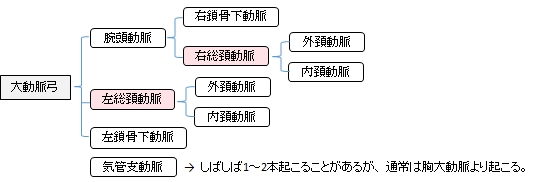
総頚動脈とは



右総頚動脈 : 腕頭動脈より分岐する。左総頚動脈よりも起始部が上部となるため短い。
左総頚動脈 : 大動脈弓から直接分岐する。
※ 左右の総頚動脈の起始部の位置にはいくつかのパターンがあり。詳しくはこのページ下部の「Wikipedia」の「variation」の項を参考のこと。 ⇒ 大動脈弓からの分岐のいろいろなパターンを表したイラスト

「 Wikipedia 」には以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 The average diameters of the common carotids in adult males and females are 6.5 mm and 6.1 mm respectively. 」
【 走 行 】
左右ともに気管 (trachea) および食道 (esophagus) の外側を垂直に上行し、甲状軟骨の上縁の高さ(およそ第4頚椎の高さ)にいたって分岐する。
「 日本人体解剖学 」には以下のような解説文が見受けられる。
「総頚動脈は下方では、胸鎖乳突筋および胸骨甲状筋に覆われ、上方の 頚動脈三角 (carotid artery triangle) 中では頚筋膜および広頸筋のみに覆われる。外側方には内頸静脈があり、総頚動脈と内頸静脈の間の後側には迷走神経が走り、また内側は交感神経幹に隣接する。」
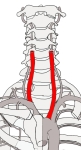
左/右総頚動脈
|
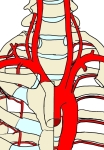
大動脈弓周辺の動脈
|
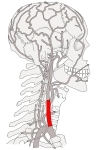
左総頚動脈
|
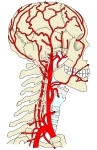
頚部・頭部の動脈
|
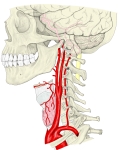
頚部の動脈 |
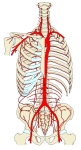
上半身の主な動脈 |
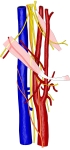
外頚動脈の枝 |
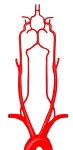
総頚動脈~前大脳動脈・模型図 |
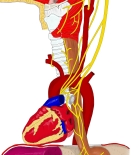
迷走神経・模型図 |
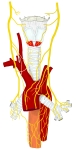
迷走神経
|
|
|
左右の総頚動脈とも甲状軟骨の上縁の高さで内頚動脈および外頚動脈に分岐する。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) (English: /k??r?t?d/[1][2]) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.[3][4]
【 structure 】
The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries, but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra.
The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck, so contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering literature that have looked into characterizing the geometric structure of the common carotid artery from both qualitative and mathematical (quantitative) standpoints.[4]
The average diameters of the common carotids in adult males and females are 6.5 mm and 6.1 mm respectively.[5]
【 語 句 】
・ oxygenated : 酸素が増加した ・ symmetrical : 対称的な ・ thyroid cartilage : 甲状軟骨
・ geometric : 幾何学的な ・ qualitative : 質的な ・ respectively : それぞれ
【 in the chest 】
Only the left common carotid artery has a substantial presence in the thorax. It originates directly from the aortic arch, and travels upward through the superior mediastinum to the level of the left sternoclavicular joint.
During the thoracic part of its course, the left common carotid artery is related to the following structures : In front, it is separated from the manubrium of the sternum by the )and sternothyroid muscles, the anterior portions of the left pleura and lung, the left brachiocephalic vein, and the remains of the thymus ; behind, it lies on the trachea, esophagus, left recurrent laryngeal nerve, and thoracic duct.
To its right side below is the brachiocephalic trunk, and above, the trachea, the inferior thyroid veins, and the remains of the thymus; to its left side are the left vagus and phrenic nerves, left pleura, and lung. The left subclavian artery is posterior and slightly lateral to it.
【 語 句 】
・ substantial : 本当の ・ mediastinum : 縦隔 ・ sternoclavicular joint : 胸鎖関節 ・ manubrium : 胸骨柄
・ sternohyoid : 胸骨舌骨筋 ・ pleura : 肋膜、胸膜 ・ thymus : 胸腺 ・ laryngeal nerve : 反回神経
・ thoracic duct : 胸管 ・ thyroid veins : 下甲状腺静脈 ・ vagus nerve : 迷走神経 ・ phrenic nerve : 横隔神経
【 in the neck 】
The cervical portions of the common carotids resemble each other so closely that one will apply to both description.
Each vessel passes obliquely upward, from behind the sternoclavicular joint to the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, where it divides.
At the lower neck the two common carotid arteries are separated from each other by a very narrow interval which contains the trachea ; but at the upper part, the thyroid gland, the larynx and pharynx separate the two arteries.
The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia and encloses also the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve, the vein lying lateral to the artery, and the nerve between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both. On opening the sheath, each of these three structures is seen to have a separate fibrous cover.
At approximately the level of the fourth cervical vertebra, the common carotid artery splits ("bifurcates" in literature) into an internal carotid artery(ICA) and an external carotid artery (ECA). While both branches travel upward, the internal carotid takes a deeper (more internal) path, eventually travelling up into the skull to supply the brain. The external carotid artery travels more closely to the surface, and sends off numerous branches that supply the neck and face.
【 語 句 】
・ resemble : 似ている ・description : 説明 ・larynx : 喉頭 ・pharynx : 咽頭 ・ carotid sheath : 頚動脈鞘
・ encloses : 囲む ・ approximately : おおよそ ・eventually : 結局は
At the lower part of the neck the common carotid artery is very deeply seated, being covered by the integument, superficial fascia, the platysma muscle, deep cervical fascia, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and the omohyoid ; in the upper part of its course it is more superficial, being covered merely by the integument, the superficial fascia, the platysma, deep cervical fascia, and medial margin of the sternocleidomastoid.
When the sternocleidomastoid muscle is drawn backward, the artery is seen to be contained in a triangular space known as the carotid triangle. This space is bounded behind by the sternocleidomastoid, above by the stylohyoid and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, and below by the superior belly of the omohyoid.
This part of the artery is crossed obliquely, from its medial to its lateral side, by the sternocleidomastoid branch of the superior thyroid artery; it is also crossed by the superior and middle thyroid veins ( which end in the internal jugular vein ; descending in front of its sheath is the descending branch of the hypoglossal nerve, this filament being joined by one or two branches from the cervical nerves, which cross the vessel obliquely.
【 語 句 】
・ integument : 外皮 ・ sternothyroid : 胸骨甲状筋 ・ omohyoid : 肩甲舌骨筋 ・ carotid triangle : 頚動脈三角
・ stylohyoid : 茎突舌骨筋 ・ digastric : 顎二腹筋 ・ hypoglossal nerve : 舌下神経
Sometimes the descending branch of the hypoglossal nerve is contained within the sheath.
The superior thyroid vein crosses the artery near its termination, and the middle thyroid vein a little below the level of the cricoid cartilage; the anterior jugular vein crosses the artery just above the clavicle, but is separated from it by the sternohyoid and sternothyroid.
Behind, the artery is separated from the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae by the longus colli and longus capitis muscles, the sympathetic trunk being interposed between it and the muscles. The inferior thyroid artery crosses behind the lower part of the vessel.
Medially, it is in relation with the esophagus, trachea, and thyroid gland (which overlaps it), the inferior thyroid artery and recurrent laryngeal nerve being interposed ; higher up, with the larynx and pharynx. Lateral to the artery, inside the carotid sheath with the common carotid, are the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve.
At the lower part of the neck, on the right side of the body, the right recurrent laryngeal nerve crosses obliquely behind the artery; the right internal jugular vein diverges from the artery. On the left side, however, the left internal jugular vein approaches and often overlaps the lower part of the artery.
Behind the angle of bifurcation of the common carotid artery is a reddish-brown oval body known as the carotid body. It is similar in structure to the coccygeal body which is situated on the median sacral artery.
The relations of the cervical region of the common carotid artery may be discussed in two points:
【 collateral circulation 】
After ligature of the common carotid, the collateral circulation can be perfectly established, by the free communication which exists between the carotid arteries of opposite sides, both without and within the cranium, and by enlargement of the branches of the subclavian artery on the side corresponding to that on which the vessel has been tied.
The chief communications outside the skull take place between the superior and inferior thyroid arteries, and the deep cervical artery and the descending branch of the occipital artery ; the vertebral artery takes the place of the internal carotid artery within the cranium.
【 variation 】
Origin
The right common carotid may arise above the level of the upper border of the sternoclavicular joint; this variation occurs in about 12 percent of cases.
In other cases the artery on the right side may arise as a separate branch from the arch of the aorta, or in conjunction with the left carotid.
The left common carotid varies in its origin more than the right.
In the majority of abnormal cases it arises with the brachiocephalic trunk; if that artery is absent, the two carotids arise usually by a single trunk.
It is rarely joined with the left subclavian artery, except in cases of transposition of the aortic arch.
【 語 句 】
・ collateral : 二次的な ・ ligature : くくること、連結? ・ cranium : 頭蓋骨
・ conjunction : 連結、接続 ・ transposition : 置き換え
Point of division
In the majority of abnormal cases, the bifurcation occurs higher than usual, the artery dividing opposite or even above the hyoid bone; more rarely, it occurs below, opposite the middle of the larynx, or the lower border of the cricoid cartilage. In at least one reported case, the artery was only 4 cm in length and divided at the root of the neck.
Very rarely, the common carotid artery ascends in the neck without any subdivision, either the external or the internal carotid being absent; and in a few cases the common carotid has itself been found to be absent, the external and internal carotids arising directly from the arch of the aorta.
This peculiarity existed on both sides in some instances, on one side in others.
Occasional branches
The common carotid usually gives off no branch previous to its bifurcation, but it occasionally gives origin to the superior thyroid artery or its laryngeal branch, the ascending pharyngeal artery, the inferior thyroid artery, or, more rarely, the vertebral artery.」
【 語 句 】
・ subdivision : 細分化 ・ peculiarity : 異常な点 ・ instance : 実例
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|