporal sulcus then to the middle temporal sulcus. This vessel supplies posterior portion of the temporal lobe and is the origin of several perforating arteries that irrigate the insula. It is readily identifiable in most radiograms.
Areas supplied by the middle cerebral artery include:
MCA occlusion site and resulting Aphasia
- Global – trunk of MCA
- Broca – anterior branch of MCA
- Wernicke – posterior branch of MCA 」
【 語 句 】
・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ :
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|