上行大動脈とは

・「 Wikipedia 」には以下のような解説が見られる。( サイトの本文は英語 )
a . 胸骨の左半分の後部において、第3肋軟骨の下縁の位置あたりくらいの高さが起始となる。
b . 起始部より斜め右前上方に進み、第2右肋軟骨の上縁の高さでカーブを描く。 ⇒ イラスト
c . 長さは約5㎝ほどとなる。
以下は大動脈の構成を簡単に表したものとなる。


・ 3つの半月弁を合わせて 大動脈弁 という。
・ 肺動脈(幹) の根部にも3つの半月弁(右半月弁、左半月弁、前半月弁)があり、これらを 肺動脈弁 という。
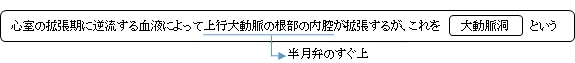
・大動脈洞は、動脈壁外側の膨らみである大動脈球に相当する。
体循環の主な動脈
|
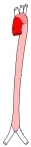
大動脈
|

大動脈
|

大動脈根(前面)
|

大動脈弁(上面)
|
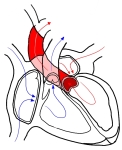
上行大動脈
|
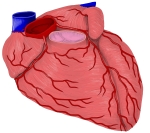
右・左冠状動脈 |
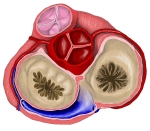
心臓弁の外観 |
上行大動脈の根部、右および左の大動脈洞に一致するところから左右の冠状動脈が出ている。

以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The ascending aorta (AAo)[1] is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.
【 structure 】
It passes obliquely upward, forward, and to the right, in the direction of the heart's axis, as high as the upper border of the second right costal cartilage, describing a slight curve in its course, and being situated, about 6 centimetres (2.4 in) behind the posterior surface of the sternum. The total length is about 5 centimetres (2.0 in).
【 components 】
The aortic root is the portion of the aorta beginning at the aortic annulus and extending to the sinotubular junction. It is sometimes regarded as a part of the ascending aorta,[2] and sometimes regarded as a separate entity from the rest of the ascending aorta.[3]
Between each commissure of the aortic valve and opposite the cusps of the aortic valve, three small dilatations called the aortic sinuses.
The sinotubular junction is the point in the ascending aorta where the aortic sinuses end and the aorta becomes a tubular structure.
【 size 】
A thoracic aortic diameter greater than 3.5 cm is generally considered dilated, whereas a diameter greater than 4.5 cm is generally considered to be a thoracic aortic aneurysm.[4] Still, the average diameter in the population varies by for example age and sex. The upper limit of standard reference range of the ascending aorta may be up to 4.3 cm among large, elderly individuals.[5]
【 relations 】
At the union of the ascending aorta with the aortic arch the caliber of the vessel is increased, owing to a bulging of its right wall.
This dilatation is termed the bulb of the aorta, and on transverse section presents a somewhat oval figure.
The ascending aorta is contained within the pericardium, and is enclosed in a tube of the serous pericardium, common to it and the pulmonary artery.
The ascending aorta is covered at its commencement by the trunk of the pulmonary artery and the right auricula, and, higher up, is separated from the sternum by the pericardium, the right pleura, the anterior margin of the right lung, some loose areolar tissue, and the remains of the thymus; posteriorly, it rests upon the left atrium and right pulmonary artery.
On the right side, it is in relation with the superior vena cava and right atrium, the former lying partly behind it; on the left side, with the pulmonary artery. 」
【 語 句 】
・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ :

|