前大脳動脈とは


・「 両側の動脈は、脳梁吻の付近で視(神経)交叉の前を横走する前交通動脈によって吻合される。」( 日本人体解剖学 )
・「 前大脳動脈の異常は約25%の脳にみられる。このなかには前大脳動脈が1本しかないもの、枝が反対側の大脳半球に分岐する例もある。」( 船戸和弥のホームページ )
1 . 視交叉と視神経の外側において内頚動脈から分岐する。
2 . 左右の前大脳動脈は視神経の背側を前内側方に走行してお互いに近づき、前交通動脈によって連絡する。
3 . 両側の前大脳動脈は大脳縦裂内を脳梁膝に沿って上方に走る。
4 . 次いで脳梁の背側面を後方に走り脳梁および脳半球の内側面に分布する。
「 日本人体解剖学 」では前大脳動脈の枝として以下のような解説文が見られる。
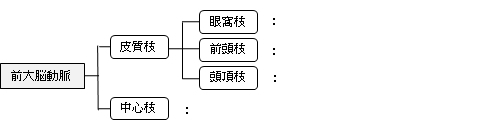
「 前大脳動脈の分枝には 皮質枝( 眼窩枝、前頭枝、頭頂枝 )および 中心枝 がある。」
それに対して「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」の神経の項の索引では以下のような動脈の名称が見られる。
「 プロメテウス解剖学アトラス 」には以下のような名称の枝が見られる。
・ 内側前頭底動脈 ・ 前頭極動脈 ・ 前内側前頭枝 ・ 中間内側前頭枝 ・ 後内側前頭枝
・ 帯状回枝 ・ 中心傍小葉枝
「 日本人体解剖学 」や「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では区分に関する言及は見られないが、「Wikipedia」では、前大脳動脈全体をA1~A5の5区に分けている。以下は、それぞれの区分を簡単に解説をしたものになるが、少し正確性に欠ける可能性もあるので、詳しくは「参考となるサイト」を参考にされたし。
A 1 : 内頚動脈の分岐から前交通動脈によって左右の前大脳動脈が連絡するまで。
A 2 : 前交通動脈による連絡部から脳梁周囲動脈と脳梁縁動脈に分かれるまで。
A 3 : 脳梁周囲動脈の部分?
A 4/5 : 脳梁縁動脈の部分?
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The anterior cerebral artery ( ACA ) is one of a pair of arteries on the brain that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery.
Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes.
【 structure 】
The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches : the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered as the A4 and A5 segments.[1]
- ・A2 extends from the AComm to the bifurcation forming the pericallosal and callosomarginal arteries. The recurrent artery of Heubner ( distal medial striate artery ), which irrigates the internal capsule, usually arises at the beginning of this segment near the AComm. Two branches arise from this segment:
- ・A3, also termed the pericallosal artery, is one of the ( or the only ) main terminal branches of the ACA, which extends posteriorly in the pericallosal sulcus to form the internal parietal arteries (superior, inferior) and the precuneal artery. This artery may form an anastomosis with the posterior cerebral artery.
【 development 】
The anterior cerebral artery develops from a primitive anterior division of the internal carotid artery that initially supplies the optic and olfactory regions. This anterior division, which appears at the twenty-eighth day of development, also forms the middle cerebral artery and the anterior choroidal artery. The anterior cerebral arteries grow toward each other and form the anterior communicating artery at the 21–24 mm stage of the embryo.[4]
【 variation 】
The anterior cerebral artery shows considerable variation. In a study made using MRA, the most common variation was an underdeveloped A1 segment (5.6%), followed by the presence of an extra A2 segment (3%). In 2% of cases there was only one A2 segment.[5]」
【 語 句 】
・ olfactory : 嗅覚の ・ anterior choroidal artery : 前脈絡叢動脈 ・ embryo : 胚
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|